Cobimetinib
Descripción general
Descripción
Cobimetinib, vendido bajo la marca Cotellic, es un medicamento contra el cáncer que se utiliza principalmente en combinación con vemurafenib para tratar el melanoma. Es un inhibidor selectivo de la quinasa 1 activada por mitógeno de proteína (MEK1) y la quinasa 2 activada por mitógeno de proteína (MEK2), que forman parte de la vía de la quinasa activada por mitógeno de proteína/quinasa regulada por señales extracelulares (MAPK/ERK) . Esta vía suele estar sobreactivada en diversos cánceres, lo que convierte a this compound en un valioso agente terapéutico .
Mecanismo De Acción
Cobimetinib es un inhibidor reversible de MEK1 y MEK2, que son reguladores ascendentes de la vía ERK . Al inhibir estas quinasas, this compound evita la fosforilación y activación de ERK, lo que conduce a una reducción de la proliferación celular y un aumento de la apoptosis en las células cancerosas . Este mecanismo es particularmente eficaz en los cánceres con mutaciones en el gen BRAF, que conducen a una activación constitutiva de la vía MAPK/ERK .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Cobimetinib plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 (MEK2). These enzymes are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation . By inhibiting MEK1 and MEK2, this compound effectively reduces the phosphorylation and activation of ERK1 and ERK2, leading to decreased cellular proliferation . This compound interacts with these enzymes through reversible binding, which allows it to inhibit their activity without permanently altering their structure .
Cellular Effects
This compound has significant effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It primarily influences cell function by inhibiting the MEK/ERK signaling pathway, which is crucial for cell proliferation and survival . In cancer cells, this compound induces apoptosis and inhibits cell growth by reducing the phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 . This inhibition leads to decreased expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression and survival, ultimately resulting in reduced cellular proliferation and increased cell death . Additionally, this compound has been shown to induce immunogenic cell death in certain cancer cell lines, further enhancing its anti-tumor effects .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its selective inhibition of MEK1 and MEK2, which are key components of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway . This compound binds to the allosteric site of MEK1 and MEK2, preventing their activation and subsequent phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 . This inhibition disrupts the downstream signaling cascade, leading to decreased cellular proliferation and increased apoptosis . This compound’s ability to maintain its inhibitory effect even when MEK is already phosphorylated further enhances its efficacy in targeting cancer cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. At lower doses, this compound effectively inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis without causing significant toxicity . At higher doses, this compound can cause adverse effects, including gastrointestinal toxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity . These toxic effects highlight the importance of optimizing the dosage of this compound to achieve maximum therapeutic benefit while minimizing adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized through the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) pathway . This metabolic pathway involves the oxidation of this compound, leading to the formation of various metabolites that are subsequently excreted in the feces and urine . The metabolism of this compound can be influenced by other drugs that inhibit or induce CYP3A4, potentially affecting its efficacy and safety . Additionally, this compound’s interaction with other enzymes and cofactors involved in its metabolism can impact its pharmacokinetics and overall therapeutic profile .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. It is highly protein-bound, with approximately 95% of the drug bound to plasma proteins . This high protein binding affects its distribution and bioavailability, as only the unbound fraction of this compound is pharmacologically active . This compound is also subject to active transport by efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, which can influence its intracellular concentration and distribution . These transport mechanisms play a crucial role in determining the localization and accumulation of this compound within different tissues and cells .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound is primarily determined by its interaction with specific targeting signals and post-translational modifications. This compound is known to localize to the cytoplasm, where it exerts its inhibitory effects on MEK1 and MEK2 . The presence of specific targeting signals, such as nuclear localization signals, can also influence the subcellular distribution of this compound, directing it to specific compartments or organelles . These localization patterns are critical for this compound’s activity and function, as they determine its ability to effectively inhibit the MEK/ERK signaling pathway and exert its anti-tumor effects .
Métodos De Preparación
La síntesis de cobimetinib implica varios pasos que comienzan con el ácido (2S)-2-piperidinocarboxílico. El proceso incluye nitrificación, hidrólisis, esterificación y protección con tert-butoxicarbonilo (Boc) para producir un intermedio, [2-oxo-2-((2S)-1-tert-butoxicarbonilpiperidin-2-il)] acetato . Este intermedio se somete a reacciones de adición, reducción y ciclación para formar (2S)-1-tert-butoxicarbonil-2-(3-hidroxazetídin-3-il)piperidina, que luego se condensa con una cadena lateral para producir this compound . El proceso está diseñado para ser económico, respetuoso con el medio ambiente y adecuado para la producción industrial .
3. Análisis de las reacciones químicas
This compound experimenta diversas reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Oxidación: This compound se metaboliza principalmente por oxidación con citocromo P450 3A4 (CYP3A4).
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción forman parte de su ruta sintética.
Sustitución: La síntesis implica reacciones de sustitución para introducir grupos funcionales
Los reactivos y condiciones comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen cloruro de tert-butoxicarbonilo para la protección con Boc y diversos agentes reductores para los pasos de reducción . Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones son intermediarios que conducen a la molécula final de this compound .
4. Aplicaciones de la investigación científica
This compound tiene varias aplicaciones en la investigación científica:
Química: Se utiliza como compuesto modelo para estudiar la inhibición de MEK y sus efectos en la vía MAPK/ERK.
Medicina: Se utiliza principalmente en combinación con vemurafenib para tratar el melanoma irresecable o metastásico con mutaciones BRAF V600 También se está estudiando su potencial para tratar otros cánceres, como el cáncer de mama.
Industria: This compound es producido y comercializado por empresas farmacéuticas para uso terapéutico.
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Cobimetinib undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: This compound is metabolized primarily by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) oxidation.
Reduction: The reduction reactions are part of its synthetic route.
Substitution: The synthesis involves substitution reactions to introduce functional groups
Common reagents and conditions used in these reactions include tert-butoxycarbonyl chloride for Boc protection, and various reducing agents for the reduction steps . The major products formed from these reactions are intermediates leading to the final this compound molecule .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Indications
Cobimetinib is primarily indicated for:
- Melanoma : Used in combination with vemurafenib for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma harboring BRAF V600E or V600K mutations.
- Colorectal Cancer : Investigated in clinical trials for patients with BRAF-mutated colorectal cancer.
Melanoma Treatment
The pivotal study for this compound's approval was the coBRIM trial , a Phase III randomized study that assessed the combination of this compound and vemurafenib versus vemurafenib alone. Key findings include:
- Overall Survival (OS) : The median OS was 22.5 months for the combination therapy compared to 17.4 months for vemurafenib alone, with 5-year OS rates of 31% versus 26%, respectively .
- Progression-Free Survival (PFS) : Median PFS was significantly improved at 12.6 months compared to 7.2 months for the control group, indicating a substantial benefit from the combination therapy .
Table 1 summarizes the efficacy results from the coBRIM study:
| Measure | This compound + Vemurafenib | Vemurafenib Alone |
|---|---|---|
| Median OS | 22.5 months | 17.4 months |
| 5-Year OS Rate | 31% | 26% |
| Median PFS | 12.6 months | 7.2 months |
| 5-Year PFS Rate | 14% | 10% |
Colorectal Cancer
This compound has also shown promise in treating colorectal cancer with BRAF mutations. In a cohort study, patients receiving this compound in combination with vemurafenib demonstrated improved outcomes compared to historical controls . However, further studies are necessary to establish definitive efficacy.
Safety Profile
The safety profile of this compound has been consistent across studies. Common adverse events include:
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Rash
- Elevated liver enzymes
In the coBRIM study, these adverse events were manageable, and no new safety signals were identified over extended follow-up periods .
Case Studies and Research Insights
- Long-Term Outcomes : Extended follow-up from the coBRIM study confirmed that patients achieving a complete response had significantly better survival outcomes, emphasizing the importance of early treatment responses .
- Combination Therapies : Ongoing research is exploring this compound's effectiveness in combination with other agents targeting different pathways, such as RMC-4630 (a SHP2 inhibitor) and KRAS inhibitors . Early results indicate potential synergistic effects that may enhance treatment efficacy.
- Quality of Life : Studies have indicated that patients receiving this compound plus vemurafenib report improved health-related quality of life metrics compared to those receiving monotherapy, suggesting that combination therapy may not only extend survival but also enhance patient well-being .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Cobimetinib es uno de los varios inhibidores de MEK que se utilizan en el tratamiento del cáncer. Compuestos similares incluyen:
Trametinib: Otro inhibidor de MEK que se utiliza para tratar el melanoma.
Binimetinib: Se utiliza en combinación con otros fármacos para el tratamiento del melanoma y otros cánceres.
Selumetinib: Se utiliza para tratar la neurofibromatosis tipo 1 y otros cánceres.
This compound es único en su uso combinado con vemurafenib, que se dirige a una quinasa diferente en la vía MAPK/ERK, lo que produce efectos sinérgicos y mejores resultados terapéuticos .
Actividad Biológica
Cobimetinib (Cotellic™) is a selective, allosteric inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK), primarily used in the treatment of advanced melanoma, particularly in combination with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, its mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and safety profile, supported by relevant data tables and research findings.
This compound specifically inhibits MEK1 and MEK2, which are critical components of the MAPK signaling pathway. This pathway is often dysregulated in various cancers due to mutations in upstream components such as BRAF. By inhibiting MEK, this compound disrupts downstream ERK signaling, leading to reduced cancer cell proliferation and survival.
- Selectivity : this compound shows a 100-fold greater potency for phosphorylated MEK1 compared to MEK2, which is crucial for its therapeutic efficacy .
Clinical Efficacy
This compound has been evaluated in several clinical trials, particularly for patients with BRAF V600E mutations. The following table summarizes key findings from major studies:
Safety Profile
While this compound has demonstrated significant antitumor activity, it is associated with various adverse effects. Common side effects include:
- Diarrhea
- Photosensitivity
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe skin rash
- Liver toxicity
Serious side effects can also occur, including heart muscle damage and retinal detachment .
Case Studies
-
Case Study on Advanced Melanoma :
A patient treated with this compound and vemurafenib exhibited a dramatic reduction in tumor size after three months of therapy, with a notable improvement in quality of life. However, they experienced severe diarrhea requiring dose adjustment. -
Combination Therapy :
In another case involving a patient with SCCHN treated with this compound plus atezolizumab, moderate antitumor activity was observed; however, the patient developed immune-related adverse effects that necessitated corticosteroid treatment .
Research Findings
Recent studies have further elucidated the biological activity of this compound:
- Inhibition of Platelet Function : Research indicates that while this compound effectively inhibits MEK activity in platelets, its impact on platelet function is less pronounced than expected at therapeutic concentrations .
- Comparative Studies : A meta-analysis highlighted that the combination of this compound with other agents might enhance efficacy compared to monotherapy approaches, particularly in resistant melanoma cases .
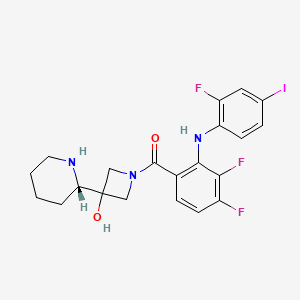
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H21F3IN3O2/c22-14-6-5-13(19(18(14)24)27-16-7-4-12(25)9-15(16)23)20(29)28-10-21(30,11-28)17-3-1-2-8-26-17/h4-7,9,17,26-27,30H,1-3,8,10-11H2/t17-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
BSMCAPRUBJMWDF-KRWDZBQOSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CCNC(C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CCN[C@@H](C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H21F3IN3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60239435 | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60239435 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
531.3 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation. BRAF V600E and K mutations result in constitutive activation of the BRAF pathway which includes MEK1 and MEK2. In mice implanted with tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600E, cobimetinib inhibited tumor cell growth. Cobimetinib and vemurafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared to either drug alone, coadministration of cobimetinib and vemurafenib resulted in increased apoptosis in vitro and reduced tumor growth in mouse implantation models of tumor cell lines harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Cobimetinib also prevented vemurafenib-mediated growth enhancement of a wild-type BRAF tumor cell line in an in vivo mouse implantation model. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05239 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
934660-93-2 | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=934660-93-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0934660932 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05239 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60239435 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | COBIMETINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/ER29L26N1X | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.















