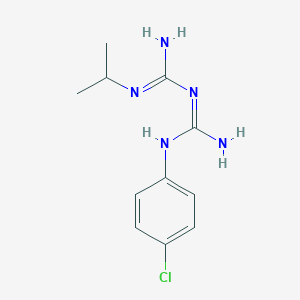
プログアニル
概要
説明
プログアニル D6: は、マラリア治療薬であるプログアニルの重水素標識誘導体です。 プログアニルは、Plasmodium falciparum および Plasmodium vivax によって引き起こされるマラリアの予防および治療に広く使用されています 。 プログアニル D6 の重水素標識は、その安定性を高め、より正確な薬物動態研究を可能にします .
科学的研究の応用
Clinical Efficacy
Proguanil is most commonly administered in combination with atovaquone, marketed as Malarone. This combination has demonstrated high efficacy rates in preventing and treating malaria. For instance, a randomized placebo-controlled study showed that this combination was 100% effective in preventing malaria among children living in endemic areas . Another study highlighted that proguanil effectively sensitizes malaria parasites to atovaquone, thereby enhancing treatment outcomes even in cases where resistance to other antimalarials is present .
Table 1: Efficacy Data from Clinical Studies
Case Studies
- Atovaquone/Proguanil-Induced Esophageal Ulcers : A case report documented a healthy medical student who developed esophageal ulcers after taking atovaquone/proguanil without water. This incident underscores the importance of proper administration methods for medications .
- Treatment of Imported Malaria : In a study involving travelers returning from endemic regions, atovaquone/proguanil was successfully used to treat multiple cases of P. falciparum and P. vivax malaria. The treatment was effective even in patients who had previously failed other treatments .
- Resistance Cases : A cluster of malaria cases treated with atovaquone/proguanil revealed resistance mutations in the P. falciparum genome. This highlights the ongoing challenge of drug resistance and the need for continuous monitoring and development of new treatment strategies .
Future Applications
Research is ongoing to explore additional applications of proguanil beyond malaria treatment. Its potential as an antifungal agent is being investigated, particularly for use in immunocompromised patients at risk for fungal infections . Furthermore, proguanil's role in combination therapies with other antimalarials continues to be a focus area due to its ability to enhance the efficacy of existing drugs.
作用機序
プログアニル D6 は、マラリア原虫の増殖に不可欠な酵素であるジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼを阻害することによって効果を発揮します 。 この阻害は、寄生虫が DNA を合成して複製することを防ぎ、感染を停止させます 。 プログアニル D6 の重水素標識により、体内の薬物の分布と代謝をより正確に追跡できます .
類似化合物の比較
類似化合物
プログアニル: プログアニル D6 の親化合物であり、マラリアの予防と治療に使用されます.
シクログアニル: プログアニルの活性代謝物であり、酸化によって形成されます.
クロロキン: プログアニルとの併用でよく使用される別のマラリア治療薬.
独自性: : プログアニル D6 は、重水素標識によって独自であり、その安定性を高め、重水素化されていない対応物と比較して、より正確な薬物動態研究を可能にします 。これは、科学研究と薬物開発における貴重なツールとなります。
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Proguanil is a biguanide derivative that is converted to an active metabolite called cycloguanil . It exerts its antimalarial action by inhibiting the enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved in the reproduction of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax . This inhibition blocks the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines, which are essential for DNA synthesis and cell multiplication .
Cellular Effects
Proguanil works by stopping the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, from reproducing once it is in the red blood cells . It does this by inhibiting the enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved in the reproduction of the parasite . This leads to failure of nuclear division at the time of schizont formation in erythrocytes and liver .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Proguanil involves the inhibition of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase of plasmodia . This inhibition blocks the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines, which are essential for DNA synthesis and cell multiplication . This leads to failure of nuclear division at the time of schizont formation in erythrocytes and liver .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Proguanil has been shown to have potent, but slow-acting, in vitro anti-plasmodial activity . The potent fast-acting activity of proguanil is attributed to the dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor cycloguanil .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
While specific dosage effects of Proguanil in animal models were not found in the search results, it is known that Proguanil is extensively absorbed in rats . In both species, toxicity was related to proguanil exposure, the principal manifestations being salivation, emesis, and loss of body weight .
Metabolic Pathways
Proguanil is variably metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes to the active triazine metabolite, cycloguanil . This variable metabolism of proguanil may have profound clinical importance in poor metabolizers such as the Asian and African populations at risk for malaria infection .
Transport and Distribution
Proguanil and its metabolite cycloguanil were found to be substrates of organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1), organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2), multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 (MATE1) and multidrug and toxin extrusion 2-K (MATE2-K) . These transporters play a crucial role in the distribution and excretion of Proguanil .
Subcellular Localization
The specific subcellular localization of Proguanil was not found in the search results. Given its mechanism of action, it can be inferred that Proguanil likely localizes to the site of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved in the reproduction of the malaria parasite .
準備方法
合成経路および反応条件: : プログアニル D6 の合成には、プログアニル分子への重水素原子の組み込みが含まれます。 これは、合成プロセス中に重水素化試薬または溶媒を使用するなど、さまざまな方法によって達成できます 。 反応条件は、通常、重水素化ジメチルスルホキシド(DMSO)または重水素化エタノールなどの重水素化溶媒の使用を含み、反応は、重水素原子の組み込みを確実にするために制御された温度と圧力下で行われます .
工業生産方法: : プログアニル D6 の工業生産は、同様の合成経路に従いますが、より大規模に行われます。 このプロセスには、自動反応器の使用と反応条件の正確な制御が含まれ、最終生成物の高収率と純度を確保します .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: : プログアニル D6 は、以下を含むさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化: プログアニル D6 は酸化されて、その活性代謝物であるシクログアニルを形成することができます.
一般的な試薬および条件
酸化: 一般的な酸化剤には、過酸化水素と過マンガン酸カリウムがあり、通常は酸性条件下で使用されます.
主な生成物
シクログアニル: プログアニル D6 の酸化から生成される主な生成物.
さまざまな誘導体: 置換反応によって形成されます.
科学研究における用途
プログアニル D6 は、以下を含む幅広い科学研究用途があります。
類似化合物との比較
Similar Compounds
Proguanil: The parent compound of Proguanil D6, used for malaria prophylaxis and treatment.
Cycloguanil: The active metabolite of Proguanil, formed through oxidation.
Chloroquine: Another antimalarial drug often used in combination with Proguanil.
Uniqueness: : Proguanil D6 is unique due to its deuterium labeling, which enhances its stability and allows for more precise pharmacokinetic studies compared to its non-deuterated counterparts . This makes it a valuable tool in scientific research and drug development.
生物活性
Proguanil is an antimalarial compound primarily used in the prevention and treatment of malaria, particularly against Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax . Its biological activity is closely linked to its metabolism into the active metabolite cycloguanil, which exerts significant effects on the malaria parasites. This article explores the biological activity of proguanil, including its mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy, and safety profile.
Proguanil functions as a dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitor , which is crucial for the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines necessary for DNA synthesis in malaria parasites. The inhibition of DHFR leads to a failure in nuclear division during the schizont formation phase within erythrocytes and liver cells .
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of Dihydrofolate Reductase : Proguanil and its metabolite cycloguanil inhibit DHFR in malaria parasites, disrupting folate metabolism essential for DNA replication .
- Synergistic Action with Atovaquone : When combined with atovaquone (as in Malarone), proguanil enhances the efficacy against resistant strains of malaria by targeting different pathways in the parasite's lifecycle .
Pharmacokinetics
Proguanil is rapidly absorbed following oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1-3 hours. It has a high bioavailability (approximately 75%) and is extensively metabolized in the liver to cycloguanil via cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP2C19) .
Pharmacokinetic Parameters:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Rapid and well absorbed |
| Bioavailability | ~75% |
| Protein Binding | ~75% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C19) |
| Elimination Half-life | 8-10 hours |
Clinical Efficacy
Numerous studies have demonstrated the high efficacy of proguanil, particularly when used in combination with atovaquone. A systematic review indicated that this combination therapy has a prophylactic efficacy of approximately 95.8% against malaria .
Case Studies:
- Study on Children : In a randomized controlled trial involving 320 children in Gabon, none of the children receiving atovaquone-proguanil developed positive blood smears during chemosuppression, compared to 25 cases in the placebo group (p<0.001)【6】【8】.
- Efficacy Against Resistant Strains : Proguanil has shown effectiveness even in regions where resistance to other antimalarial drugs is prevalent. For example, high antimalarial efficacy was observed in patients with poor metabolizer genotypes for CYP2C19【4】【5】.
Safety Profile
Proguanil is generally well-tolerated, with a lower incidence of adverse effects compared to alternative treatments. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting【5】【6】. A meta-analysis reported fewer treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation among patients taking atovaquone-proguanil compared to those on other regimens【2】.
Adverse Effects Overview:
| Adverse Effect | Incidence (%) |
|---|---|
| Nausea | 33% |
| Vomiting | 29% |
| Abdominal Pain | Varies |
特性
Key on ui mechanism of action |
Proguanil inhibits the dihydrofolate reductase of plasmodia and thereby blocks the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines, which are essential for DNA synthesis and cell multiplication. This leads to failure of nuclear division at the time of schizont formation in erythrocytes and liver. |
|---|---|
CAS番号 |
500-92-5 |
分子式 |
C11H16ClN5 |
分子量 |
259.77 g/mol |
IUPAC名 |
1-[amino-(4-chloroanilino)methylidene]-2-(1,1,1,3,3,3-hexadeuteriopropan-2-yl)guanidine |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H16ClN5/c1-7(2)15-10(13)17-11(14)16-9-5-3-8(12)4-6-9/h3-7H,1-2H3,(H5,13,14,15,16,17)/i1D3,2D3 |
InChIキー |
SSOLNOMRVKKSON-WFGJKAKNSA-N |
SMILES |
CC(C)N=C(N)N=C(N)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl |
異性体SMILES |
[2H]C([2H])([2H])C(C([2H])([2H])[2H])N=C(N)N=C(N)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl |
正規SMILES |
CC(C)N=C(N)N=C(N)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl |
melting_point |
129 °C |
Key on ui other cas no. |
500-92-5 |
物理的記述 |
Solid |
純度 |
> 95% |
数量 |
Milligrams-Grams |
関連するCAS |
637-32-1 (hydrochloride) |
溶解性 |
2.86e-01 g/L |
同義語 |
Bigumal Chlorguanid Chloriguane Chloroguanide Chloroguanide Hydrochloride Hydrochloride, Chloroguanide Hydrochloride, Proguanil Paludrin Paludrine Proguanil Proguanil Hydrochloride |
製品の起源 |
United States |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: How does Proguanil exert its antimalarial effect?
A1: Proguanil itself has weak antimalarial activity. Its effectiveness stems from its active metabolite, Cycloguanil, a potent inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) []. DHFR is a crucial enzyme in the folate metabolic pathway, essential for DNA synthesis and cellular replication in parasites like Plasmodium falciparum []. By inhibiting DHFR, Cycloguanil disrupts DNA synthesis and ultimately kills the parasite [, ].
Q2: Are there other mechanisms by which Proguanil impacts Plasmodium falciparum?
A2: Research suggests Proguanil, in combination with Atovaquone, might interfere with mitochondrial electron transport and collapse mitochondrial membrane potential in the parasite, further contributing to its antimalarial activity [].
Q3: Does Proguanil affect other stages of the Plasmodium life cycle besides the erythrocytic stage?
A3: Yes, both Proguanil and Atovaquone demonstrate activity against gametocytes and pre-erythrocytic (hepatic) stages of malaria parasites []. This is supported by studies indicating that short-term Proguanil administration might provide causal prophylaxis for Plasmodium vivax by inhibiting liver-stage schizonts, although it doesn't seem to prevent late attacks related to hypnozoite reactivation [].
Q4: How is Proguanil metabolized in the human body?
A4: Proguanil is primarily metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, specifically CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 [, ]. The primary metabolic pathway involves CYP2C19-mediated conversion to its active metabolite, Cycloguanil [, ].
Q5: What factors contribute to the variability in Proguanil metabolism among individuals?
A5: Inter-individual variability in Proguanil metabolism is influenced by several factors, primarily genetic polymorphisms in the CYP2C19 gene [, ]. Individuals homozygous for the CYP2C19*2 allele exhibit significantly reduced metabolic capacity, leading to higher Proguanil and lower Cycloguanil levels []. Other factors include co-administration of drugs that are CYP2C19 inducers or inhibitors [], and variations in the expression and activity of other enzymes involved in Proguanil metabolism, like CYP3A4 [].
Q6: How is Proguanil eliminated from the body?
A6: Both Proguanil and Cycloguanil are predominantly eliminated through the kidneys []. Therefore, dosage adjustments are necessary for patients with renal impairment to prevent drug accumulation [].
Q7: Are there documented cases of resistance to Proguanil?
A7: Yes, Proguanil resistance has been observed and is primarily attributed to point mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) gene of Plasmodium falciparum [, ]. The S108N mutation is particularly associated with Proguanil resistance [, ].
Q8: Is there cross-resistance between Proguanil and other antimalarial drugs?
A8: Yes, cross-resistance has been observed between Proguanil and Pyrimethamine, another antifolate drug []. This is attributed to their shared mechanism of action, both targeting the DHFR enzyme in the parasite. The presence of the triple mutant DHFR haplotype (S108N+N51I+C59N) in Plasmodium falciparum has been linked to resistance to both drugs [, ].
Q9: Does Proguanil interact with other drugs?
A9: Yes, Proguanil's metabolism can be affected by co-administration with other drugs metabolized by CYP2C19, such as Phenytoin []. Concomitant use of Phenytoin, a CYP2C19 inducer, can decrease Proguanil's area under the curve (AUC) and maximum concentration (Cmax), potentially impacting its efficacy [].
Q10: Beyond malaria, are there other potential therapeutic applications for Proguanil?
A10: Emerging research suggests that Proguanil may have anti-cancer properties, particularly in breast cancer. Studies have shown that Proguanil inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, potentially by inducing oxidative stress, disrupting mitochondrial function, and triggering apoptosis [, ].
Q11: What are the key considerations in formulating Proguanil for therapeutic use?
A11: Proguanil formulations aim to optimize solubility, bioavailability, and stability []. The choice of excipients and manufacturing processes can significantly influence these factors. For instance, some herbal formulations may significantly impact the dissolution profile of Proguanil tablets, potentially altering its bioavailability and warranting further investigation for potential herb-drug interactions [].
Q12: What analytical techniques are commonly employed to quantify Proguanil and its metabolites?
A12: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is widely used to measure Proguanil and its metabolites in biological samples like plasma and urine [, , ]. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) offers enhanced speed and sensitivity for pharmacokinetic studies [].
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















