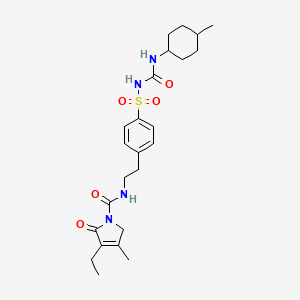
Glimepiride
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Glimepirid ist ein Antidiabetikum aus der Klasse der Sulfonylharnstoffe, das hauptsächlich zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus verschrieben wird. Es gilt als Zweitlinienoption im Vergleich zu Metformin, da Metformin eine gut etablierte Sicherheit und Wirksamkeit aufweist . Glimepirid wirkt in erster Linie durch die Steigerung der Insulinproduktion in der Bauchspeicheldrüse . Es wurde 1979 patentiert und 1995 für die medizinische Anwendung zugelassen .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Syntheserouten und Reaktionsbedingungen
Glimepirid wird durch einen mehrstufigen Prozess synthetisiert, der mehrere Zwischenprodukte beinhaltet. Die wichtigsten Schritte umfassen die Bildung des Pyrrolrings und die Anlagerung der Sulfonylharnstoffgruppe. Die Reaktionsbedingungen beinhalten typischerweise die Verwendung organischer Lösungsmittel, Katalysatoren und kontrollierter Temperaturen, um die gewünschten chemischen Umwandlungen sicherzustellen .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Die industrielle Produktion von Glimepirid beinhaltet die großtechnische Synthese unter optimierten Reaktionsbedingungen, um die Ausbeute und Reinheit zu maximieren. Der Prozess umfasst Reinigungsschritte wie Kristallisation und Filtration, um das Endprodukt in einer für die pharmazeutische Verwendung geeigneten Form zu erhalten .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
Arten von Reaktionen
Glimepirid unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Beinhaltet die Zugabe von Sauerstoff oder die Entfernung von Wasserstoff.
Reduktion: Beinhaltet die Zugabe von Wasserstoff oder die Entfernung von Sauerstoff.
Substitution: Beinhaltet den Austausch einer funktionellen Gruppe durch eine andere.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Häufige Reagenzien, die bei diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, umfassen Oxidationsmittel wie Kaliumpermanganat, Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid und verschiedene Katalysatoren, um die Reaktionen zu erleichtern .
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen entstehen, hängen von den spezifischen Bedingungen und Reagenzien ab, die verwendet werden. Zum Beispiel kann die Oxidation von Glimepirid zur Bildung von Sulfoxiden oder Sulfonen führen .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Glimepirid hat eine breite Palette an wissenschaftlichen Forschungsanwendungen:
Biologie: Untersucht auf seine Auswirkungen auf zelluläre Prozesse und die Insulinsekretion.
Industrie: Wird bei der Entwicklung neuer pharmazeutischer Formulierungen und Wirkstofffreisetzungssysteme verwendet.
Wirkmechanismus
Glimepirid wirkt als Insulinstimulans. Es stimuliert die Freisetzung von Insulin aus den Betazellen der Bauchspeicheldrüse, indem es ATP-sensitive Kaliumkanäle blockiert, was zu einer Depolarisation der Betazellen und einer anschließenden Insulinsekretion führt . Zusätzlich erhöht es die Aktivität intrazellulärer Insulinrezeptoren und verstärkt die Reaktion des Körpers auf Insulin .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Types of Reactions
Glimepiride undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen.
Reduction: Involves the addition of hydrogen or the removal of oxygen.
Substitution: Involves the replacement of one functional group with another.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in these reactions include oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate, reducing agents like sodium borohydride, and various catalysts to facilitate the reactions .
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific conditions and reagents used. For example, oxidation of this compound can lead to the formation of sulfoxides or sulfones .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Glimepiride is a second-generation sulfonylurea drug used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by improving glycemic control . It stimulates the secretion of insulin from pancreatic beta cells and enhances the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin, increasing glucose uptake and reducing blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels .
Clinical Applications and Efficacy
Monotherapy: this compound is effective as a monotherapy for patients with T2DM who have not achieved adequate glycemic control through diet alone . A randomized, placebo-controlled trial demonstrated that this compound (1–8 mg) significantly reduced fasting plasma glucose (FPG) by 46 mg/dL, post-prandial glucose (PPG) by 72 mg/dL, and HbA1c by 1.4% compared to placebo . In this study, 69% of patients taking this compound achieved good glycemic control (HbA1c ≤ 7.2%) compared to 32% on placebo .
Combination Therapy: this compound can be used in combination with other antidiabetic medications, such as metformin, to improve glycemic control .
Cardiovascular Benefits: Long-term use of this compound is associated with better survival rates and reduced hospitalizations for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and stroke in patients with T2DM and congestive heart failure (CHF) . High-dose this compound may offer greater cardiovascular protection compared to low-dose regimens . The cardiovascular protective effect of this compound may be related to increased levels of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET) through soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibition .
Comparison with Other Sulfonylureas: Studies suggest that this compound may have a beneficial effect on insulin resistance compared to glibenclamide . this compound treatment was associated with increased adiponectin concentrations and reduced waist circumference, while glibenclamide showed an inverse correlation between changes in serum adiponectin and HOMA-IR .
Dosing and Administration
This compound is typically administered orally once daily, with dosages ranging from 1 to 8 mg . Some studies have explored the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once- versus twice-daily dosing, with varying results . One study found lower glucose levels throughout the day with once-daily dosing compared to twice-daily, while another observed a significant decrease in FPG with twice-daily administration .
Safety and Tolerability
Wirkmechanismus
Glimepiride acts as an insulin secretagogue. It stimulates the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells by blocking ATP-sensitive potassium channels, causing depolarization of the beta cells and subsequent insulin secretion . Additionally, it increases the activity of intracellular insulin receptors, enhancing the body’s response to insulin .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
- Glipizid
- Glyburid
- Metformin
- Semaglutid
Einzigartigkeit
Glimepirid ist unter den Sulfonylharnstoffen einzigartig, da es eine längere Wirkungsdauer und ein geringeres Risiko für Hypoglykämie im Vergleich zu anderen Sulfonylharnstoffen der zweiten Generation aufweist . Es hat auch weniger kardiovaskuläre Auswirkungen, was es zu einer sichereren Option für Patienten mit kardiovaskulären Problemen macht .
Biologische Aktivität
Glimepiride is an oral antidiabetic medication belonging to the sulfonylurea class, primarily used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Its primary mechanism of action involves stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, supported by various studies, case reports, and clinical trials.
This compound functions by binding to ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K_ATP channels) on the plasma membrane of pancreatic beta cells. This binding leads to cell membrane depolarization, which opens voltage-dependent calcium channels. The influx of calcium ions triggers the exocytosis of insulin granules into the bloodstream. The overall process can be summarized as follows:
- Binding to K_ATP Channels : this compound inhibits these channels, preventing potassium from exiting the cell.
- Depolarization : This inhibition causes depolarization of the beta cell membrane.
- Calcium Influx : Voltage-dependent calcium channels open, allowing calcium to enter the cell.
- Insulin Secretion : Increased intracellular calcium stimulates insulin release.
Additionally, this compound enhances peripheral insulin sensitivity and promotes glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissues by increasing the translocation of GLUT4 transporters .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is well-absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations typically occurring within 2-3 hours. It undergoes hepatic metabolism primarily via the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2C9, producing active metabolites that contribute to its pharmacological effects. The elimination half-life is approximately 5-9 hours .
Glycemic Control
Several clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of this compound in controlling blood glucose levels:
- In a randomized controlled trial involving 249 patients with T2DM, this compound significantly reduced fasting plasma glucose (FPG) by an average of 46 mg/dL and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) by 1.4% compared to placebo .
- A meta-analysis indicated that this compound treatment led to a reduction in postprandial glucose levels by 72 mg/dL more than placebo .
| Study | Population | This compound Dose | FPG Reduction | HbA1c Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goldberg et al. (2012) | 304 T2DM patients | 1-8 mg/day | 43-74 mg/dL | 1.2%-1.9% |
| Placebo-Controlled Trial (1998) | 249 patients | 1-8 mg/day | 46 mg/dL | 1.4% |
Extrapancreatic Effects
This compound also exhibits extrapancreatic effects that enhance insulin sensitivity and promote glucose utilization in peripheral tissues. In vitro studies suggest that it may potentiate lipogenesis and glycogenesis, although its clinical relevance remains uncertain .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of this compound has been extensively studied:
- A large-scale study indicated that the incidence of hypoglycemia was low (0.9%) among patients using this compound over an extended period .
- Cardiovascular safety has been supported by trials such as CARMELINA and CAROLINA, which showed no significant increase in major adverse cardiovascular events compared to other antidiabetic agents .
Case Studies and Observations
Case studies have highlighted the effectiveness of this compound in specific patient populations:
- Elderly Patients : In older adults with T2DM, this compound has been shown to effectively lower blood glucose levels without significant adverse effects.
- Patients with Comorbidities : In patients with concurrent heart failure and diabetes, this compound use was associated with reduced all-cause mortality and hospitalizations .
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What validated analytical methods are recommended for detecting glimepiride in biological matrices?
To ensure reproducibility, use gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) with derivatization. Derivatize this compound using agents like N-methyl-N-(trimethylsilyl) trifluoroacetamide (MSTFA) to improve thermal stability and volatility. Validate the method using a Plackett-Burman experimental design (8-run, 4 variables) to assess robustness and ruggedness, with peak area as the response variable .
Q. How should dissolution rate studies for hydrophobic this compound formulations be designed?
Employ the slurry method to enhance dissolution. Validate dissolution profiles using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) per International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines. Characterize formulations via X-ray diffraction (XRD) to confirm crystalline/amorphous transitions (2θ range: 2°–40°, step width 2°/min) .
Q. What statistical approaches are suitable for analyzing this compound pharmacokinetic data?
Use one-tailed t-tests (Type 2 error) and ANOVA for robustness testing. For multi-variable interactions, apply Plackett-Burman designs to isolate significant factors (e.g., pH, temperature) affecting analytical responses like peak area .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can contradictions in this compound-protein binding affinity data be resolved across studies?
Perform frontal analysis using high-performance affinity chromatography (HPAC) with human serum albumin (HSA) columns. Compare one-site vs. two-site binding models using residual plots and F-tests. For example, this compound binding at 0.5–50 μM concentrations showed deviations at low concentrations, favoring a two-site model .
Q. What experimental strategies optimize this compound polymorph synthesis and characterization?
Synthesize novel polymorphs via solvent evaporation or crystallization. Characterize using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) for thermodynamic solubility and XRD for structural analysis. Rod-shaped crystalline structures (observed at 10X–100X magnification) indicate distinct polymorphic forms .
Q. How does this compound modulate neurodegenerative pathways in prion disease models?
In vitro, this compound activates glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (GPI-PLC), shedding cellular prion protein (PrP<sup>C</sup>) and reducing PrP<sup>Sc</sup> formation. Use neuronal cell lines exposed to PrP82–146 for survival assays and cPLA2 activity measurements to validate neuroprotective effects .
Q. What methodologies address this compound’s multi-site interactions in complex biological systems?
Combine HPAC with competitive binding assays. For example, frontal analysis of this compound-HSA interactions revealed two binding sites with average relative standard deviations of ±0.04–3.2%. Validate using equilibrium dialysis or surface plasmon resonance (SPR) for kinetic parameter estimation .
Q. Methodological Considerations
- Data Imputation in Clinical Trials: For longitudinal studies (e.g., 104-week HbA1c comparisons), apply multiple imputation to handle missing data (e.g., 13.9% imputed for this compound arms). Use ANCOVA with last observation carried forward (LOCF) to maintain statistical power .
- Reference Standards: Source certified this compound reference compounds (e.g., Related Compounds A, B, C) for impurity profiling. Store at controlled temperatures (±2°C) to prevent degradation .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
4-ethyl-3-methyl-N-[2-[4-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-oxo-2H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H34N4O5S/c1-4-21-17(3)15-28(22(21)29)24(31)25-14-13-18-7-11-20(12-8-18)34(32,33)27-23(30)26-19-9-5-16(2)6-10-19/h7-8,11-12,16,19H,4-6,9-10,13-15H2,1-3H3,(H,25,31)(H2,26,27,30) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WIGIZIANZCJQQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCC1=C(CN(C1=O)C(=O)NCCC2=CC=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)NC3CCC(CC3)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H34N4O5S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID5040675, DTXSID20861130 | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID5040675 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-N-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
490.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>73.6 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), Partly miscible, 3.84e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | SID49648856 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells that are gated by intracellular ATP and ADP. The hetero-octomeric complex of the channel is composed of four pore-forming Kir6.2 subunits and four regulatory sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits. Alternative splicing allows the formation of channels composed of varying subunit isoforms expressed at different concentrations in different tissues. In pancreatic beta cells, ATP-sensitive potassium channels play a role as essential metabolic sensors and regulators that couple membrane excitability with glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). When there is a decrease in the ATP:ADP ratio, the channels are activated and open, leading to K+ efflux from the cell, membrane hyperpolarization, and suppression of insulin secretion. In contrast, increased uptake of glucose into the cell leads to elevated intracellular ATP:ADP ratio, leading to the closure of channels and membrane depolarization. Depolarization leads to activation and opening of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and consequently an influx of calcium ions into the cell. Elevated intracellular calcium levels causes the contraction of the filaments of actomyosin responsible for the exocytosis of insulin granules stored in vesicles. Glimepiride blocks the ATP-sensitive potassium channel by binding non-specifically to the B sites of both sulfonylurea receptor-1 (SUR1) and sulfonylurea receptor-2A (SUR2A) subunits as well as the A site of SUR1 subunit of the channel to promote insulin secretion from the beta cell. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
261361-60-8, 93479-97-1, 684286-46-2 | |
| Record name | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-N-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=261361-60-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0093479971 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride, cis- | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0684286462 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | glimepiride | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759809 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID5040675 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-N-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | GLIMEPIRIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6KY687524K | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | GLIMEPIRIDE, CIS- | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/24T6XIR2MZ | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
207 °C | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.















