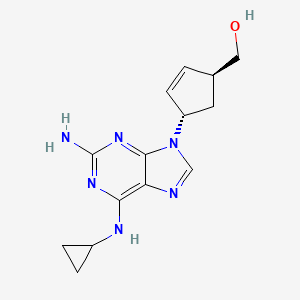
Abacavir
Descripción general
Descripción
Abacavir es un análogo de nucleósido carbocíclico sintético inhibidor de la transcriptasa inversa utilizado principalmente en el tratamiento del Virus de Inmunodeficiencia Humana (VIH) y el Síndrome de Inmunodeficiencia Adquirida (SIDA). Se comercializa bajo el nombre de marca Ziagen, entre otros. This compound se usa normalmente en combinación con otros medicamentos antirretrovirales y no se recomienda su uso en solitario . Se conoce por su capacidad de inhibir la replicación del VIH al dirigirse a la enzima transcriptasa inversa, que es crucial para el proceso de replicación del virus .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Clinical Efficacy in HIV Treatment
Abacavir is FDA-approved for use in adults and children over three months old as part of combination antiretroviral therapy (ART). It is often administered alongside other agents such as lamivudine and dolutegravir.
Clinical Trials and Outcomes
- A pivotal study compared this compound with zidovudine combined with lamivudine. At week 48, 70% of patients on this compound achieved plasma HIV-1 RNA levels of ≤50 copies/mL, similar to the zidovudine group (69%) .
- The median increase in CD4+ cell counts was significantly higher in the this compound group (209 cells/mm³) compared to the zidovudine group (155 cells/mm³), indicating a robust immunological response .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits a two-compartment pharmacokinetic model with high oral bioavailability. Key pharmacokinetic parameters include:
- Clearance : Increased from a mean of 3.33 to 5.86 L/h/7 kg from day 1 to day 14 in severely malnourished children .
- Central Nervous System Penetration : Studies indicate that this compound penetrates the central nervous system effectively, with a CSF/plasma concentration ratio of approximately 31% to 44% .
Safety Profile and Side Effects
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it has been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, particularly in individuals with the HLA-B*57:01 allele. This genetic predisposition can lead to severe allergic reactions upon exposure to the drug.
Cardiovascular Risks
Recent analyses have linked this compound use to an increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). A meta-analysis indicated that current or past use of this compound may elevate cardiovascular disease risk among HIV patients .
Off-Label Uses
This compound has been explored for various off-label applications, including:
- HIV Treatment in Special Populations : Research has demonstrated its efficacy in severely malnourished children, showing that WHO weight-band dosing recommendations are appropriate for this demographic .
- Potential Role in Cancer Therapy : Emerging studies are investigating the immunomodulatory effects of this compound that may enhance responses to cancer therapies.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Several studies have documented the diverse applications and outcomes associated with this compound:
Mecanismo De Acción
Abacavir se convierte intracelularmente en su metabolito activo, carbovir trifosfato. Este metabolito es un análogo de la desoxiguanosina-5’-trifosfato (dGTP) y compite por la incorporación al ADN viral por la enzima transcriptasa inversa del VIH. Una vez incorporado, actúa como un terminador de cadena, impidiendo la elongación del ADN viral y, por lo tanto, inhibiendo la replicación del virus .
Compuestos Similares:
Lamivudina: Otro inhibidor de la transcriptasa inversa de nucleósidos utilizado en combinación con this compound.
Zidovudina: Un inhibidor de la transcriptasa inversa de nucleósidos más antiguo con un mecanismo de acción similar.
Tenofovir: Un inhibidor de la transcriptasa inversa de nucleótidos con una estructura química diferente pero actividad antiviral similar.
Comparación:
Singularidad: this compound es único en su estructura como análogo de nucleósido carbocíclico. Tiene un grupo de ciclopropilamina distintivo que lo diferencia de otros análogos de nucleósidos.
Perfil de Seguridad: this compound tiene un perfil de seguridad bien documentado, aunque está asociado con un riesgo de reacciones de hipersensibilidad y posibles riesgos cardiovasculares.
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas Sintéticas y Condiciones de Reacción: La síntesis de abacavir implica varios pasos, comenzando con un compuesto de di-halo aminopirimidina adecuado. Los pasos clave incluyen:
Reacción con Aminoalcohol: La di-halo aminopirimidina reacciona con un aminoalcohol para formar un compuesto intermedio.
Ciclización: Este intermedio se somete a ciclización para formar un intermedio clave.
Introducción de Ciclopropilamina: El átomo de cloro en el intermedio se desplaza con ciclopropilamina para producir this compound como una base libre.
Métodos de Producción Industrial: La producción industrial de this compound a menudo implica la optimización de las condiciones de reacción para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza. Esto incluye controlar la temperatura, el pH y el uso de catalizadores específicos para facilitar las reacciones. El proceso también puede incluir pasos de purificación, como la cristalización y la cromatografía, para aislar el producto final .
Tipos de Reacciones:
Oxidación: this compound sufre degradación oxidativa, que puede estudiarse utilizando métodos electroquímicos.
Reducción: Si bien las reacciones de reducción específicas de this compound están menos documentadas, es posible que en ciertas condiciones, this compound pueda sufrir reducción.
Reactivos y Condiciones Comunes:
Oxidación: Peróxido de hidrógeno, electrodos de platino, electrodos de diamante dopado con boro.
Sustitución: Ciclopropilamina, varios solventes y catalizadores.
Productos Principales:
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Lamivudine: Another nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in combination with abacavir.
Zidovudine: An older nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a similar mechanism of action.
Tenofovir: A nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a different chemical structure but similar antiviral activity.
Comparison:
Uniqueness: this compound is unique in its structure as a carbocyclic nucleoside analog. It has a distinct cyclopropylamine group that differentiates it from other nucleoside analogs.
Safety Profile: this compound has a well-documented safety profile, though it is associated with a risk of hypersensitivity reactions and potential cardiovascular risks.
Actividad Biológica
Abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) primarily used in the treatment of HIV infection. Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic efficacy, safety profile, and potential side effects, including hypersensitivity reactions. This article synthesizes findings from various studies and case reports to provide a comprehensive overview of this compound's biological activity.
This compound is metabolized intracellularly to its active form, carbovir triphosphate (CBV-TP), which competes with natural deoxyguanosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA. This incorporation results in chain termination during reverse transcription, effectively inhibiting viral replication. This compound has demonstrated potency against HIV strains resistant to other NRTIs, making it a valuable option in antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of this compound reveals significant insights into its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion:
- Absorption : this compound is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1.5 to 2 hours.
- Distribution : The drug penetrates the central nervous system (CNS) effectively, with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations significantly exceeding the inhibitory concentration for HIV .
- Metabolism : this compound is primarily metabolized by the liver through non-CYP450 pathways, reducing the risk of drug-drug interactions commonly associated with other antiretrovirals .
- Excretion : The drug is eliminated mainly via renal clearance, with minimal hepatic metabolism .
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
This compound has been evaluated in numerous clinical trials demonstrating its efficacy as part of ART regimens:
- In a comparative study with zidovudine and lamivudine, this compound showed non-inferior efficacy in maintaining viral suppression (70% vs. 69% at week 48) and a favorable CD4+ cell response (209 cells/mm³ vs. 155 cells/mm³) .
- A meta-analysis indicated that viral suppression rates ranged from 50% to 70% at six months and from 57% to 78% at twelve months in pediatric populations treated with this compound .
Safety Profile and Hypersensitivity Reactions
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs) in a subset of patients. The incidence of HSRs can be influenced by genetic factors such as HLA-B*5701 status:
- Case Study Example : A patient developed gastrointestinal symptoms and fever within days of initiating therapy with this compound. Upon discontinuation, symptoms resolved rapidly, indicating a probable hypersensitivity reaction .
Table 1: Summary of this compound Hypersensitivity Reactions
| Study/Case | Population | Symptoms | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case #3 | Adult male | Vomiting, diarrhea, fever | Symptoms resolved post-discontinuation |
| Patel et al. (2020) | Pediatric patients | Variable symptoms | Incidence rate varied from 0% to 5.49% |
Research Findings on Oncogenic Activity
Recent studies have also explored the potential oncogenic effects of this compound. Research indicates that this compound can activate oncogenic transcription factors in gastric cancer cells, suggesting a complex role beyond its antiviral activity:
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
[4-[2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)purin-9-yl]cyclopent-2-en-1-yl]methanol | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H18N6O/c15-14-18-12(17-9-2-3-9)11-13(19-14)20(7-16-11)10-4-1-8(5-10)6-21/h1,4,7-10,21H,2-3,5-6H2,(H3,15,17,18,19) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MCGSCOLBFJQGHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1NC2=C3C(=NC(=N2)N)N(C=N3)C4CC(C=C4)CO | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C14H18N6O | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID20861337 | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
286.33 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
136470-78-5, 914348-29-1 | |
| Record name | NSC742406 | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=742406 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.
















