Abacavir
Vue d'ensemble
Description
L’abacavir est un analogue nucléosidique carbocyclique synthétique inhibiteur de la transcriptase inverse utilisé principalement dans le traitement du virus de l’immunodéficience humaine (VIH) et du syndrome d’immunodéficience acquise (SIDA). Il est commercialisé sous le nom de marque Ziagen, entre autres. L’this compound est généralement utilisé en association avec d’autres médicaments antirétroviraux et n’est pas recommandé pour une utilisation en monothérapie . Il est connu pour sa capacité à inhiber la réplication du VIH en ciblant l’enzyme transcriptase inverse, qui est cruciale pour le processus de réplication du virus .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Clinical Efficacy in HIV Treatment
Abacavir is FDA-approved for use in adults and children over three months old as part of combination antiretroviral therapy (ART). It is often administered alongside other agents such as lamivudine and dolutegravir.
Clinical Trials and Outcomes
- A pivotal study compared this compound with zidovudine combined with lamivudine. At week 48, 70% of patients on this compound achieved plasma HIV-1 RNA levels of ≤50 copies/mL, similar to the zidovudine group (69%) .
- The median increase in CD4+ cell counts was significantly higher in the this compound group (209 cells/mm³) compared to the zidovudine group (155 cells/mm³), indicating a robust immunological response .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits a two-compartment pharmacokinetic model with high oral bioavailability. Key pharmacokinetic parameters include:
- Clearance : Increased from a mean of 3.33 to 5.86 L/h/7 kg from day 1 to day 14 in severely malnourished children .
- Central Nervous System Penetration : Studies indicate that this compound penetrates the central nervous system effectively, with a CSF/plasma concentration ratio of approximately 31% to 44% .
Safety Profile and Side Effects
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it has been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, particularly in individuals with the HLA-B*57:01 allele. This genetic predisposition can lead to severe allergic reactions upon exposure to the drug.
Cardiovascular Risks
Recent analyses have linked this compound use to an increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). A meta-analysis indicated that current or past use of this compound may elevate cardiovascular disease risk among HIV patients .
Off-Label Uses
This compound has been explored for various off-label applications, including:
- HIV Treatment in Special Populations : Research has demonstrated its efficacy in severely malnourished children, showing that WHO weight-band dosing recommendations are appropriate for this demographic .
- Potential Role in Cancer Therapy : Emerging studies are investigating the immunomodulatory effects of this compound that may enhance responses to cancer therapies.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Several studies have documented the diverse applications and outcomes associated with this compound:
Mécanisme D'action
L’abacavir est converti en son métabolite actif, le carbovir triphosphate, à l’intérieur des cellules. Ce métabolite est un analogue de la désoxyguanosine-5’-triphosphate (dGTP) et entre en compétition pour son incorporation dans l’ADN viral par l’enzyme transcriptase inverse du VIH. Une fois incorporé, il agit comme un terminateur de chaîne, empêchant l’élongation de l’ADN viral et inhibant ainsi la réplication du virus .
Composés Similaires :
Lamivudine : Un autre inhibiteur de la transcriptase inverse nucléosidique utilisé en association avec l’this compound.
Zidovudine : Un ancien inhibiteur de la transcriptase inverse nucléosidique ayant un mécanisme d’action similaire.
Ténofovir : Un inhibiteur de la transcriptase inverse nucléotidique ayant une structure chimique différente mais une activité antivirale similaire.
Comparaison :
Unicité : L’this compound est unique dans sa structure en tant qu’analogue nucléosidique carbocyclique. Il possède un groupe cyclopropylamine distinct qui le différencie des autres analogues nucléosidiques.
Profil de Sécurité : L’this compound a un profil de sécurité bien documenté, bien qu’il soit associé à un risque de réactions d’hypersensibilité et de risques cardiovasculaires potentiels.
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de Synthèse et Conditions de Réaction : La synthèse de l’abacavir implique plusieurs étapes, à partir d’un composé di-halo aminopyrimidine approprié. Les étapes clés incluent :
Réaction avec l’Aminoalcool : La di-halo aminopyrimidine est mise à réagir avec un aminoalcool pour former un composé intermédiaire.
Cyclisation : Ce composé intermédiaire subit une cyclisation pour former un intermédiaire clé.
Introduction de la Cyclopropylamine : L’atome de chlore dans l’intermédiaire est déplacé par la cyclopropylamine pour donner l’this compound sous forme de base libre.
Méthodes de Production Industrielle : La production industrielle de l’this compound implique souvent l’optimisation des conditions de réaction pour assurer un rendement élevé et une pureté élevée. Cela comprend le contrôle de la température, du pH et l’utilisation de catalyseurs spécifiques pour faciliter les réactions. Le processus peut également impliquer des étapes de purification telles que la cristallisation et la chromatographie pour isoler le produit final .
Types de Réactions :
Oxydation : L’this compound subit une dégradation oxydative, qui peut être étudiée à l’aide de méthodes électrochimiques.
Réduction : Bien que les réactions de réduction spécifiques de l’this compound soient moins documentées, il est possible que dans certaines conditions, l’this compound puisse subir une réduction.
Substitution : La synthèse de l’this compound elle-même implique des réactions de substitution, en particulier le déplacement du chlore par la cyclopropylamine.
Réactifs et Conditions Courants :
Oxydation : Peroxyde d’hydrogène, électrodes en platine, électrodes en diamant dopé au bore.
Substitution : Cyclopropylamine, divers solvants et catalyseurs.
Principaux Produits :
Produits d’Oxydation : Les produits de dégradation identifiés comprennent des composés ayant une masse moléculaire de 319,20 et 247,19.
Produits de Substitution : Le produit principal est l’this compound lui-même, formé par la substitution du chlore par la cyclopropylamine.
4. Applications de la Recherche Scientifique
L’this compound a un large éventail d’applications dans la recherche scientifique, en particulier dans les domaines de la chimie, de la biologie et de la médecine :
Chimie : L’this compound sert de composé modèle pour étudier les analogues nucléosidiques et leurs interactions avec les enzymes.
Biologie : Il est utilisé pour étudier les mécanismes de réplication virale et le développement de la résistance au VIH.
Médecine : L’this compound est un élément essentiel de la thérapie antirétrovirale pour le VIH/SIDA.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Lamivudine: Another nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in combination with abacavir.
Zidovudine: An older nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a similar mechanism of action.
Tenofovir: A nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor with a different chemical structure but similar antiviral activity.
Comparison:
Uniqueness: this compound is unique in its structure as a carbocyclic nucleoside analog. It has a distinct cyclopropylamine group that differentiates it from other nucleoside analogs.
Safety Profile: this compound has a well-documented safety profile, though it is associated with a risk of hypersensitivity reactions and potential cardiovascular risks.
Activité Biologique
Abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) primarily used in the treatment of HIV infection. Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic efficacy, safety profile, and potential side effects, including hypersensitivity reactions. This article synthesizes findings from various studies and case reports to provide a comprehensive overview of this compound's biological activity.
This compound is metabolized intracellularly to its active form, carbovir triphosphate (CBV-TP), which competes with natural deoxyguanosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA. This incorporation results in chain termination during reverse transcription, effectively inhibiting viral replication. This compound has demonstrated potency against HIV strains resistant to other NRTIs, making it a valuable option in antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of this compound reveals significant insights into its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion:
- Absorption : this compound is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1.5 to 2 hours.
- Distribution : The drug penetrates the central nervous system (CNS) effectively, with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations significantly exceeding the inhibitory concentration for HIV .
- Metabolism : this compound is primarily metabolized by the liver through non-CYP450 pathways, reducing the risk of drug-drug interactions commonly associated with other antiretrovirals .
- Excretion : The drug is eliminated mainly via renal clearance, with minimal hepatic metabolism .
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
This compound has been evaluated in numerous clinical trials demonstrating its efficacy as part of ART regimens:
- In a comparative study with zidovudine and lamivudine, this compound showed non-inferior efficacy in maintaining viral suppression (70% vs. 69% at week 48) and a favorable CD4+ cell response (209 cells/mm³ vs. 155 cells/mm³) .
- A meta-analysis indicated that viral suppression rates ranged from 50% to 70% at six months and from 57% to 78% at twelve months in pediatric populations treated with this compound .
Safety Profile and Hypersensitivity Reactions
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs) in a subset of patients. The incidence of HSRs can be influenced by genetic factors such as HLA-B*5701 status:
- Case Study Example : A patient developed gastrointestinal symptoms and fever within days of initiating therapy with this compound. Upon discontinuation, symptoms resolved rapidly, indicating a probable hypersensitivity reaction .
Table 1: Summary of this compound Hypersensitivity Reactions
| Study/Case | Population | Symptoms | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case #3 | Adult male | Vomiting, diarrhea, fever | Symptoms resolved post-discontinuation |
| Patel et al. (2020) | Pediatric patients | Variable symptoms | Incidence rate varied from 0% to 5.49% |
Research Findings on Oncogenic Activity
Recent studies have also explored the potential oncogenic effects of this compound. Research indicates that this compound can activate oncogenic transcription factors in gastric cancer cells, suggesting a complex role beyond its antiviral activity:
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
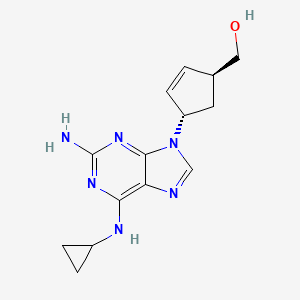
[4-[2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)purin-9-yl]cyclopent-2-en-1-yl]methanol | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H18N6O/c15-14-18-12(17-9-2-3-9)11-13(19-14)20(7-16-11)10-4-1-8(5-10)6-21/h1,4,7-10,21H,2-3,5-6H2,(H3,15,17,18,19) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MCGSCOLBFJQGHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1NC2=C3C(=NC(=N2)N)N(C=N3)C4CC(C=C4)CO | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C14H18N6O | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID20861337 | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
286.33 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
136470-78-5, 914348-29-1 | |
| Record name | NSC742406 | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=742406 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861337 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
















