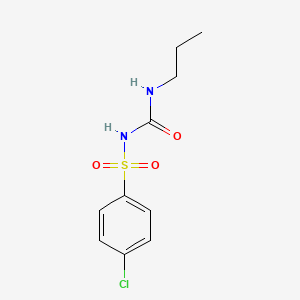
Chlorpropamide
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Chlorpropamid ist ein Antidiabetikum, das zur Klasse der Sulfonylharnstoffe gehört. Es wird hauptsächlich zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus eingesetzt, indem es die Freisetzung von Insulin aus den Betazellen der Bauchspeicheldrüse stimuliert. Chlorpropamid ist ein lang wirkendes Sulfonylharnstoff der ersten Generation und bekannt für seine Fähigkeit, den Blutzuckerspiegel über einen längeren Zeitraum zu halten .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Chlorpropamid kann durch einen mehrstufigen Prozess synthetisiert werden, der die Reaktion von 4-Chlorbenzolsulfonylchlorid mit Propylamin zur Bildung von 4-Chlorbenzolsulfonamid umfasst. Dieses Zwischenprodukt wird dann mit Phosgen und Ammoniak umgesetzt, um Chlorpropamid zu erhalten. Die Reaktionsbedingungen umfassen typischerweise kontrollierte Temperaturen und die Verwendung von Lösungsmitteln wie Dichlormethan .
Industrielle Produktionsverfahren
Die industrielle Produktion von Chlorpropamid folgt ähnlichen Synthesewegen, jedoch in größerem Maßstab. Das Verfahren umfasst die Verwendung großer Reaktoren und die präzise Kontrolle der Reaktionsbedingungen, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten. Das Endprodukt wird strengen Qualitätskontrollen unterzogen, um pharmazeutische Standards zu erfüllen .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Chlorpropamid unterliegt verschiedenen Arten von chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Chlorpropamid kann zu Sulfoxiden und Sulfonen oxidiert werden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können Chlorpropamid in seine entsprechenden Amin-Derivate umwandeln.
Substitution: Chlorpropamid kann nukleophile Substitutionsreaktionen eingehen, insbesondere an der Sulfonylgruppe
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Kaliumpermanganat.
Reduktion: Als Reduktionsmittel werden Lithiumaluminiumhydrid und Natriumborhydrid verwendet.
Substitution: Nukleophile wie Amine und Thiole können unter milden Bedingungen mit Chlorpropamid reagieren
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Oxidation: Sulfoxide und Sulfone.
Reduktion: Aminderivate.
Substitution: Verschiedene substituierte Sulfonamide
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Chlorpropamide is an antidiabetic drug in the sulfonylurea class, used to manage diabetes mellitus type 2 . It is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for treating non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus . this compound stimulates the pancreas' β cells to release insulin, increasing both basal insulin secretion and meal-stimulated insulin release .
Clinical Applications in Diabetes Management
This compound is primarily used to lower blood glucose levels in conjunction with diet in patients with type II diabetes mellitus . Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels:
- A six-year study involving 479 patients indicated that 58% (196 out of 339) achieved satisfactory blood sugar control with this compound .
- In a study comparing this compound to tolbutamide, this compound was more effective in reducing fasting blood sugar levels . 83% of patients responded positively to this compound, compared to 60% for tolbutamide .
- This compound has shown a lower primary failure rate compared to glibenclamide in long-term trials .
Case Study: Long-Term Use of this compound
A study published in JAMA observed 479 patients over six years, with 339 patients completing the analysis. The findings indicated that 58% of patients achieved satisfactory glycemic control . However, 42% experienced unsatisfactory control, including 31 patients with primary and 17 with secondary failure. Notably, 95 patients had previously shown unsatisfactory responses to other sulfonylureas .
Adverse Effects:
- Gastrointestinal issues (9 patients)
- Skin rash (7 patients)
- Symptomatic hypoglycemia (4 patients)
- Jaundice due to this compound hypersensitivity (1 patient)
Off-Label Use in Diabetes Insipidus
This compound is also used off-label to manage vasopressin-sensitive diabetes insipidus . It appears that this compound needs some level of endogenous antidiuretic hormone (ADH) to be present to produce an antidiuresis . this compound may enhance the effect of submaximal levels of endogenous ADH, leading to an antidiuretic effect .
Case Study: this compound in Diabetes Insipidus
In a study of 13 patients with vasopressin-sensitive diabetes insipidus, 10 experienced an antidiuresis with this compound treatment . The drug's antidiuretic action is similar to that of Pitressin, decreasing "free" water clearance without altering creatinine excretion . The effect of exogenous Pitressin was also potentiated when patients were pretreated with this compound, suggesting that this compound enhances the action of existing ADH in patients with diabetes insipidus .
Potential Adverse Effects
While this compound is effective, it is associated with several potential adverse effects :
- Hypoglycemia: Risk is increased in elderly, debilitated, and malnourished individuals . Consistent food intake is necessary to mitigate this risk .
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Including nausea and diarrhea .
- Skin Reactions: Such as rash .
- Cholestatic Jaundice: A case study reported cholestatic jaundice and pseudomembranous colitis in a 59-year-old man treated with this compound .
Drug Interactions and Metabolism
Wirkmechanismus
Chlorpropamide exerts its effects by binding to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the pancreatic beta-cell surface. This binding reduces potassium conductance, causing depolarization of the cell membrane. The depolarization triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, leading to an influx of calcium ions. The increased intracellular calcium concentration stimulates the exocytosis of insulin-containing granules, thereby increasing insulin secretion .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Chlorpropamid wird mit anderen Sulfonylharnstoffen verglichen, wie z. B.:
- Gliclazid
- Tolbutamid
- Glipizid
Einzigartigkeit
Chlorpropamid ist einzigartig durch seine lange Wirkdauer und seine Fähigkeit, über einen längeren Zeitraum stabile Blutzuckerspiegel zu halten. Es birgt ein höheres Risiko, Hypoglykämie zu verursachen als kürzer wirkende Sulfonylharnstoffe wie Gliclazid und Tolbutamid .
Ähnliche Verbindungen
- Gliclazid : Kürzer wirkendes Sulfonylharnstoff mit einem geringeren Risiko für Hypoglykämie.
- Tolbutamid : Ein weiteres Sulfonylharnstoff der ersten Generation mit einer kürzeren Wirkdauer.
- Glipizid : Sulfonylharnstoff der zweiten Generation mit einem günstigeren Nebenwirkungsprofil .
Biologische Aktivität
Chlorpropamide is a second-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent primarily used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Its biological activity is characterized by its ability to stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. This article delves into the mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy, and associated side effects of this compound, supported by relevant case studies and research findings.
This compound acts by binding to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the surface of pancreatic beta cells. This binding reduces potassium conductance, leading to membrane depolarization. The depolarization triggers an influx of calcium ions through voltage-sensitive calcium channels, which subsequently stimulates the exocytosis of insulin. Additionally, this compound enhances peripheral glucose utilization and decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis, contributing to its hypoglycemic effect .
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption : this compound is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 2-4 hours post-administration. The onset of action is typically within one hour, and the maximal effect is observed between 3-6 hours after ingestion .
- Distribution : It is highly bound to plasma proteins, with a half-life averaging approximately 36 hours (ranging from 25 to 60 hours) and a duration of effect lasting at least 24 hours .
- Metabolism and Excretion : About 80% of this compound is metabolized in the liver into various metabolites, including 2-hydroxylthis compound and p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea. The drug and its metabolites are primarily excreted through urine within 96 hours .
Clinical Efficacy
A long-term study involving 479 patients demonstrated that this compound effectively controlled blood glucose levels in approximately 58% of participants over a six-year period. Among those who had previously shown unsatisfactory responses to other sulfonylureas, this compound proved beneficial for many .
Case Study: Hyponatremia Risk
Research indicated that this compound treatment was associated with an incidence of hyponatremia (low serum sodium levels) in about 6.3% of patients. This condition was notably higher compared to patients treated with other sulfonylureas such as tolbutamide or glibenclamide. Elderly patients and those on thiazide diuretics were identified as having increased risk factors for this adverse effect .
Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, this compound can cause several side effects:
- Hypoglycemia : A common risk associated with sulfonylureas, hypoglycemia can occur especially in elderly or malnourished individuals .
- Gastrointestinal Issues : Reports indicated gastrointestinal disturbances in some patients during long-term therapy .
- Skin Reactions : Skin rashes were observed in a subset of patients .
- Jaundice : Cases of jaundice linked to hypersensitivity reactions have been documented .
Comparative Efficacy
In a comparative study between this compound and tolbutamide, this compound demonstrated superior efficacy in lowering fasting blood sugar levels. It was successful in achieving satisfactory control in 83% of cases compared to 60% for tolbutamide. Additionally, this compound required lower maximum dosages among responders .
Summary Table of Key Findings
| Parameter | This compound | Tolbutamide |
|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | 83% | 60% |
| Common Side Effects | Hypoglycemia, Jaundice | Less frequent |
| Risk of Hyponatremia | Higher (6.3%) | Lower (0.6%) |
| Half-Life | ~36 hours | ~8 hours |
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What are the validated analytical methods for quantifying chlorpropamide in pharmaceutical formulations, and how do their parameters compare?
The British Pharmacopeia recommends spectrophotometry, while the United States Pharmacopeia adopts HPLC . A spectrophotometric method using chloranilic acid (π-acceptor) forms a violet complex (λmax 530 nm) with this compound, validated for linearity (5–25 µg/mL), accuracy (recovery studies), and precision (RSD <2%) . HPLC offers higher specificity for complex matrices but requires costly instrumentation. Researchers should prioritize method selection based on laboratory resources and required sensitivity .
Q. How can researchers design reproducible clinical studies to assess this compound-alcohol flushing (CPAF) responses?
Key considerations include:
- Blinding : Double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover designs (e.g., this compound vs. placebo administered one week apart) to minimize bias .
- Exclusion criteria : Participants on NSAIDs (e.g., aspirin) or other drugs that may block flushing responses must be excluded .
- Standardized questionnaires : Avoid leading questions; instead, use symptom lists (e.g., "flushing of the face") to capture self-reported responses objectively .
- Compliance monitoring : Address attrition rates (e.g., 34–37% non-completion in diabetic cohorts) through reminders and simplified protocols .
Q. What statistical approaches are suitable for analyzing this compound efficacy data in heterogeneous diabetic populations?
Use Yates’s χ² test for categorical outcomes (e.g., CPAF incidence) and unpaired Student’s t-test for continuous variables (e.g., HbA1c reduction). For longitudinal data, mixed-effects models can account for repeated measures and dropout biases .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can researchers resolve discrepancies in this compound’s pharmacokinetic data across studies, particularly regarding plasma half-life variability?
Confounding factors include:
- Genetic polymorphisms : CYP2C9 enzyme variants alter this compound metabolism, affecting half-life (reported range: 24–42 hrs) .
- Drug interactions : Co-administration with NSAIDs or sulfonamides may displace this compound from plasma proteins, altering free concentrations . Mitigation strategies:
- Conduct in vitro hepatic microsome assays to identify metabolic pathways.
- Use population pharmacokinetic modeling to quantify inter-individual variability .
Q. What experimental frameworks optimize this compound assay robustness in biological matrices (e.g., plasma)?
- Sample pretreatment : Protein precipitation with acetonitrile or solid-phase extraction to reduce matrix interference .
- Validation parameters : Include selectivity (against endogenous compounds), recovery (>95%), and stability under storage conditions .
- Cross-validation : Compare results with LC-MS/MS for confirmation .
Q. How does this compound induce SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion), and what mechanistic studies are needed?
this compound enhances renal tubular sensitivity to ADH by upregulating aquaporin-2 channels and increasing Na<sup>+</sup>/Cl<sup>−</sup> reabsorption in the loop of Henle . Unresolved questions:
- Dose dependency : Is SIADH risk correlated with this compound dosage or duration?
- Genetic susceptibility : Do polymorphisms in ADH receptor genes (e.g., AVPR2) modulate this effect? Proposed methodology:
- In vitro models: Use collecting duct cell lines to quantify ADH receptor expression post-exposure.
- In vivo studies**: Measure urinary osmolality and serum sodium in patients on long-term therapy .
Q. What strategies improve the reproducibility of this compound’s polymorphic transformation studies during tablet formulation?
- In situ monitoring : Employ mechanical Raman spectroscopy to track crystal structure changes during compression .
- Environmental controls : Regulate humidity and temperature to prevent hydrate formation.
- Excipient screening : Test stabilizers (e.g., cellulose derivatives) to inhibit polymorphic shifts .
Q. Methodological Guidance
- Literature Review : Prioritize primary sources (e.g., Journal of Scientific Research) over unverified databases .
- Ethical Compliance : Obtain IRB approval for human studies; exclude vulnerable populations (e.g., pregnant women) unless benefits outweigh risks .
- Data Reporting : Use FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) for supplementary materials .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
1-(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl-3-propylurea | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H13ClN2O3S/c1-2-7-12-10(14)13-17(15,16)9-5-3-8(11)4-6-9/h3-6H,2,7H2,1H3,(H2,12,13,14) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
RKWGIWYCVPQPMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCNC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H13ClN2O3S | |
| Record name | CHLOROPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20013 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID9020322 | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9020322 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
276.74 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Chloropropamide is a white crystalline powder with a slight odor. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | CHLOROPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20013 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014810 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>41.5 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), less than 1 mg/mL at 57 °F (NTP, 1992), 2.2 mg/ml in water @ pH 6; practically insol in water @ pH 7.3; sol in alcohol; moderately sol in chloroform; sparingly sol in ether, benzene, In water, 258 mg/l @ 37 °C, 1.57e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855559 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | CHLOROPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20013 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00672 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CHLORPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2051 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014810 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfonylureas such as chlorpropamide bind to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the pancreatic cell surface, reducing potassium conductance and causing depolarization of the membrane. Depolarization stimulates calcium ion influx through voltage-sensitive calcium channels, raising intracellular concentrations of calcium ions, which induces the secretion, or exocytosis, of insulin., ...ACTION OF SULFONYLUREAS APPEARS TO BE STIMULATION OF RELEASE OF INSULIN FROM BETA CELLS. ...TO BE EFFECTIVE, PT MUST HAVE SOME FUNCTIONAL ISLET CELLS... /HYPOGLYCEMIC SULFONYLUREAS/, Sulfonylureas cause hypoglycemia by stimulating insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. Their effects in the treatment of diabetes ... are more complex. /Sulfonylureas/, Sulfonylureas are now...thought to act by a number of different mechanisms. 1. ...produce a depolarization of the pancreatic islet beta cell membrane potassium ion permeability. This results in a release of preformed insulin into the circulation and occurs mostly in non-insulin dependent diabetics. 2. ...reduce basal glucose output from the liver... 3. increase insulin receptor binding... 4. ...increasing intracellular levels of AMP... 5. increase insulin secretion by suppressing the release of glucagon and somatostatin from alpha and delta pancreatic cells. /Sulfonylureas/, Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose in NIDDM by directly stimulating the acute release of insulin from functioning beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue by an unknown process that involves a sulfonylurea receptor on the beta cell. Sulfonylureas inhibit the ATP potassium channels on the beta cell membrane and potassium efflux, which results in depolarization and calcium influx, calcium-calmodulin binding, kinase activation, and release of insulin containing granules by exocytosis, an effect similar to that of glucose. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood glucose and controls the storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Therefore, sulfonylureas are effective only in patients whose pancreata are capable of producing insulin. /Sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents/ | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00672 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CHLORPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2051 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from dil ethanol, WHITE, CRYSTALLINE POWDER, White, crystalline powder | |
CAS No. |
94-20-2 | |
| Record name | CHLOROPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20013 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=94-20-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000094202 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00672 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | chlorpropamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=756690 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | chlorpropamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=44634 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9020322 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.002.104 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CHLORPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/WTM2C3IL2X | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | CHLORPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2051 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014810 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
261 to 264 °F (NTP, 1992), 129.2-129.8, 127-129 °C, 127 - 129 °C | |
| Record name | CHLOROPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20013 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00672 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CHLORPROPAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/2051 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Chlorpropamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014810 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.













