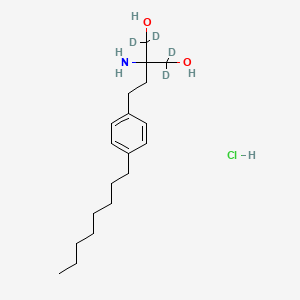
Fingolimod-d4 Clorhidrato
Descripción general
Descripción
Fingolimod-D4 Hydrochloride is a labelled analogue of Fingolimod. Fingolimod is an immunosuppressive agent used for the treatment of relapsing multiple sclerosis. It is a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator preventing lymphocyte emigration to participate in the autoimmune reaction.
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Multiple Sclerosis Treatment
FTY720 (Fingolimod) has been widely studied for its efficacy in treating relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Clinical trials have demonstrated that FTY720 significantly reduces the frequency of relapses and the progression of disability in MS patients. For example:
- Phase II Trials : A study involving 281 patients showed that FTY720 at doses of 1.25 mg and 5.0 mg daily resulted in a significant reduction in gadolinium-enhancing lesions on MRI compared to placebo .
- Phase III FREEDOMS Study : This study confirmed that patients receiving FTY720 had lower annualized relapse rates (0.18 and 0.16) compared to the placebo group (0.40) .
Neuroprotective Effects
Recent investigations have explored the neuroprotective effects of FTY720 in models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In APP/PS1 transgenic mice, chronic treatment with FTY720:
- Rescued synaptic pathology and improved spatial memory performance.
- Reduced microglial activation and astrogliosis, indicating a decrease in neuroinflammation .
- Decreased amyloid-beta plaque formation in the hippocampus, suggesting a potential role in mitigating AD pathology .
Organ Transplantation
FTY720 has shown promise in preventing acute rejection in renal transplantation:
- In a multicenter study, FTY720 was compared with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and demonstrated comparable efficacy in preventing acute rejection at a dose of 2.5 mg .
- The drug's unique mechanism allows it to enhance allograft survival without impairing T cell function, making it an attractive option for immunosuppression .
Case Studies
Mecanismo De Acción
Target of Action
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride, also known as FTY720-d4 Hydrochloride, primarily targets the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors (S1PRs) found on lymphocytes and other organs . The modulation of these receptors is crucial in managing multiple sclerosis (MS) symptoms .
Mode of Action
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride acts as a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator . It is metabolized to its active form, fingolimod-phosphate, which binds to sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5 .
Biochemical Pathways
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride affects several biochemical pathways. It induces metabolic reprogramming in brain regions, upregulating oxidative phosphorylation while downregulating glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway . It also modulates neuroinflammation by upregulating retrograde endocannabinoid signaling and autophagy pathways, and downregulating neuroinflammation-related pathways including neutrophil degranulation and the IL-12 mediated signaling pathway .
Pharmacokinetics
It’s known that the compound is given orally . More research is needed to fully understand the ADME properties of Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride and their impact on bioavailability.
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride’s action are profound. It reduces the number of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood, which is believed to be effective in treating MS due to the reduced lymphocytes into the CNS . It also induces numerous biological effects, including endothelial cell-cell adhesion, angiogenesis, vascular integrity, and cardiovascular function .
Action Environment
The action environment of Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride is primarily within the immune system and the CNS . The interaction with s1p receptors in various tissues accounts for the reported adverse effects
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride interacts with sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors (S1PRs) to bring about an array of pharmacological effects . It exerts inhibitory effects on sphingolipid pathway enzymes, inhibits histone deacetylases, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 7 (TRMP7), cytosolic phospholipase A2α (cPLA2α), reduces lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) plasma levels, and activates protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) .
Cellular Effects
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride has profound effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It can profoundly reduce T-cell numbers in circulation and the CNS, thereby suppressing inflammation and MS . It also induces apoptosis, autophagy, cell cycle arrest, epigenetic regulations, macrophages M1/M2 shift and enhances BDNF expression .
Molecular Mechanism
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride exerts its effects at the molecular level through several mechanisms. It binds to S1P receptor4 (S1PR4) that is primarily expressed in lymphocytes and hematopoietic tissues . It can induce apoptotic pathways by activation of caspase cascades, enhancing PTEN which inhibits pAkt, and inducing (ROS-JNK-p53) loop-dependent autophagy .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It has been shown that the drug has a significant therapeutic effect in immunodeficient mice, not in immunocompetent mice .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In an animal model of genetic absence epilepsy, Fingolimod (1 mg/kg) showed transient antiepileptic effects and longer-lasting anti-cognition decline . During the chronic epileptic phase of the mouse kainate model, 6 mg/kg of the drug also showed neuroprotective and anti-gliotic effects besides reducing seizure frequency .
Metabolic Pathways
Fingolimod-d4 Hydrochloride is involved in the sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) pathway . It is phosphorylated to Fingolimod-phosphate by two protein kinases, type-1 and type-2 sphingosine kinase (SphK1 and -2), enabling it to interact with sphingosine receptors .
Transport and Distribution
It is known that Fingolimod binds to S1P receptor4 (S1PR4) that is primarily expressed in lymphocytes and hematopoietic tissues .
Subcellular Localization
It is known that Fingolimod activates PP2A that plays a principal role as a regulator of cell cycle/division and growth .
Actividad Biológica
FTY720-d4 Hydrochloride, a deuterated form of Fingolimod (FTY720), is a potent immunomodulatory compound primarily recognized for its role in treating multiple sclerosis (MS) and other autoimmune diseases. This article delves into the biological activity of FTY720-d4, including its mechanisms of action, effects on immune cell trafficking, and therapeutic implications based on diverse research findings.
Overview of FTY720-d4 Hydrochloride
FTY720 is a sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator that exerts its effects by phosphorylating into FTY720-P, which acts as an agonist for S1P receptors. The deuterated version, FTY720-d4, is designed to enhance pharmacokinetic properties and reduce metabolic degradation, potentially leading to improved therapeutic efficacy and safety profiles.
The primary mechanism through which FTY720-d4 functions involves the modulation of lymphocyte trafficking. Upon phosphorylation, FTY720-P binds to S1P receptors on lymphocytes, leading to their internalization and subsequent sequestration in lymphoid organs. This action effectively reduces the number of circulating lymphocytes and inhibits their migration into inflamed tissues.
Table 1: Comparison of FTY720 and FTY720-d4 Hydrochloride
| Feature | FTY720 | FTY720-d4 Hydrochloride |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Non-deuterated | Deuterated |
| Mechanism of Action | S1P receptor agonist | S1P receptor agonist |
| Pharmacokinetics | Rapid metabolism | Slower metabolism |
| Therapeutic Use | MS treatment | Potentially enhanced MS treatment |
| Side Effects | Bradycardia, headache | Reduced side effects? |
Multiple Sclerosis
FTY720 has demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing relapse rates in patients with relapsing forms of MS. A clinical trial showed that patients receiving 5 mg daily had a lower incidence of gadolinium-enhancing lesions compared to placebo groups .
In animal models of MS, such as the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model, FTY720 treatment resulted in reduced clinical severity and inflammatory cell infiltration into the central nervous system (CNS) . The application of FTY720-d4 could enhance these effects due to its altered pharmacokinetics.
Alzheimer's Disease
Recent studies have explored the potential neuroprotective effects of FTY720 in models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In APP/PS1 transgenic mice, chronic administration of FTY720 improved long-term potentiation (LTP) deficits and reduced microglial activation, suggesting that it may ameliorate synaptic dysfunction associated with AD . The ability of FTY720-d4 to offer similar or enhanced benefits warrants further investigation.
Case Studies and Clinical Evidence
In a Phase II clinical trial involving renal transplantation, FTY720 was shown to be effective in preventing acute rejection. Patients receiving varying doses displayed a significant reduction in biopsy-confirmed acute rejection rates compared to those on standard therapies . The potential application of FTY720-d4 in this context could lead to improved outcomes due to its enhanced stability and efficacy.
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
2-amino-1,1,3,3-tetradeuterio-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol;hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H33NO2.ClH/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-17-9-11-18(12-10-17)13-14-19(20,15-21)16-22;/h9-12,21-22H,2-8,13-16,20H2,1H3;1H/i15D2,16D2; | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
SWZTYAVBMYWFGS-JWIOGAFXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCCCCCCC1=CC=C(C=C1)CCC(CO)(CO)N.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
[2H]C([2H])(C(CCC1=CC=C(C=C1)CCCCCCCC)(C([2H])([2H])O)N)O.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C19H34ClNO2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
348.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.













