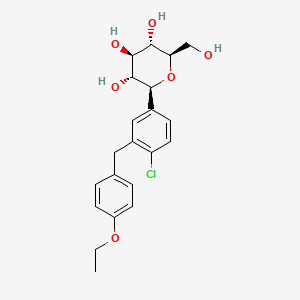
Dapagliflozin
描述
达格列净是一种主要用于治疗2型糖尿病的药物。它属于钠-葡萄糖协同转运体2抑制剂类。通过抑制这种转运体,达格列净减少肾脏对葡萄糖的重吸收,导致尿液中葡萄糖排泄增加。这有助于降低血糖水平。 此外,达格列净还用于治疗心力衰竭和慢性肾脏病 .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件: 达格列净的合成涉及几个关键步骤:
格氏试剂的制备: 最初的原料1-氯-2-(4-乙氧基苄基)-4-碘苯,与镁在碘颗粒作为引发剂的作用下反应,制备格氏试剂。
溴化反应: 过乙酰化的糖在乙酸溶液中与溴化氢反应,制备2,3,4,6-四乙酰基葡萄糖胺溴。
中间体化合物的形成: 格氏试剂加入甲苯/四氢呋喃溶液中,然后加入稀土催化剂和2,3,4,6-四乙酰基葡萄糖胺溴,生成中间体化合物。
工业生产方法: 达格列净的工业生产遵循类似的合成路线,但规模更大,确保高纯度和高产率。 该过程涉及严格的质量控制措施,以最大限度地减少杂质,并确保最终产品的稳定性 .
反应类型:
氧化: 达格列净可以发生氧化反应,导致形成代谢产物,例如氧代达格列净。
还原: 还原反应可以将达格列净转化为其还原形式。
取代: 取代反应可以在达格列净分子的不同位置发生,导致形成不同的衍生物。
常用试剂和条件:
氧化: 常用的氧化剂包括过氧化氢和高锰酸钾。
还原: 使用硼氢化钠和氢化铝锂等还原剂。
取代: 在取代反应中使用各种卤化剂和亲核试剂。
主要产物:
苄基羟基达格列净: 通过羟基化形成。
氧代达格列净: 通过氧化形成。
脱乙基达格列净: 通过脱乙基化形成.
科学研究应用
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Efficacy in Glycemic Control
Dapagliflozin is primarily indicated for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels and promoting weight loss. For instance, a study indicated that this compound significantly reduced HbA1c levels compared to placebo across various age groups, with consistent results showing reductions of approximately 0.5% to 0.6% after one year of treatment .
Weight Loss and Cardiovascular Benefits
In addition to glycemic control, this compound has been associated with weight loss. Patients treated with this compound showed a greater likelihood of achieving a 5% weight loss compared to those on placebo . Furthermore, it has been linked to cardiovascular benefits, reducing the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure .
Heart Failure Management
Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
This compound has shown significant benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The DAPA-HF trial demonstrated that this compound reduced the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in these patients, regardless of the presence of diabetes .
Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Recent studies have also highlighted the efficacy of this compound in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). In the DELIVER trial, this compound led to early and sustained reductions in clinical events related to worsening heart failure, with significant benefits observed within two weeks of treatment initiation .
Renal Protection
Chronic Kidney Disease
This compound has shown promise in protecting renal function among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Evidence suggests that it may slow the progression of kidney disease and reduce the risk of end-stage renal disease . A study utilizing organ-on-a-chip models indicated that this compound could reduce cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease models, suggesting potential applications in renal pathology .
Pharmacokinetics and Administration Routes
Transdermal Delivery Systems
Recent research has explored alternative delivery methods for this compound, including transdermal patches. A study involving minipigs found that repeated application of this compound patches significantly increased drug accumulation in serum and tissues, indicating potential for effective transdermal delivery systems . This could enhance patient compliance and expand therapeutic options.
Data Summary Tables
Case Studies
- DAPA-HF Trial : In this landmark trial involving patients with HFrEF, this compound was shown to significantly reduce hospitalizations for heart failure by 26% compared to placebo over a median follow-up period .
- DELIVER Trial : This trial focused on patients with HFpEF and found that this compound led to a significant reduction in cardiovascular events within just two weeks of starting treatment .
- Renal Study Using Organ-on-a-Chip : Research demonstrated that this compound could reduce cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease models, highlighting its potential role in renal protection strategies .
作用机制
达格列净通过抑制近端肾小管中的钠-葡萄糖协同转运体2发挥作用。这种转运体负责从肾小管腔中重吸收葡萄糖。通过抑制这种转运体,达格列净减少葡萄糖重吸收,导致尿液中葡萄糖排泄增加。这导致血糖水平降低。 此外,达格列净减少钠的重吸收,这可能会影响一些生理功能,包括降低心脏的前负荷和后负荷以及下调交感神经活性 .
类似化合物:
- 恩格列净
- 卡格列净
- 伊格列净
比较:
- 恩格列净: 达格列净和恩格列净都是钠-葡萄糖协同转运体2抑制剂,用于治疗2型糖尿病。 与恩格列净相比,达格列净的心力衰竭住院风险较高 .
- 卡格列净: 与达格列净类似,卡格列净用于治疗2型糖尿病,并且在减少心血管事件方面具有额外的好处。卡格列净与下肢截肢风险较高有关。
- 伊格列净: 另一种钠-葡萄糖协同转运体2抑制剂,具有类似的降糖效果。 在生殖器感染方面,达格列净具有更有利的安全性 .
达格列净在治疗2型糖尿病、心力衰竭和慢性肾脏病方面的综合益处,以及其相对有利的安全性,使其脱颖而出。
相似化合物的比较
- Empagliflozin
- Canagliflozin
- Ipragliflozin
Comparison:
- Empagliflozin: Both dapagliflozin and empagliflozin are sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors used to treat type 2 diabetes. this compound has shown a higher risk of hospitalization for heart failure compared to empagliflozin .
- Canagliflozin: Similar to this compound, canagliflozin is used to treat type 2 diabetes and has additional benefits in reducing cardiovascular events. canagliflozin has been associated with a higher risk of lower limb amputations.
- Ipragliflozin: Another sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor with similar glucose-lowering effects. this compound has a more favorable safety profile in terms of genital infections .
This compound stands out due to its comprehensive benefits in treating type 2 diabetes, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease, along with its relatively favorable safety profile.
生物活性
Dapagliflozin is a selective sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, primarily used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Its biological activity is characterized by its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, efficacy in clinical settings, and safety profile. This article delves into these aspects, supported by data from various studies.
This compound functions by inhibiting SGLT2, which is predominantly located in the proximal tubule of the nephron. This transporter is responsible for approximately 90% of glucose reabsorption in the kidneys. By blocking SGLT2, this compound promotes the excretion of glucose through urine, thereby aiding in glycemic control and potentially leading to weight loss in patients with T2DM .
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption : this compound is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with maximum plasma concentrations occurring within 2 hours. The bioavailability is around 78% with a 10 mg dose taken once daily .
- Metabolism : It undergoes glucuronidation to form inactive metabolites, primarily mediated by UGT1A9. The terminal half-life is approximately 13 hours .
- Elimination : The drug and its metabolites are primarily excreted via urine, with about 15% excreted unaltered through feces .
Efficacy in Clinical Studies
This compound has been extensively studied for its efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels and improving other metabolic parameters. Below are key findings from notable clinical trials:
Safety Profile
The safety of this compound has been evaluated across multiple studies. Notably, it was found not to significantly prolong the QTc interval at doses up to 150 mg, indicating a favorable cardiac safety profile . Common adverse effects include urinary tract infections and genital mycotic infections due to increased glucose excretion.
Case Study 1: Efficacy in Elderly Patients
In a study focusing on elderly patients (≥65 years), this compound demonstrated consistent reductions in HbA1c compared to placebo across all age groups. The hazard ratio for cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure was noted at 0.88, suggesting significant benefits even in older populations .
Case Study 2: Combination Therapy
Another case involved patients with T2DM receiving this compound in combination with saxagliptin. This combination therapy led to enhanced glycemic control and a notable decrease in albuminuria over a 24-week period .
常见问题
Q. What are the key methodological considerations when designing a clinical trial to evaluate dapagliflozin’s cardiorenal benefits in non-diabetic populations?
Answer:
Trials should prioritize patient stratification by comorbidities (e.g., heart failure [HF] or chronic kidney disease [CKD]) and ensure endpoints reflect clinically relevant outcomes (e.g., composite of cardiovascular death and HF hospitalization). The DAPA-HF trial (NCT03036124) demonstrated efficacy in both diabetic and non-diabetic HFrEF patients by using a placebo-controlled, double-blind design with rigorous inclusion criteria (NYHA class II–IV, ejection fraction ≤40%) . Methodological rigor includes pre-specified subgroup analyses to assess treatment heterogeneity and standardized safety monitoring for volume depletion or renal events.
Q. How can population pharmacokinetic (PK) modeling address covariate effects on this compound exposure across patient subgroups?
Answer:
Population PK models should incorporate covariates such as renal function, body mass index, and diabetes status to quantify variability in drug exposure. For example, a phase IIa/III study used nonlinear mixed-effects modeling to identify baseline glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albuminuria as key covariates influencing this compound’s PK in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) patients, enabling dose adjustments for renal impairment . Advanced modeling software (e.g., NONMEM) and bootstrapping validation are critical for robustness.
Q. What analytical techniques are recommended for stability profiling and impurity detection in this compound formulations?
Answer:
Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) coupled with Design of Experiments (DOE) optimizes parameters like mobile phase composition and column temperature. A validated RP-HPLC method achieved separation of this compound from six process-related impurities using a C18 column and gradient elution (acetonitrile-phosphate buffer). Forced degradation studies under ICH conditions (acid/base hydrolysis, oxidation) identified major degradants, with LC-MS/MS confirming structural changes .
Q. How should researchers reconcile conflicting data on this compound’s metabolic effects in heart failure using targeted metabolomics?
Answer:
Targeted metabolomics can clarify mechanisms by quantifying pathway-specific biomarkers (e.g., acylcarnitines, amino acids). The DEFINE-HF trial (NCT02653482) used principal component analysis (PCA) to cluster metabolites, revealing that this compound increased ketone-related and medium-chain acylcarnitines—suggesting enhanced fatty acid oxidation—without inducing pathological ketosis. Adjusting for false discovery rates (FDR) and baseline covariates mitigates false-positive associations .
Q. What challenges arise in extrapolating this compound’s efficacy from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to real-world settings?
Answer:
Real-world studies must address confounding factors (e.g., adherence, comorbidities) through propensity score matching or inverse probability weighting. A 2023 retrospective cohort study replicated RCT findings by demonstrating HbA1c reductions (−0.8%) and weight loss (−1.5 kg) in Indian T2DM patients on this compound + metformin, but emphasized rigorous exclusion criteria to mirror RCT populations . Sensitivity analyses and subgroup stratification enhance generalizability.
Q. How can pediatric trials for this compound address safety and efficacy gaps in type 1 diabetes (T1DM)?
Answer:
Pediatric trials require adaptive designs with dose-escalation phases and frequent safety monitoring for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). A 2022 systematic review highlighted the need for long-term studies in T1DM, as existing pediatric data are limited to single-dose pharmacokinetics. Incorporating continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and ketone sensors improves safety assessments .
Q. What statistical approaches resolve contradictions in this compound’s renoprotective effects across heterogeneous CKD populations?
Answer:
Bayesian hierarchical models or meta-regression can account for heterogeneity in baseline proteinuria or GFR. The DAPA-CKD trial (NCT03036150) stratified outcomes by albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), showing consistent renal benefits. Sensitivity analyses should test the robustness of effect estimates across subgroups, while competing risk models address mortality as a confounder .
Q. How does DOE enhance robustness in developing this compound quantification methods?
Answer:
DOE systematically optimizes HPLC parameters (e.g., flow rate, pH) using factorial designs. A study employing central composite design (CCD) identified sodium lauryl sulfate concentration and wavelength (225 nm) as critical factors for this compound quantification, achieving a linear range of 2–12 µg/mL with R² >0.999. Validation followed ICH Q2(R1) guidelines for accuracy (±2%) and precision (RSD <2%) .
Q. What mechanisms underlie this compound’s cardioprotective effects beyond glucose control?
Answer:
Preclinical models suggest hemodynamic improvements (reduced preload/afterload) and anti-inflammatory effects via NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Clinical metabolomic data link this compound to increased β-hydroxybutyrate (a cardioprotective ketone) and reduced aromatic amino acids (associated with HF progression). Mechanistic trials should integrate transcriptomic and proteomic profiling .
Q. How do researchers validate novel biomarkers for this compound response in diabetic kidney disease (DKD)?
Answer:
Cohort studies with longitudinal biospecimen collection (e.g., urine TGF-β1, serum TNF-α) paired with GFR slope analysis are essential. The DERIVE study (NCT02413398) used machine learning to identify urinary C-mannosyl tryptophan as a predictive biomarker for this compound’s albuminuria-lowering effect. Replication in independent cohorts and assay standardization (e.g., ELISA vs. mass spectrometry) ensure validity .
属性
IUPAC Name |
(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H25ClO6/c1-2-27-15-6-3-12(4-7-15)9-14-10-13(5-8-16(14)22)21-20(26)19(25)18(24)17(11-23)28-21/h3-8,10,17-21,23-26H,2,9,11H2,1H3/t17-,18-,19+,20-,21+/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
JVHXJTBJCFBINQ-ADAARDCZSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)C3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H25ClO6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID20905104 | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20905104 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
408.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Dapagliflozin inhibits the sodium-glucose contransporter 2(SGLT2) which is primarily located in the proximal tubule of the nephron. SGLT2 facilitates 90% of glucose reabsorption in the kidneys and so its inhibition allows for glucose to be excreted in the urine. This excretion allows for better glycemic control and potentially weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06292 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
461432-26-8 | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=461432-26-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0461432268 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06292 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Dapagliflozin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20905104 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (1S)-1,5-anhydro-1-C-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-D-glucitol | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DAPAGLIFLOZIN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/1ULL0QJ8UC | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。
















