コビメチニブ
説明
コビメチニブは、コテリックという商品名で販売されている抗がん剤であり、主にメラノーマの治療に、ベムラフェニブとの併用で用いられます。 それは、マイトジェン活性化プロテインキナーゼキナーゼ1(MEK1)およびマイトジェン活性化プロテインキナーゼキナーゼ2(MEK2)の選択的阻害剤であり、マイトジェン活性化プロテインキナーゼ/細胞外シグナル調節キナーゼ(MAPK/ERK)経路の一部です 。 この経路は、さまざまな癌でしばしば過剰に活性化されており、コビメチニブを貴重な治療薬としています .
2. 製法
(2S)-2-ピペリジンカルボン酸から始まるいくつかのステップで、コビメチニブの合成が行われます。 このプロセスには、ニトロ化、加水分解、エステル化、およびtert-ブトキシカルボニル(Boc)保護が含まれており、中間体である[2-オキソ-2-((2S)-1-tert-ブトキシカルボニルピペリジン-2-イル)]酢酸が生成されます 。 この中間体は、付加、還元、および環化反応を受けて、(2S)-1-tert-ブトキシカルボニル-2-(3-ヒドロキシアゼチジン-3-イル)ピペリジンを形成し、その後、側鎖と縮合してコビメチニブが生成されます 。 このプロセスは、経済的で環境に優しく、工業生産に適するように設計されています .
3. 化学反応の分析
コビメチニブは、次のようなさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
これらの反応で使用される一般的な試薬と条件には、Boc保護のためのtert-ブトキシカルボニルクロリド、および還元ステップのためのさまざまな還元剤があります 。 これらの反応から生成される主要な生成物は、最終的なコビメチニブ分子に至る中間体です .
4. 科学研究への応用
コビメチニブには、いくつかの科学研究への応用があります。
科学的研究の応用
Indications
Cobimetinib is primarily indicated for:
- Melanoma : Used in combination with vemurafenib for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma harboring BRAF V600E or V600K mutations.
- Colorectal Cancer : Investigated in clinical trials for patients with BRAF-mutated colorectal cancer.
Melanoma Treatment
The pivotal study for cobimetinib's approval was the coBRIM trial , a Phase III randomized study that assessed the combination of cobimetinib and vemurafenib versus vemurafenib alone. Key findings include:
- Overall Survival (OS) : The median OS was 22.5 months for the combination therapy compared to 17.4 months for vemurafenib alone, with 5-year OS rates of 31% versus 26%, respectively .
- Progression-Free Survival (PFS) : Median PFS was significantly improved at 12.6 months compared to 7.2 months for the control group, indicating a substantial benefit from the combination therapy .
Table 1 summarizes the efficacy results from the coBRIM study:
| Measure | Cobimetinib + Vemurafenib | Vemurafenib Alone |
|---|---|---|
| Median OS | 22.5 months | 17.4 months |
| 5-Year OS Rate | 31% | 26% |
| Median PFS | 12.6 months | 7.2 months |
| 5-Year PFS Rate | 14% | 10% |
Colorectal Cancer
Cobimetinib has also shown promise in treating colorectal cancer with BRAF mutations. In a cohort study, patients receiving cobimetinib in combination with vemurafenib demonstrated improved outcomes compared to historical controls . However, further studies are necessary to establish definitive efficacy.
Safety Profile
The safety profile of cobimetinib has been consistent across studies. Common adverse events include:
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Rash
- Elevated liver enzymes
In the coBRIM study, these adverse events were manageable, and no new safety signals were identified over extended follow-up periods .
Case Studies and Research Insights
- Long-Term Outcomes : Extended follow-up from the coBRIM study confirmed that patients achieving a complete response had significantly better survival outcomes, emphasizing the importance of early treatment responses .
- Combination Therapies : Ongoing research is exploring cobimetinib's effectiveness in combination with other agents targeting different pathways, such as RMC-4630 (a SHP2 inhibitor) and KRAS inhibitors . Early results indicate potential synergistic effects that may enhance treatment efficacy.
- Quality of Life : Studies have indicated that patients receiving cobimetinib plus vemurafenib report improved health-related quality of life metrics compared to those receiving monotherapy, suggesting that combination therapy may not only extend survival but also enhance patient well-being .
作用機序
コビメチニブは、ERK経路の上流レギュレーターであるMEK1とMEK2の可逆的阻害剤です 。 これらのキナーゼを阻害することにより、コビメチニブはERKのリン酸化と活性化を防ぎ、癌細胞の細胞増殖を抑制し、アポトーシスを増加させます 。 この機序は、MAPK/ERK経路の構成的活性化につながるBRAF遺伝子の変異がある癌において特に有効です .
6. 類似の化合物との比較
コビメチニブは、癌治療に使用されるいくつかのMEK阻害剤の1つです。類似の化合物には、以下のようなものがあります。
トラメチニブ: メラノーマの治療に使用される別のMEK阻害剤です。
ビニメチニブ: メラノーマやその他の癌の治療に、他の薬との併用で用いられています.
セルメチニブ: 神経線維腫症1型やその他の癌の治療に使用されます.
コビメチニブは、MAPK/ERK経路の別のキナーゼを標的にするベムラフェニブとの併用使用が特徴であり、相乗効果と治療効果の改善につながります .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Cobimetinib plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 (MEK2). These enzymes are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation . By inhibiting MEK1 and MEK2, cobimetinib effectively reduces the phosphorylation and activation of ERK1 and ERK2, leading to decreased cellular proliferation . Cobimetinib interacts with these enzymes through reversible binding, which allows it to inhibit their activity without permanently altering their structure .
Cellular Effects
Cobimetinib has significant effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It primarily influences cell function by inhibiting the MEK/ERK signaling pathway, which is crucial for cell proliferation and survival . In cancer cells, cobimetinib induces apoptosis and inhibits cell growth by reducing the phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 . This inhibition leads to decreased expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression and survival, ultimately resulting in reduced cellular proliferation and increased cell death . Additionally, cobimetinib has been shown to induce immunogenic cell death in certain cancer cell lines, further enhancing its anti-tumor effects .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of cobimetinib involves its selective inhibition of MEK1 and MEK2, which are key components of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway . Cobimetinib binds to the allosteric site of MEK1 and MEK2, preventing their activation and subsequent phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 . This inhibition disrupts the downstream signaling cascade, leading to decreased cellular proliferation and increased apoptosis . Cobimetinib’s ability to maintain its inhibitory effect even when MEK is already phosphorylated further enhances its efficacy in targeting cancer cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of cobimetinib vary with different dosages in animal models. At lower doses, cobimetinib effectively inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis without causing significant toxicity . At higher doses, cobimetinib can cause adverse effects, including gastrointestinal toxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity . These toxic effects highlight the importance of optimizing the dosage of cobimetinib to achieve maximum therapeutic benefit while minimizing adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
Cobimetinib is primarily metabolized through the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) pathway . This metabolic pathway involves the oxidation of cobimetinib, leading to the formation of various metabolites that are subsequently excreted in the feces and urine . The metabolism of cobimetinib can be influenced by other drugs that inhibit or induce CYP3A4, potentially affecting its efficacy and safety . Additionally, cobimetinib’s interaction with other enzymes and cofactors involved in its metabolism can impact its pharmacokinetics and overall therapeutic profile .
Transport and Distribution
Cobimetinib is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. It is highly protein-bound, with approximately 95% of the drug bound to plasma proteins . This high protein binding affects its distribution and bioavailability, as only the unbound fraction of cobimetinib is pharmacologically active . Cobimetinib is also subject to active transport by efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, which can influence its intracellular concentration and distribution . These transport mechanisms play a crucial role in determining the localization and accumulation of cobimetinib within different tissues and cells .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of cobimetinib is primarily determined by its interaction with specific targeting signals and post-translational modifications. Cobimetinib is known to localize to the cytoplasm, where it exerts its inhibitory effects on MEK1 and MEK2 . The presence of specific targeting signals, such as nuclear localization signals, can also influence the subcellular distribution of cobimetinib, directing it to specific compartments or organelles . These localization patterns are critical for cobimetinib’s activity and function, as they determine its ability to effectively inhibit the MEK/ERK signaling pathway and exert its anti-tumor effects .
準備方法
The synthesis of cobimetinib involves several steps starting from (2S)-2-piperidinecarboxylic acid. The process includes nitrification, hydrolysis, esterification, and tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) protection to produce an intermediate, [2-oxo-2-((2S)-1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidin-2-yl)] acetate . This intermediate undergoes addition, reduction, and cyclization reactions to form (2S)-1-tert-butoxycarbonyl-2-(3-hydroxyazetidin-3-yl)piperidine, which is then condensed with a side chain to yield cobimetinib . The process is designed to be economical, environmentally friendly, and suitable for industrial production .
化学反応の分析
Cobimetinib undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Cobimetinib is metabolized primarily by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) oxidation.
Reduction: The reduction reactions are part of its synthetic route.
Substitution: The synthesis involves substitution reactions to introduce functional groups
Common reagents and conditions used in these reactions include tert-butoxycarbonyl chloride for Boc protection, and various reducing agents for the reduction steps . The major products formed from these reactions are intermediates leading to the final cobimetinib molecule .
類似化合物との比較
Cobimetinib is one of several MEK inhibitors used in cancer treatment. Similar compounds include:
Trametinib: Another MEK inhibitor used to treat melanoma.
Binimetinib: Used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of melanoma and other cancers.
Selumetinib: Used for treating neurofibromatosis type 1 and other cancers.
Cobimetinib is unique in its combination use with vemurafenib, which targets a different kinase in the MAPK/ERK pathway, leading to synergistic effects and improved therapeutic outcomes .
生物活性
Cobimetinib (Cotellic™) is a selective, allosteric inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK), primarily used in the treatment of advanced melanoma, particularly in combination with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib. This article explores the biological activity of cobimetinib, its mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and safety profile, supported by relevant data tables and research findings.
Cobimetinib specifically inhibits MEK1 and MEK2, which are critical components of the MAPK signaling pathway. This pathway is often dysregulated in various cancers due to mutations in upstream components such as BRAF. By inhibiting MEK, cobimetinib disrupts downstream ERK signaling, leading to reduced cancer cell proliferation and survival.
- Selectivity : Cobimetinib shows a 100-fold greater potency for phosphorylated MEK1 compared to MEK2, which is crucial for its therapeutic efficacy .
Clinical Efficacy
Cobimetinib has been evaluated in several clinical trials, particularly for patients with BRAF V600E mutations. The following table summarizes key findings from major studies:
Safety Profile
While cobimetinib has demonstrated significant antitumor activity, it is associated with various adverse effects. Common side effects include:
- Diarrhea
- Photosensitivity
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe skin rash
- Liver toxicity
Serious side effects can also occur, including heart muscle damage and retinal detachment .
Case Studies
-
Case Study on Advanced Melanoma :
A patient treated with cobimetinib and vemurafenib exhibited a dramatic reduction in tumor size after three months of therapy, with a notable improvement in quality of life. However, they experienced severe diarrhea requiring dose adjustment. -
Combination Therapy :
In another case involving a patient with SCCHN treated with cobimetinib plus atezolizumab, moderate antitumor activity was observed; however, the patient developed immune-related adverse effects that necessitated corticosteroid treatment .
Research Findings
Recent studies have further elucidated the biological activity of cobimetinib:
- Inhibition of Platelet Function : Research indicates that while cobimetinib effectively inhibits MEK activity in platelets, its impact on platelet function is less pronounced than expected at therapeutic concentrations .
- Comparative Studies : A meta-analysis highlighted that the combination of cobimetinib with other agents might enhance efficacy compared to monotherapy approaches, particularly in resistant melanoma cases .
特性
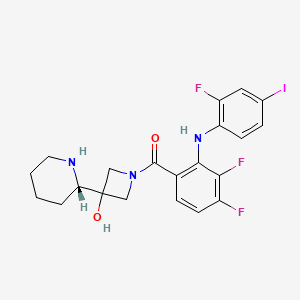
IUPAC Name |
[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H21F3IN3O2/c22-14-6-5-13(19(18(14)24)27-16-7-4-12(25)9-15(16)23)20(29)28-10-21(30,11-28)17-3-1-2-8-26-17/h4-7,9,17,26-27,30H,1-3,8,10-11H2/t17-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
BSMCAPRUBJMWDF-KRWDZBQOSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CCNC(C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CCN[C@@H](C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H21F3IN3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60239435 | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60239435 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
531.3 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation. BRAF V600E and K mutations result in constitutive activation of the BRAF pathway which includes MEK1 and MEK2. In mice implanted with tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600E, cobimetinib inhibited tumor cell growth. Cobimetinib and vemurafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared to either drug alone, coadministration of cobimetinib and vemurafenib resulted in increased apoptosis in vitro and reduced tumor growth in mouse implantation models of tumor cell lines harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Cobimetinib also prevented vemurafenib-mediated growth enhancement of a wild-type BRAF tumor cell line in an in vivo mouse implantation model. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05239 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
934660-93-2 | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=934660-93-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0934660932 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05239 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60239435 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | COBIMETINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/ER29L26N1X | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















