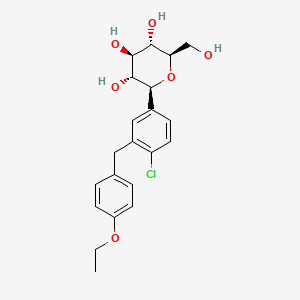
Dapagliflozin
Descripción general
Descripción
La dapagliflozina es un medicamento que se utiliza principalmente para tratar la diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Pertenece a la clase de inhibidores del cotransportador 2 de sodio-glucosa. Al inhibir este transportador, la dapagliflozina reduce la reabsorción de glucosa en los riñones, lo que lleva a una mayor excreción de glucosa en la orina. Esto ayuda a disminuir los niveles de glucosa en sangre. Además, la dapagliflozina se utiliza para tratar la insuficiencia cardíaca y la enfermedad renal crónica .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción: La síntesis de la dapagliflozina implica varios pasos clave:
Preparación del reactivo de Grignard: La materia prima inicial, 1-cloro-2-(4-etoxi-bencil)-4-yodobenceno, reacciona con magnesio utilizando gránulos de yodo como iniciador para preparar un reactivo de Grignard.
Reacción de bromación: El azúcar peracetilado reacciona con bromuro de hidrógeno en una solución de ácido acético para preparar 2,3,4,6-tetraacetilglucosamina bromuro.
Formación del compuesto intermedio: El reactivo de Grignard se añade a una solución de metilbenceno/tetrahidrofurano, seguido de la adición de un catalizador de tierras raras y 2,3,4,6-tetraacetilglucosamina bromuro, dando como resultado un compuesto intermedio.
Hidrólisis y recristalización: El compuesto intermedio se somete a hidrólisis alcalina en una solución de hidróxido de sodio de tetrahidrofurano/etanol/agua, seguido de recristalización para obtener dapagliflozina.
Métodos de producción industrial: La producción industrial de dapagliflozina sigue rutas sintéticas similares pero a mayor escala, asegurando una alta pureza y rendimiento. El proceso implica estrictas medidas de control de calidad para minimizar las impurezas y garantizar la consistencia del producto final .
Tipos de reacciones:
Oxidación: La dapagliflozina puede sufrir reacciones de oxidación, lo que lleva a la formación de metabolitos como la oxo-dapagliflozina.
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción pueden convertir la dapagliflozina en sus formas reducidas.
Sustitución: Las reacciones de sustitución pueden ocurrir en varias posiciones de la molécula de dapagliflozina, lo que lleva a la formación de diferentes derivados.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes:
Oxidación: Los agentes oxidantes comunes incluyen el peróxido de hidrógeno y el permanganato de potasio.
Reducción: Se utilizan agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio y el hidruro de litio y aluminio.
Sustitución: Se emplean diversos agentes halogenantes y nucleófilos en las reacciones de sustitución.
Productos principales:
Dapagliflozina hidroxibencílica: Formada mediante hidroxilación.
Oxo-dapagliflozina: Formada mediante oxidación.
Desetil-dapagliflozina: Formada mediante desetilación.
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Efficacy in Glycemic Control
Dapagliflozin is primarily indicated for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels and promoting weight loss. For instance, a study indicated that this compound significantly reduced HbA1c levels compared to placebo across various age groups, with consistent results showing reductions of approximately 0.5% to 0.6% after one year of treatment .
Weight Loss and Cardiovascular Benefits
In addition to glycemic control, this compound has been associated with weight loss. Patients treated with this compound showed a greater likelihood of achieving a 5% weight loss compared to those on placebo . Furthermore, it has been linked to cardiovascular benefits, reducing the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure .
Heart Failure Management
Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
This compound has shown significant benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The DAPA-HF trial demonstrated that this compound reduced the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in these patients, regardless of the presence of diabetes .
Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Recent studies have also highlighted the efficacy of this compound in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). In the DELIVER trial, this compound led to early and sustained reductions in clinical events related to worsening heart failure, with significant benefits observed within two weeks of treatment initiation .
Renal Protection
Chronic Kidney Disease
This compound has shown promise in protecting renal function among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Evidence suggests that it may slow the progression of kidney disease and reduce the risk of end-stage renal disease . A study utilizing organ-on-a-chip models indicated that this compound could reduce cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease models, suggesting potential applications in renal pathology .
Pharmacokinetics and Administration Routes
Transdermal Delivery Systems
Recent research has explored alternative delivery methods for this compound, including transdermal patches. A study involving minipigs found that repeated application of this compound patches significantly increased drug accumulation in serum and tissues, indicating potential for effective transdermal delivery systems . This could enhance patient compliance and expand therapeutic options.
Data Summary Tables
Case Studies
- DAPA-HF Trial : In this landmark trial involving patients with HFrEF, this compound was shown to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure by 26% compared to placebo over a median follow-up period .
- DELIVER Trial : This trial focused on patients with HFpEF and found that this compound led to a significant reduction in cardiovascular events within just two weeks of starting treatment .
- Renal Study Using Organ-on-a-Chip : Research demonstrated that this compound could reduce cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease models, highlighting its potential role in renal protection strategies .
Mecanismo De Acción
La dapagliflozina actúa inhibiendo el cotransportador 2 de sodio-glucosa en los túbulos renales proximales. Este transportador es responsable de la reabsorción de glucosa desde la luz tubular. Al inhibir este transportador, la dapagliflozina reduce la reabsorción de glucosa, lo que lleva a una mayor excreción de glucosa urinaria. Esto da como resultado niveles más bajos de glucosa en sangre. Además, la dapagliflozina reduce la reabsorción de sodio, lo que puede influir en varias funciones fisiológicas, incluida la reducción de la precarga y la poscarga del corazón y la regulación a la baja de la actividad simpática .
Compuestos similares:
- Empagliflozina
- Canagliflozina
- Ipragliflozina
Comparación:
- Empagliflozina: Tanto la dapagliflozina como la empagliflozina son inhibidores del cotransportador 2 de sodio-glucosa que se utilizan para tratar la diabetes tipo 2. La dapagliflozina ha mostrado un mayor riesgo de hospitalización por insuficiencia cardíaca en comparación con la empagliflozina .
- Canagliflozina: Al igual que la dapagliflozina, la canagliflozina se utiliza para tratar la diabetes tipo 2 y tiene beneficios adicionales para reducir los eventos cardiovasculares. La canagliflozina se ha asociado con un mayor riesgo de amputaciones de miembros inferiores.
- Ipragliflozina: Otro inhibidor del cotransportador 2 de sodio-glucosa con efectos similares de reducción de la glucosa. La dapagliflozina tiene un perfil de seguridad más favorable en términos de infecciones genitales .
La dapagliflozina destaca por sus beneficios integrales en el tratamiento de la diabetes tipo 2, la insuficiencia cardíaca y la enfermedad renal crónica, junto con su perfil de seguridad relativamente favorable.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
- Empagliflozin
- Canagliflozin
- Ipragliflozin
Comparison:
- Empagliflozin: Both dapagliflozin and empagliflozin are sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors used to treat type 2 diabetes. this compound has shown a higher risk of hospitalization for heart failure compared to empagliflozin .
- Canagliflozin: Similar to this compound, canagliflozin is used to treat type 2 diabetes and has additional benefits in reducing cardiovascular events. canagliflozin has been associated with a higher risk of lower limb amputations.
- Ipragliflozin: Another sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor with similar glucose-lowering effects. this compound has a more favorable safety profile in terms of genital infections .
This compound stands out due to its comprehensive benefits in treating type 2 diabetes, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease, along with its relatively favorable safety profile.
Actividad Biológica
Dapagliflozin is a selective sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, primarily used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, efficacy in clinical settings, and safety profile. This article delves into these aspects, supported by data from various studies.
This compound functions by inhibiting SGLT2, which is predominantly located in the proximal tubule of the nephron. This transporter is responsible for approximately 90% of glucose reabsorption in the kidneys. By blocking SGLT2, this compound promotes the excretion of glucose through urine, thereby aiding in glycemic control and potentially leading to weight loss in patients with T2DM .
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption : this compound is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with maximum plasma concentrations occurring within 2 hours. The bioavailability is around 78% with a 10 mg dose taken once daily .
- Metabolism : It undergoes glucuronidation to form inactive metabolites, primarily mediated by UGT1A9. The terminal half-life is approximately 13 hours .
- Elimination : The drug and its metabolites are primarily excreted via urine, with about 15% excreted unaltered through feces .
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
This compound has been extensively studied for its efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels and improving other metabolic parameters. Below are key findings from notable clinical trials:
Safety Profile
The safety of this compound has been evaluated across multiple studies. Notably, it was found not to significantly prolong the QTc interval at doses up to 150 mg, indicating a favorable cardiac safety profile . Common adverse effects include urinary tract infections and genital mycotic infections due to increased glucose excretion.
Case Study 1: Efficacy in Elderly Patients
In a study focusing on elderly patients (≥65 years), this compound demonstrated consistent reductions in HbA1c compared to placebo across all age groups. The hazard ratio for cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure was noted at 0.88, suggesting significant benefits even in older populations .
Case Study 2: Combination Therapy
Another case involved patients with T2DM receiving this compound in combination with saxagliptin. This combination therapy led to enhanced glycemic control and a notable decrease in albuminuria over a 24-week period .
Q & A
Q. What are the key methodological considerations when designing a clinical trial to evaluate dapagliflozin’s cardiorenal benefits in non-diabetic populations?
Answer:
Trials should prioritize patient stratification by comorbidities (e.g., heart failure [HF] or chronic kidney disease [CKD]) and ensure endpoints reflect clinically relevant outcomes (e.g., composite of cardiovascular death and HF hospitalization). The DAPA-HF trial (NCT03036124) demonstrated efficacy in both diabetic and non-diabetic HFrEF patients by using a placebo-controlled, double-blind design with rigorous inclusion criteria (NYHA class II–IV, ejection fraction ≤40%) . Methodological rigor includes pre-specified subgroup analyses to assess treatment heterogeneity and standardized safety monitoring for volume depletion or renal events.
Q. How can population pharmacokinetic (PK) modeling address covariate effects on this compound exposure across patient subgroups?
Answer:
Population PK models should incorporate covariates such as renal function, body mass index, and diabetes status to quantify variability in drug exposure. For example, a phase IIa/III study used nonlinear mixed-effects modeling to identify baseline glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albuminuria as key covariates influencing this compound’s PK in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) patients, enabling dose adjustments for renal impairment . Advanced modeling software (e.g., NONMEM) and bootstrapping validation are critical for robustness.
Q. What analytical techniques are recommended for stability profiling and impurity detection in this compound formulations?
Answer:
Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) coupled with Design of Experiments (DOE) optimizes parameters like mobile phase composition and column temperature. A validated RP-HPLC method achieved separation of this compound from six process-related impurities using a C18 column and gradient elution (acetonitrile-phosphate buffer). Forced degradation studies under ICH conditions (acid/base hydrolysis, oxidation) identified major degradants, with LC-MS/MS confirming structural changes .
Q. How should researchers reconcile conflicting data on this compound’s metabolic effects in heart failure using targeted metabolomics?
Answer:
Targeted metabolomics can clarify mechanisms by quantifying pathway-specific biomarkers (e.g., acylcarnitines, amino acids). The DEFINE-HF trial (NCT02653482) used principal component analysis (PCA) to cluster metabolites, revealing that this compound increased ketone-related and medium-chain acylcarnitines—suggesting enhanced fatty acid oxidation—without inducing pathological ketosis. Adjusting for false discovery rates (FDR) and baseline covariates mitigates false-positive associations .
Q. What challenges arise in extrapolating this compound’s efficacy from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to real-world settings?
Answer:
Real-world studies must address confounding factors (e.g., adherence, comorbidities) through propensity score matching or inverse probability weighting. A 2023 retrospective cohort study replicated RCT findings by demonstrating HbA1c reductions (−0.8%) and weight loss (−1.5 kg) in Indian T2DM patients on this compound + metformin, but emphasized rigorous exclusion criteria to mirror RCT populations . Sensitivity analyses and subgroup stratification enhance generalizability.
Q. How can pediatric trials for this compound address safety and efficacy gaps in type 1 diabetes (T1DM)?
Answer:
Pediatric trials require adaptive designs with dose-escalation phases and frequent safety monitoring for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). A 2022 systematic review highlighted the need for long-term studies in T1DM, as existing pediatric data are limited to single-dose pharmacokinetics. Incorporating continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and ketone sensors improves safety assessments .
Q. What statistical approaches resolve contradictions in this compound’s renoprotective effects across heterogeneous CKD populations?
Answer:
Bayesian hierarchical models or meta-regression can account for heterogeneity in baseline proteinuria or GFR. The DAPA-CKD trial (NCT03036150) stratified outcomes by albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), showing consistent renal benefits. Sensitivity analyses should test the robustness of effect estimates across subgroups, while competing risk models address mortality as a confounder .
Q. How does DOE enhance robustness in developing this compound quantification methods?
Answer:
DOE systematically optimizes HPLC parameters (e.g., flow rate, pH) using factorial designs. A study employing central composite design (CCD) identified sodium lauryl sulfate concentration and wavelength (225 nm) as critical factors for this compound quantification, achieving a linear range of 2–12 µg/mL with R² >0.999. Validation followed ICH Q2(R1) guidelines for accuracy (±2%) and precision (RSD <2%) .
Q. What mechanisms underlie this compound’s cardioprotective effects beyond glucose control?
Answer:
Preclinical models suggest hemodynamic improvements (reduced preload/afterload) and anti-inflammatory effects via NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Clinical metabolomic data link this compound to increased β-hydroxybutyrate (a cardioprotective ketone) and reduced aromatic amino acids (associated with HF progression). Mechanistic trials should integrate transcriptomic and proteomic profiling .
Q. How do researchers validate novel biomarkers for this compound response in diabetic kidney disease (DKD)?
Answer:
Cohort studies with longitudinal biospecimen collection (e.g., urine TGF-β1, serum TNF-α) paired with GFR slope analysis are essential. The DERIVE study (NCT02413398) used machine learning to identify urinary C-mannosyl tryptophan as a predictive biomarker for this compound’s albuminuria-lowering effect. Replication in independent cohorts and assay standardization (e.g., ELISA vs. mass spectrometry) ensure validity .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H25ClO6/c1-2-27-15-6-3-12(4-7-15)9-14-10-13(5-8-16(14)22)21-20(26)19(25)18(24)17(11-23)28-21/h3-8,10,17-21,23-26H,2,9,11H2,1H3/t17-,18-,19+,20-,21+/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
JVHXJTBJCFBINQ-ADAARDCZSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)C3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H25ClO6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID20905104 | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20905104 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
408.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Dapagliflozin inhibits the sodium-glucose contransporter 2(SGLT2) which is primarily located in the proximal tubule of the nephron. SGLT2 facilitates 90% of glucose reabsorption in the kidneys and so its inhibition allows for glucose to be excreted in the urine. This excretion allows for better glycemic control and potentially weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06292 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
461432-26-8 | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=461432-26-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0461432268 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06292 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20905104 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (1S)-1,5-anhydro-1-C-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-D-glucitol | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DAPAGLIFLOZIN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/1ULL0QJ8UC | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.
















