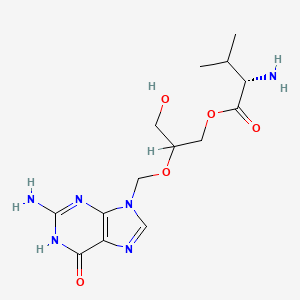
Valganciclovir
- Haga clic en CONSULTA RÁPIDA para recibir una cotización de nuestro equipo de expertos.
- Con productos de calidad a un precio COMPETITIVO, puede centrarse más en su investigación.
Descripción general
Descripción
Valganciclovir es un medicamento antiviral utilizado principalmente para tratar infecciones por citomegalovirus, particularmente en pacientes inmunocomprometidos como aquellos con síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida o después de un trasplante de órgano . Es el éster L-valil del ganciclovir y actúa como un profármaco, lo que significa que se convierte en su forma activa, ganciclovir, después de la administración . This compound es conocido por su efectividad para prevenir la propagación del citomegalovirus al inhibir la síntesis de ADN viral .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Clinical Applications
1. Treatment of Cytomegalovirus Retinitis
Valganciclovir is effective in treating CMV retinitis, particularly in patients with HIV/AIDS. Studies have shown that it has comparable efficacy to intravenous ganciclovir while offering the advantage of oral administration, which reduces hospital visits and associated costs .
2. Prophylaxis in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
In solid organ transplant recipients, this compound is utilized for both preemptive therapy and treatment of CMV disease. A study indicated that it can effectively prevent CMV infections post-transplant, reducing the incidence of CMV disease compared to no prophylaxis or other antiviral therapies .
3. Treatment in Pediatric Populations
Research has demonstrated that this compound is also effective in treating CMV infections in children, with pharmacokinetic studies indicating appropriate dosing adjustments based on age and renal function .
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
This compound's pharmacokinetics involve its conversion to ganciclovir, which is then metabolized and excreted by the kidneys. A recent population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model developed for kidney transplant patients showed that appropriate dosing can achieve significant viral load reductions within weeks of therapy initiation .
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Lung Transplant Recipient
A notable case involved a female lung transplant recipient who maintained this compound prophylaxis effectively through therapeutic drug monitoring. After experiencing complications post-surgery, she was able to achieve viral suppression with careful management of her this compound dosage .
Case Study 2: Solid Organ Transplant Efficacy
In a clinical trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, this compound was shown to be noninferior to intravenous ganciclovir for treating established CMV disease. The trial highlighted its safety profile and efficacy in eradicating CMV from patients, demonstrating its role as a standard treatment option .
Comparative Efficacy
| Study | Population | Treatment Comparison | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| VICTOR Trial | Solid organ transplant recipients | Oral this compound vs. IV ganciclovir | Noninferior efficacy; similar success rates |
| Pediatric Pharmacokinetics | Children with CMV infection | This compound dosing adjustments | Effective treatment with adjusted dosing |
| Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Case | Lung transplant recipient | This compound prophylaxis | Successful viral suppression under monitoring |
Mecanismo De Acción
Valganciclovir es un profármaco que se convierte rápidamente en ganciclovir por las esterasas hepáticas e intestinales . Ganciclovir es un análogo acíclico del nucleósido guanosina. Una vez dentro de la célula, ganciclovir es fosforilado por las quinasas virales para formar ganciclovir trifosfato . Esta forma trifosfato inhibe la ADN polimerasa viral al competir con el desoxiguanosina trifosfato, lo que lleva a la terminación de la elongación del ADN viral . Este mecanismo previene eficazmente la replicación del citomegalovirus y otros herpesvirus .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Valganciclovir plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting viral DNA synthesis. Upon administration, this compound is rapidly converted to Ganciclovir by intestinal and hepatic esterases . Ganciclovir then undergoes phosphorylation by viral protein kinase UL97 and subsequently by cellular kinases to form Ganciclovir triphosphate . This triphosphate form inhibits viral DNA polymerase, thereby preventing viral DNA replication . This compound interacts with enzymes such as viral protein kinase UL97 and cellular kinases, which are essential for its activation and antiviral activity .
Cellular Effects
This compound exerts significant effects on various cell types, particularly those infected with cytomegalovirus. It inhibits viral replication within infected cells, thereby reducing viral load and preventing the spread of infection . This compound influences cell function by interfering with cell signaling pathways involved in viral replication and gene expression . Additionally, it impacts cellular metabolism by inhibiting the synthesis of viral DNA, which is crucial for viral proliferation .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its conversion to Ganciclovir, which is then phosphorylated to its active triphosphate form . Ganciclovir triphosphate competes with deoxyguanosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA by viral DNA polymerase . Once incorporated, it acts as a chain terminator, preventing further elongation of the viral DNA strand . This inhibition of viral DNA synthesis is the primary mechanism by which this compound exerts its antiviral effects .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound have been observed to change over time. The stability of this compound is influenced by factors such as pH and temperature, with degradation occurring under extreme conditions . Long-term studies have shown that this compound maintains its antiviral activity over extended periods, although its efficacy may decrease with prolonged exposure . In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that this compound effectively reduces viral load and prevents viral replication over time .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. At therapeutic doses, this compound effectively inhibits viral replication and reduces viral load without causing significant toxicity . At higher doses, this compound can cause adverse effects such as bone marrow suppression and renal toxicity . Threshold effects have been observed, with higher doses leading to increased toxicity and reduced efficacy .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is metabolized primarily in the liver and intestines, where it is converted to Ganciclovir by esterases . Ganciclovir is then phosphorylated by viral protein kinase UL97 and cellular kinases to form Ganciclovir triphosphate . This active metabolite inhibits viral DNA polymerase, preventing viral DNA synthesis . The metabolic pathways of this compound involve interactions with enzymes such as esterases, viral protein kinase UL97, and cellular kinases .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. After oral administration, this compound is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and transported to the liver, where it is converted to Ganciclovir . Ganciclovir is then distributed to various tissues, including the kidneys, liver, and spleen . Transporters and binding proteins play a role in the distribution and localization of this compound within cells .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound and its active metabolite, Ganciclovir triphosphate, is primarily within the nucleus of infected cells . This localization is crucial for its antiviral activity, as it allows for the inhibition of viral DNA synthesis within the nucleus . Targeting signals and post-translational modifications may influence the localization and activity of this compound within specific cellular compartments .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción: Valganciclovir se sintetiza mediante un proceso de varios pasos que involucra la esterificación de ganciclovir con L-valina. La síntesis comienza con la protección de ganciclovir, seguida de la esterificación con L-valina utilizando reactivos como diciclohexilcarbodiimida y 4-dimetilaminopiridina . El producto final se obtiene a través de pasos de desprotección y purificación .
Métodos de producción industrial: La producción industrial de this compound involucra rutas sintéticas similares pero a mayor escala. El proceso incluye el uso de cromatografía líquida de alta resolución para la purificación y el control de calidad . La producción se optimiza para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza, cumpliendo con estrictos estándares farmacéuticos .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones: Valganciclovir se somete a hidrólisis para convertirse en su forma activa, ganciclovir . Esta hidrólisis es facilitada por las esterasas intestinales y hepáticas . El compuesto no sufre reacciones de oxidación o reducción significativas en condiciones fisiológicas.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes: La hidrólisis de this compound a ganciclovir es catalizada por las esterasas presentes en el hígado e intestinos . No se requieren reactivos adicionales para esta conversión.
Principales productos formados: El producto principal formado a partir de la hidrólisis de this compound es ganciclovir, que es el agente antiviral activo .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Valganciclovir a menudo se compara con otros agentes antivirales como valaciclovir y aciclovir. Si bien los tres compuestos son análogos de nucleósidos, this compound es único en su capacidad de convertirse rápidamente en ganciclovir, que tiene un espectro más amplio de actividad contra el citomegalovirus . Valaciclovir y aciclovir se utilizan principalmente para tratar infecciones por virus del herpes simple y tienen perfiles farmacocinéticos diferentes .
Compuestos similares:
Ganciclovir: La forma activa de this compound, utilizada para tratar infecciones por citomegalovirus.
Valaciclovir: Un profármaco antiviral que se convierte en aciclovir, utilizado para tratar infecciones por virus del herpes simple.
This compound destaca por su eficacia en el tratamiento de infecciones por citomegalovirus y su capacidad de administrarse por vía oral, lo que proporciona una opción conveniente para el tratamiento a largo plazo .
Actividad Biológica
Valganciclovir (VGC) is an antiviral medication primarily used for the prevention and treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients such as those undergoing organ transplantation. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, focusing on its pharmacological properties, clinical efficacy, and emerging research findings.
Pharmacological Properties
This compound is a prodrug of ganciclovir, which means it is converted into its active form after administration. The addition of a valine ester significantly enhances its oral bioavailability, making it a preferred option for outpatient therapy. The pharmacokinetics of VGC demonstrate that it achieves plasma concentrations comparable to those obtained with intravenous ganciclovir when administered at appropriate doses.
Key Pharmacokinetic Data
| Parameter | This compound (900 mg) | Ganciclovir (5 mg/kg IV) |
|---|---|---|
| Bioavailability | ~60% | ~6% |
| Peak Plasma Concentration | Achieved within 1-2 hours | Achieved within 1 hour |
| Half-life | 3-4 hours | 2-4 hours |
This enhanced bioavailability allows for effective outpatient management of CMV infections, reducing the need for intravenous therapy, which is often associated with higher costs and complications.
Clinical Efficacy
This compound has been shown to be effective in preventing and treating CMV disease in various patient populations, including organ transplant recipients and those with HIV. The VICTOR study established that oral this compound is noninferior to intravenous ganciclovir for treating CMV disease in solid organ transplant recipients, leading to its recommendation in clinical guidelines .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
- VICTOR Study : This randomized trial compared oral this compound to intravenous ganciclovir in solid organ transplant recipients. It demonstrated comparable efficacy in eradicating CMV after 21 days of treatment and highlighted the importance of tailoring therapy based on initial viral load and immunosuppression levels .
- Phase I Trial in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) : A recent study investigated this compound as an adjunct therapy in patients with IPF. Results indicated that while the primary endpoint was not met, there was a trend towards improved lung function metrics among those treated with this compound compared to placebo .
- Glioblastoma Treatment : Emerging research suggests that this compound may have potential applications beyond antiviral therapy. A study indicated that it improved survival rates in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma, particularly in those with unmethylated MGMT promoter genes. This finding opens avenues for further exploration into the drug's effects on tumor biology .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of this compound is critical, especially given its use in vulnerable populations. Common adverse effects include hematological toxicities such as leukopenia and neutropenia. A comparative analysis revealed that lower doses (450 mg) may be equally effective with a reduced risk of adverse events compared to higher doses (900 mg) .
Adverse Events Data
| Adverse Event | 450 mg VGC | 900 mg VGC |
|---|---|---|
| Leucopenia | 10% | 40% |
| Neutropenia | 5% | 20% |
| Discontinuation due to AE | 5% | 15% |
Propiedades
Key on ui mechanism of action |
Valganciclovir is an L-valyl ester (prodrug) of ganciclovir that exists as a mixture of two diastereomers. After oral administration, both diastereomers are rapidly converted to ganciclovir by intestinal and hepatic esterases. Ganciclovir is a synthetic analogue of 2'-deoxyguanosine, which inhibits replication of human CMV in cell culture and in vivo. In CMV-infected cells ganciclovir is initially phosphorylated to ganciclovir monophosphate by the viral protein kinase, pUL97. Further phosphorylation occurs by cellular kinases to produce ganciclovir triphosphate, which is then slowly metabolized intracellularly (half-life 18 hours). As the phosphorylation is largely dependent on the viral kinase, phosphorylation of ganciclovir occurs preferentially in virus-infected cells. The virustatic activity of ganciclovir is due to inhibition of the viral DNA polymerase, pUL54, synthesis by ganciclovir triphosphate. |
|---|---|
Número CAS |
175865-60-8 |
Fórmula molecular |
C14H22N6O5 |
Peso molecular |
354.36 g/mol |
Nombre IUPAC |
[2-[(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)methoxy]-3-hydroxypropyl] 2-amino-3-methylbutanoate |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H22N6O5/c1-7(2)9(15)13(23)24-4-8(3-21)25-6-20-5-17-10-11(20)18-14(16)19-12(10)22/h5,7-9,21H,3-4,6,15H2,1-2H3,(H3,16,18,19,22) |
Clave InChI |
WPVFJKSGQUFQAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)OCC(CO)OCN1C=NC2=C1N=C(NC2=O)N)N |
SMILES isomérico |
CC(C)C(C(=O)OC[C@H](CO)OCN1C=NC2=C1N=C(NC2=O)N)N |
SMILES canónico |
CC(C)C(C(=O)OCC(CO)OCN1C=NC2=C1N=C(NC2=O)N)N |
Descripción física |
Solid |
Pureza |
> 95% |
Cantidad |
Milligrams-Grams |
Solubilidad |
4.79e+00 g/L |
Sinónimos |
5-Amino-3-[1-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(L-valyloxy)ethoxymethyl]-6,7- dihydro-3H-imidazo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-7-one; (2S)-2-((2-AMino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9(6H)-yl)Methoxy)-3-hydroxypropyl 2-aMino-3-Methylbutanoate |
Origen del producto |
United States |
Q1: How does Valganciclovir exert its antiviral effect?
A: this compound itself is a prodrug, rapidly hydrolyzed in vivo to its active form, Ganciclovir. [] Ganciclovir is a nucleoside analogue that inhibits viral DNA polymerase. [, , , ] Once phosphorylated by viral and cellular kinases, it competitively inhibits CMV DNA polymerase, effectively halting viral DNA synthesis. [, , , ]
Q2: How does Ganciclovir's inhibition of DNA polymerase differ from that of other antiviral agents?
A: Unlike acyclovir, which requires viral thymidine kinase for initial phosphorylation, Ganciclovir can be phosphorylated by cellular kinases, making it effective against a broader range of CMV strains. []
Q3: What are the downstream effects of Ganciclovir inhibiting CMV DNA polymerase?
A: By blocking viral DNA synthesis, Ganciclovir effectively halts CMV replication, preventing further spread of the virus and allowing the immune system to control the infection. [, , ]
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A4: The molecular formula of this compound is C20H28N10O7, and its molecular weight is 504.5 g/mol.
Q5: How stable is this compound in solution?
A: While this compound has good oral bioavailability, it can undergo degradation in aqueous solutions. []
Q6: How is this compound absorbed and metabolized in the body?
A: this compound exhibits excellent oral bioavailability (around 60%) due to its rapid hydrolysis to Ganciclovir. [, ] This is significantly higher than the bioavailability of oral Ganciclovir. [, , ]
Q7: Does renal function affect this compound dosing?
A: Yes, this compound dosage adjustments are crucial for patients with renal impairment, as its clearance is primarily renal. [, , , ] Dosage adjustments based on estimated creatinine clearance are frequently necessary, especially in the context of solid organ transplantation. [, ]
Q8: Has the pharmacokinetic profile of this compound been studied in specific populations, like children?
A: Yes, research indicates the need for careful dose individualization in children, as younger patients and those with lower body surface area may exhibit significantly lower Ganciclovir exposure. [, ]
Q9: Is this compound effective for both prophylaxis and treatment of CMV infection?
A: Research supports the use of this compound for both the prevention and treatment of CMV infection in various clinical settings, including solid organ transplant recipients and individuals with AIDS. [, , , , , , ]
Q10: What is the evidence supporting this compound's efficacy in preventing CMV retinitis?
A: Clinical trials have demonstrated that oral this compound is as effective as intravenous Ganciclovir for both induction and maintenance treatment of CMV retinitis in patients with AIDS. [, ]
Q11: How does the efficacy of this compound prophylaxis compare to preemptive therapy in kidney transplant recipients?
A: While both strategies can effectively prevent CMV disease, studies suggest that this compound prophylaxis may be associated with a lower incidence of CMV infection and disease, particularly in donor-positive/recipient-positive patients. [, , ]
Q12: Does resistance to this compound develop?
A: Resistance to Ganciclovir, and therefore this compound, can emerge, primarily through mutations in the UL97 gene encoding the viral kinase that phosphorylates Ganciclovir. [, , ]
Q13: Are there specific drug delivery strategies being explored for this compound?
A: While the provided research primarily focuses on oral administration, the development of targeted drug delivery systems could potentially enhance its efficacy and minimize off-target effects. []
Q14: What are some important research tools and resources for studying this compound?
A14: Key resources include:
- In vitro cell culture models: These allow for investigating the antiviral activity of this compound and studying resistance mechanisms. []
- Animal models: These are crucial for preclinical evaluation of efficacy and safety. [, ]
- Clinical trial databases: These provide valuable data on the efficacy and safety of this compound in various patient populations. [, , , , , , , ]
- Pharmacokinetic modeling software: This aids in understanding the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of this compound, especially in specific populations. []
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.















