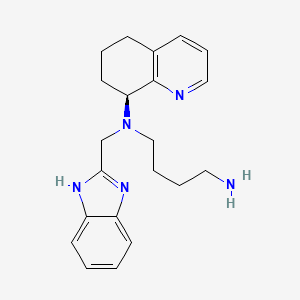
Mavorixafor
Descripción general
Descripción
Mavorixafor es un antagonista selectivo del receptor 4 de quimiocina C-X-C (CXCR4) biodisponible por vía oral. Se desarrolla principalmente para el tratamiento del síndrome de verrugas, hipogammaglobulinemia, infecciones y mielocatexis (WHIM), un trastorno de inmunodeficiencia primaria raro. This compound también se está investigando por su potencial en el tratamiento de varios cánceres, incluido el melanoma, y otros trastornos neutropénicos crónicos .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción
La síntesis de mavorixafor implica múltiples pasos, comenzando con materiales de partida disponibles comercialmenteLas condiciones de reacción suelen implicar el uso de disolventes orgánicos, catalizadores y temperaturas controladas para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza .
Métodos de producción industrial
La producción industrial de this compound sigue una ruta sintética similar, pero está optimizada para la fabricación a gran escala. Esto incluye el uso de reactores de flujo continuo, sistemas de purificación automatizados y estrictas medidas de control de calidad para garantizar la coherencia y el cumplimiento de las normas reglamentarias .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones
Mavorixafor experimenta varias reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Oxidación: this compound se puede oxidar en condiciones específicas para formar derivados oxidados.
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción se pueden usar para modificar la porción de quinolina.
Sustitución: Las reacciones de sustitución se emplean para introducir diferentes grupos funcionales en el núcleo de benzimidazol.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes
Oxidación: Los agentes oxidantes comunes incluyen peróxido de hidrógeno y permanganato de potasio.
Reducción: Se utilizan agentes reductores como borohidruro de sodio e hidruro de aluminio y litio.
Sustitución: Se utilizan reactivos como haluros de alquilo y haluros de arilo para reacciones de sustitución.
Productos principales
Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen varios derivados de this compound con grupos funcionales modificados, que se pueden investigar más a fondo por sus propiedades farmacológicas .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
WHIM Syndrome
WHIM syndrome (warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis) is a rare immunodeficiency caused by gain-of-function mutations in the CXCR4 gene. Mavorixafor has been shown to significantly improve clinical outcomes in patients with WHIM syndrome:
- Clinical Trial Results : In a Phase 3 randomized trial, this compound demonstrated a 60% reduction in annualized infection rates compared to placebo (1.7 vs. 4.2 infections) and improved absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) .
- Mechanism : By antagonizing CXCR4, this compound facilitates the release of neutrophils into circulation, thereby enhancing the immune response .
Chronic Neutropenia
This compound is also being investigated for its efficacy in treating chronic neutropenia (CN), a condition characterized by persistently low levels of neutrophils:
- Phase 2 Trial Findings : A six-month study indicated that this compound treatment led to durable increases in ANC and allowed for significant reductions in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) dosing without compromising ANC levels .
- Safety Profile : The treatment was well tolerated with mild to moderate side effects predominantly gastrointestinal in nature .
Table 1: Summary of Clinical Trials Involving this compound
Cancer Treatment
This compound's role extends into oncology, where it is being explored for its potential to enhance the efficacy of existing cancer therapies:
- Immune Modulation : In a study involving melanoma patients, this compound was administered alongside pembrolizumab to evaluate its effect on immune cell infiltration into tumors. Results suggested improved immune profiles within the tumor microenvironment .
- Potential Indications : Research indicates that this compound could be beneficial for various malignancies including hematologic cancers and solid tumors due to its ability to mobilize immune cells effectively .
Mecanismo De Acción
Mavorixafor ejerce sus efectos uniéndose selectivamente al receptor CXCR4, bloqueando la unión de su ligando natural, el ligando 12 de la quimiocina C-X-C (también conocido como factor derivado del estroma-1). Esta inhibición previene la activación de las vías de señalización CXCR4, que están involucradas en el tráfico de células inmunitarias, la localización de células madre hematopoyéticas y la progresión tumoral. Al modular estas vías, this compound mejora la infiltración y activación de células inmunitarias en el microambiente tumoral, lo que lleva a respuestas antitumorales mejoradas .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Compuestos similares
Plerixafor: Otro antagonista de CXCR4 utilizado para la movilización de células madre en pacientes con linfoma no Hodgkin y mieloma múltiple.
Unicidad
Mavorixafor es único en su biodisponibilidad oral y selectividad para el receptor CXCR4. A diferencia de plerixafor y AMD3100, que se administran mediante inyección, this compound se puede tomar por vía oral, lo que lo hace más conveniente para los pacientes. Además, su selectividad para CXCR4 reduce la probabilidad de efectos fuera del objetivo, mejorando su perfil de seguridad .
Actividad Biológica
Mavorixafor is an orally bioavailable, selective antagonist of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor, primarily developed for treating conditions such as WHIM syndrome and chronic neutropenia. Its biological activity is characterized by the modulation of immune cell trafficking, enhancing the mobilization of neutrophils and lymphocytes from the bone marrow into circulation. This article synthesizes findings from various studies to elucidate the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its mechanisms, clinical efficacy, and safety profile.
This compound functions by inhibiting the CXCR4 receptor, which plays a critical role in the retention of immune cells in the bone marrow. By blocking this receptor, this compound facilitates the release of white blood cells into the bloodstream, thereby increasing their availability for immune responses.
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of CXCR4 : Reduces retention of immune cells in bone marrow.
- Increased Immune Cell Mobilization : Enhances circulating neutrophil and lymphocyte counts.
- Modulation of Tumor Microenvironment (TME) : Increases CD8+ T-cell infiltration in tumors, potentially improving responses to immunotherapies.
Phase Ib Study in Melanoma
A biomarker-driven Phase Ib study (NCT02823405) evaluated this compound's effects on immune cell profiles within the TME of melanoma patients.
| Parameter | Results |
|---|---|
| CD8+ T-cell Infiltration | Increased significantly after 3 weeks of monotherapy |
| Granzyme B Signal | Enhanced expression observed |
| Cytokines (CXCL9, CXCL10) | Elevated levels when combined with pembrolizumab |
| Adverse Events | Diarrhea, fatigue, rash (all ≤ grade 3) |
The study concluded that this compound enhances immune cell infiltration and activation within tumors, suggesting its potential to improve outcomes for patients unresponsive to checkpoint inhibitors .
Phase II Study in WHIM Syndrome
A Phase II open-label study assessed this compound's safety and efficacy in patients with WHIM syndrome.
| Parameter | Results |
|---|---|
| Neutrophil Count (ANC) | Statistically significant increases; maintained >500 cells/µL for 12.6 hours at doses ≥300 mg/day |
| Lymphocyte Count (ALC) | Maintained >1000 cells/µL for up to 16.9 hours |
| Safety Profile | Well-tolerated; no serious adverse events reported |
The study demonstrated that this compound effectively mobilizes neutrophils and lymphocytes, contributing to improved clinical outcomes in patients with this rare immunodeficiency .
Phase III Trial Outcomes
In a Phase III trial involving patients with WHIM syndrome, this compound was compared to placebo over 52 weeks.
| Parameter | This compound Group | Placebo Group |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil Count Increase | Significant increase observed | Not applicable |
| Infection Rate Reduction | Statistically significant decrease | Not applicable |
Adverse effects included low platelet counts and mild rashes but were generally manageable .
Case Studies
- Case Study 1 : A patient with WHIM syndrome treated with this compound exhibited a two-fold increase in ANC after three months, leading to a marked reduction in infection frequency.
- Case Study 2 : In melanoma patients, combination therapy with this compound and pembrolizumab resulted in enhanced tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte activity, correlating with improved overall survival metrics.
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What is the pharmacological mechanism of Mavorixafor as a CXCR4 antagonist, and how does it modulate immune responses?
this compound is a selective, orally available CXCR4 antagonist with an IC50 of 13 nM against CXCR4 binding. By blocking the CXCR4 receptor, it inhibits the interaction of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1), a chemokine critical for neutrophil retention in bone marrow. This antagonism promotes neutrophil mobilization into peripheral blood, addressing conditions like WHIM syndrome and chronic neutropenia (CN) . Preclinical studies demonstrate its efficacy in increasing absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) in CN models, supported by Phase 2/3 clinical trials showing sustained ANC normalization .
Q. How do Phase 3 clinical trials for this compound in WHIM syndrome establish primary efficacy endpoints?
The Phase 3 4WHIM trial (NCT02393184) defined primary endpoints as annualized infection rate reduction and ANC normalization. This compound achieved a ~60% reduction in infections (p<0.01) and a >70% decrease in infection duration compared to placebo. Secondary endpoints included infection severity (75% reduction in Grade ≥3 infections) and ANC levels, which remained above the lower limit of normal (≥1,500 cells/µL) in 100% of participants . Statistical analysis used Poisson regression for infection rates and mixed-effects models for ANC trends .
Q. What standard biomarkers are used to evaluate this compound’s efficacy in chronic neutropenia research?
Key biomarkers include ANC levels (target: >500 cells/µL for infection risk mitigation), duration of severe neutropenia (ANC <500 cells/µL), and infection-related metrics (e.g., frequency, severity, antibiotic use). Phase 2 trials in CN reported 100% of participants achieving target ANC increases at Months 3 and 6, with mean ANC levels exceeding 1,500 cells/µL in monotherapy cohorts .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. What methodological considerations are critical when designing combination therapy trials with this compound and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)?
Trials must address pharmacokinetic interactions, dosing synchronization (e.g., once-daily oral this compound vs. injectable G-CSF), and endpoint harmonization. In Phase 2 CN trials, this compound + stable-dose G-CSF cohorts showed mean ANC increases >1,000 cells/µL, with no drug-drug interactions or safety concerns . Researchers should stratify participants by baseline G-CSF use and employ longitudinal ANC monitoring to isolate synergistic effects .
Q. How can researchers reconcile discrepancies between in vitro CXCR4 binding assays and in vivo efficacy outcomes for this compound?
In vitro assays (e.g., CXCR4 I-SDF binding IC50) may not fully capture in vivo dynamics like bone marrow niche competition or immune cell trafficking. Preclinical-to-clinical translation requires validating neutrophil mobilization in animal models (e.g., murine WHIM) before human trials. Phase 3 data confirmed in vitro predictions, with ANC increases correlating to infection rate reductions, supporting mechanism-based efficacy .
Q. What statistical approaches are optimal for analyzing time-dependent efficacy in this compound trials?
Time-to-event analysis (e.g., Kaplan-Meier for infection-free survival) and mixed-effects models account for longitudinal ANC trends. In the 4WHIM trial, infection rate reductions became more pronounced over time (p<0.005 at 6 months), necessitating covariate adjustment for baseline ANC and G-CSF use . For CN trials, repeated-measures ANOVA or GEE models are recommended to handle ANC variability .
Q. How should researchers address potential biases in open-label extension studies of this compound?
Open-label extensions (e.g., 4WHIM trial’s 90% participant retention) require intention-to-treat analysis and sensitivity analyses comparing blinded vs. unblinded phases. Researchers should track adherence via drug diaries and ANC measurements to mitigate performance bias. Secondary endpoints like patient-reported outcomes (e.g., infection-related quality of life) add rigor .
Q. What strategies ensure robust characterization of this compound’s safety profile in heterogeneous neutropenia populations?
Phase 3 trials employed AE grading (CTCAE v5.0) and adjudication committees for infection severity. In CN studies, stratified safety analyses by etiology (congenital vs. idiopathic) and G-CSF use identified no treatment-related SAEs, supporting general tolerability . Long-term monitoring in extension studies (>52 weeks) is critical for rare AEs .
Q. Methodological Frameworks
- Experimental Design : Prioritize randomized, placebo-controlled trials with adaptive designs for dose optimization (e.g., Phase 2/3 seamless trials) .
- Data Contradiction Analysis : Use sensitivity analyses to validate primary endpoints across subgroups (e.g., severe vs. moderate CN) and adjust for confounders like concomitant therapies .
- Literature Integration : Cross-reference CXCR4 antagonist studies (e.g., plerixafor) to contextualize this compound’s unique oral bioavailability and safety profile .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
N'-(1H-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-N'-[(8S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl]butane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H27N5/c22-12-3-4-14-26(15-20-24-17-9-1-2-10-18(17)25-20)19-11-5-7-16-8-6-13-23-21(16)19/h1-2,6,8-10,13,19H,3-5,7,11-12,14-15,22H2,(H,24,25)/t19-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WVLHHLRVNDMIAR-IBGZPJMESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC(C2=C(C1)C=CC=N2)N(CCCCN)CC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1C[C@@H](C2=C(C1)C=CC=N2)N(CCCCN)CC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H27N5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60971247 | |
| Record name | N~1~-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-N~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60971247 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
349.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Chemokine receptors expressed on the surface of immune cells are known to play a critical role in virus infection and transmission. CXCR4, and another chemokine receptor CCR5, are involved in HIV infection. The process of HIV entry begins with binding of the viral envelope glycoprotein to both the CD4 receptor and one of only two chemokine receptors, and ends with fusion of viral and cell membranes. Viral entry provides novel therapeutic targets against HIV. To date, at least 3 sub classes of HIV viral entry/fusion inhibitors have emerged: 1. CD4 binding or attachment - targets initial recognition and binding of the viral glycoprotein gp120 to the cell-surface CD4 antigen. 2. Chemokine co-receptor binding - targets binding of virus to the CCR5 or CXCR4 co-receptor. 3. Fusion Inhibition - targets the viral glycoprotein gp41 inhibiting the fusion of virus with the cell. Different strains of HIV prefer one receptor or the other, or may use either receptor to infect cells. * 35% of strains use both CXCR4 and CCR5 * 5% of strains are pure CXCR4 using * 60% of strains are pure CCR5 using * An infected individual may harbor different levels of both CXCR4 and CCR5 using virus * CXCR4 using virus independently predicts CD4 decline and HIV clinical progression and is associated with earlier mortality | |
| Record name | AMD-070 | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05501 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
558447-26-0 | |
| Record name | Mavorixafor [USAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0558447260 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | AMD-070 | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05501 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | N~1~-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-N~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60971247 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | MAVORIXAFOR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0G9LGB5O2W | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.













