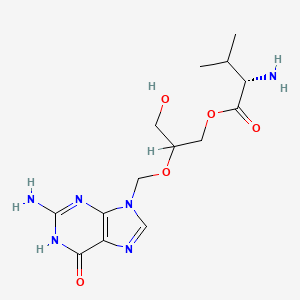
伐甘昔洛韦
- 点击 快速询问 获取最新报价。
- 提供有竞争力价格的高质量产品,您可以更专注于研究。
描述
Valganciclovir is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat cytomegalovirus infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients such as those with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or following organ transplantation . It is the L-valyl ester of ganciclovir and acts as a prodrug, which means it is converted into its active form, ganciclovir, after administration . Valganciclovir is known for its effectiveness in preventing the spread of cytomegalovirus by inhibiting viral DNA synthesis .
科学研究应用
Clinical Applications
1. Treatment of Cytomegalovirus Retinitis
Valganciclovir is effective in treating CMV retinitis, particularly in patients with HIV/AIDS. Studies have shown that it has comparable efficacy to intravenous ganciclovir while offering the advantage of oral administration, which reduces hospital visits and associated costs .
2. Prophylaxis in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
In solid organ transplant recipients, valganciclovir is utilized for both preemptive therapy and treatment of CMV disease. A study indicated that it can effectively prevent CMV infections post-transplant, reducing the incidence of CMV disease compared to no prophylaxis or other antiviral therapies .
3. Treatment in Pediatric Populations
Research has demonstrated that valganciclovir is also effective in treating CMV infections in children, with pharmacokinetic studies indicating appropriate dosing adjustments based on age and renal function .
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Valganciclovir's pharmacokinetics involve its conversion to ganciclovir, which is then metabolized and excreted by the kidneys. A recent population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model developed for kidney transplant patients showed that appropriate dosing can achieve significant viral load reductions within weeks of therapy initiation .
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Lung Transplant Recipient
A notable case involved a female lung transplant recipient who maintained valganciclovir prophylaxis effectively through therapeutic drug monitoring. After experiencing complications post-surgery, she was able to achieve viral suppression with careful management of her valganciclovir dosage .
Case Study 2: Solid Organ Transplant Efficacy
In a clinical trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, valganciclovir was shown to be noninferior to intravenous ganciclovir for treating established CMV disease. The trial highlighted its safety profile and efficacy in eradicating CMV from patients, demonstrating its role as a standard treatment option .
Comparative Efficacy
| Study | Population | Treatment Comparison | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| VICTOR Trial | Solid organ transplant recipients | Oral valganciclovir vs. IV ganciclovir | Noninferior efficacy; similar success rates |
| Pediatric Pharmacokinetics | Children with CMV infection | Valganciclovir dosing adjustments | Effective treatment with adjusted dosing |
| Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Case | Lung transplant recipient | Valganciclovir prophylaxis | Successful viral suppression under monitoring |
作用机制
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Valganciclovir plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting viral DNA synthesis. Upon administration, Valganciclovir is rapidly converted to Ganciclovir by intestinal and hepatic esterases . Ganciclovir then undergoes phosphorylation by viral protein kinase UL97 and subsequently by cellular kinases to form Ganciclovir triphosphate . This triphosphate form inhibits viral DNA polymerase, thereby preventing viral DNA replication . Valganciclovir interacts with enzymes such as viral protein kinase UL97 and cellular kinases, which are essential for its activation and antiviral activity .
Cellular Effects
Valganciclovir exerts significant effects on various cell types, particularly those infected with cytomegalovirus. It inhibits viral replication within infected cells, thereby reducing viral load and preventing the spread of infection . Valganciclovir influences cell function by interfering with cell signaling pathways involved in viral replication and gene expression . Additionally, it impacts cellular metabolism by inhibiting the synthesis of viral DNA, which is crucial for viral proliferation .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Valganciclovir involves its conversion to Ganciclovir, which is then phosphorylated to its active triphosphate form . Ganciclovir triphosphate competes with deoxyguanosine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA by viral DNA polymerase . Once incorporated, it acts as a chain terminator, preventing further elongation of the viral DNA strand . This inhibition of viral DNA synthesis is the primary mechanism by which Valganciclovir exerts its antiviral effects .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of Valganciclovir have been observed to change over time. The stability of Valganciclovir is influenced by factors such as pH and temperature, with degradation occurring under extreme conditions . Long-term studies have shown that Valganciclovir maintains its antiviral activity over extended periods, although its efficacy may decrease with prolonged exposure . In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that Valganciclovir effectively reduces viral load and prevents viral replication over time .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Valganciclovir vary with different dosages in animal models. At therapeutic doses, Valganciclovir effectively inhibits viral replication and reduces viral load without causing significant toxicity . At higher doses, Valganciclovir can cause adverse effects such as bone marrow suppression and renal toxicity . Threshold effects have been observed, with higher doses leading to increased toxicity and reduced efficacy .
Metabolic Pathways
Valganciclovir is metabolized primarily in the liver and intestines, where it is converted to Ganciclovir by esterases . Ganciclovir is then phosphorylated by viral protein kinase UL97 and cellular kinases to form Ganciclovir triphosphate . This active metabolite inhibits viral DNA polymerase, preventing viral DNA synthesis . The metabolic pathways of Valganciclovir involve interactions with enzymes such as esterases, viral protein kinase UL97, and cellular kinases .
Transport and Distribution
Valganciclovir is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. After oral administration, Valganciclovir is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and transported to the liver, where it is converted to Ganciclovir . Ganciclovir is then distributed to various tissues, including the kidneys, liver, and spleen . Transporters and binding proteins play a role in the distribution and localization of Valganciclovir within cells .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of Valganciclovir and its active metabolite, Ganciclovir triphosphate, is primarily within the nucleus of infected cells . This localization is crucial for its antiviral activity, as it allows for the inhibition of viral DNA synthesis within the nucleus . Targeting signals and post-translational modifications may influence the localization and activity of Valganciclovir within specific cellular compartments .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件: 缬更昔洛韦是通过多步过程合成的,该过程涉及更昔洛韦与L-缬氨酸的酯化反应。 合成始于更昔洛韦的保护,然后使用二环己基碳二酰亚胺和4-二甲氨基吡啶等试剂与L-缬氨酸酯化 . 最终产品通过脱保护和纯化步骤获得 .
工业生产方法: 缬更昔洛韦的工业生产涉及类似的合成路线,但规模更大。 该过程包括使用高效液相色谱法进行纯化和质量控制 . 生产过程经过优化,以确保高产率和高纯度,符合严格的药物标准 .
化学反应分析
反应类型: 缬更昔洛韦发生水解,转化为其活性形式更昔洛韦 . 这种水解是由肠道和肝脏酯酶促进的 . 该化合物在生理条件下不会发生明显的氧化或还原反应。
常见试剂和条件: 缬更昔洛韦水解为更昔洛韦的过程由肝脏和肠道中存在的酯酶催化 . 此转化不需要任何额外的试剂。
主要形成的产物: 缬更昔洛韦水解的主要产物是更昔洛韦,它是一种有效的抗病毒剂 .
相似化合物的比较
缬更昔洛韦经常与其他抗病毒剂如伐昔洛韦和阿昔洛韦进行比较。 虽然这三种化合物都是核苷类似物,但缬更昔洛韦的独特之处在于它可以迅速转化为更昔洛韦,更昔洛韦对巨细胞病毒具有更广泛的活性 . 伐昔洛韦和阿昔洛韦主要用于治疗单纯疱疹病毒感染,并具有不同的药代动力学特征 .
类似化合物:
更昔洛韦: 缬更昔洛韦的活性形式,用于治疗巨细胞病毒感染.
伐昔洛韦: 一种抗病毒前药,转化为阿昔洛韦,用于治疗单纯疱疹病毒感染.
生物活性
Valganciclovir (VGC) is an antiviral medication primarily used for the prevention and treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients such as those undergoing organ transplantation. This article delves into the biological activity of Valganciclovir, focusing on its pharmacological properties, clinical efficacy, and emerging research findings.
Pharmacological Properties
Valganciclovir is a prodrug of ganciclovir, which means it is converted into its active form after administration. The addition of a valine ester significantly enhances its oral bioavailability, making it a preferred option for outpatient therapy. The pharmacokinetics of VGC demonstrate that it achieves plasma concentrations comparable to those obtained with intravenous ganciclovir when administered at appropriate doses.
Key Pharmacokinetic Data
| Parameter | Valganciclovir (900 mg) | Ganciclovir (5 mg/kg IV) |
|---|---|---|
| Bioavailability | ~60% | ~6% |
| Peak Plasma Concentration | Achieved within 1-2 hours | Achieved within 1 hour |
| Half-life | 3-4 hours | 2-4 hours |
This enhanced bioavailability allows for effective outpatient management of CMV infections, reducing the need for intravenous therapy, which is often associated with higher costs and complications.
Clinical Efficacy
Valganciclovir has been shown to be effective in preventing and treating CMV disease in various patient populations, including organ transplant recipients and those with HIV. The VICTOR study established that oral Valganciclovir is noninferior to intravenous ganciclovir for treating CMV disease in solid organ transplant recipients, leading to its recommendation in clinical guidelines .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
- VICTOR Study : This randomized trial compared oral Valganciclovir to intravenous ganciclovir in solid organ transplant recipients. It demonstrated comparable efficacy in eradicating CMV after 21 days of treatment and highlighted the importance of tailoring therapy based on initial viral load and immunosuppression levels .
- Phase I Trial in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) : A recent study investigated Valganciclovir as an adjunct therapy in patients with IPF. Results indicated that while the primary endpoint was not met, there was a trend towards improved lung function metrics among those treated with Valganciclovir compared to placebo .
- Glioblastoma Treatment : Emerging research suggests that Valganciclovir may have potential applications beyond antiviral therapy. A study indicated that it improved survival rates in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma, particularly in those with unmethylated MGMT promoter genes. This finding opens avenues for further exploration into the drug's effects on tumor biology .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of Valganciclovir is critical, especially given its use in vulnerable populations. Common adverse effects include hematological toxicities such as leukopenia and neutropenia. A comparative analysis revealed that lower doses (450 mg) may be equally effective with a reduced risk of adverse events compared to higher doses (900 mg) .
Adverse Events Data
| Adverse Event | 450 mg VGC | 900 mg VGC |
|---|---|---|
| Leucopenia | 10% | 40% |
| Neutropenia | 5% | 20% |
| Discontinuation due to AE | 5% | 15% |
属性
Key on ui mechanism of action |
Valganciclovir is an L-valyl ester (prodrug) of ganciclovir that exists as a mixture of two diastereomers. After oral administration, both diastereomers are rapidly converted to ganciclovir by intestinal and hepatic esterases. Ganciclovir is a synthetic analogue of 2'-deoxyguanosine, which inhibits replication of human CMV in cell culture and in vivo. In CMV-infected cells ganciclovir is initially phosphorylated to ganciclovir monophosphate by the viral protein kinase, pUL97. Further phosphorylation occurs by cellular kinases to produce ganciclovir triphosphate, which is then slowly metabolized intracellularly (half-life 18 hours). As the phosphorylation is largely dependent on the viral kinase, phosphorylation of ganciclovir occurs preferentially in virus-infected cells. The virustatic activity of ganciclovir is due to inhibition of the viral DNA polymerase, pUL54, synthesis by ganciclovir triphosphate. |
|---|---|
CAS 编号 |
175865-60-8 |
分子式 |
C14H22N6O5 |
分子量 |
354.36 g/mol |
IUPAC 名称 |
[2-[(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)methoxy]-3-hydroxypropyl] 2-amino-3-methylbutanoate |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C14H22N6O5/c1-7(2)9(15)13(23)24-4-8(3-21)25-6-20-5-17-10-11(20)18-14(16)19-12(10)22/h5,7-9,21H,3-4,6,15H2,1-2H3,(H3,16,18,19,22) |
InChI 键 |
WPVFJKSGQUFQAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)OCC(CO)OCN1C=NC2=C1N=C(NC2=O)N)N |
手性 SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)OC[C@H](CO)OCN1C=NC2=C1N=C(NC2=O)N)N |
规范 SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)OCC(CO)OCN1C=NC2=C1N=C(NC2=O)N)N |
物理描述 |
Solid |
纯度 |
> 95% |
数量 |
Milligrams-Grams |
溶解度 |
4.79e+00 g/L |
同义词 |
5-Amino-3-[1-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(L-valyloxy)ethoxymethyl]-6,7- dihydro-3H-imidazo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-7-one; (2S)-2-((2-AMino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9(6H)-yl)Methoxy)-3-hydroxypropyl 2-aMino-3-Methylbutanoate |
产品来源 |
United States |
Q1: How does Valganciclovir exert its antiviral effect?
A: Valganciclovir itself is a prodrug, rapidly hydrolyzed in vivo to its active form, Ganciclovir. [] Ganciclovir is a nucleoside analogue that inhibits viral DNA polymerase. [, , , ] Once phosphorylated by viral and cellular kinases, it competitively inhibits CMV DNA polymerase, effectively halting viral DNA synthesis. [, , , ]
Q2: How does Ganciclovir's inhibition of DNA polymerase differ from that of other antiviral agents?
A: Unlike acyclovir, which requires viral thymidine kinase for initial phosphorylation, Ganciclovir can be phosphorylated by cellular kinases, making it effective against a broader range of CMV strains. []
Q3: What are the downstream effects of Ganciclovir inhibiting CMV DNA polymerase?
A: By blocking viral DNA synthesis, Ganciclovir effectively halts CMV replication, preventing further spread of the virus and allowing the immune system to control the infection. [, , ]
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of Valganciclovir?
A4: The molecular formula of Valganciclovir is C20H28N10O7, and its molecular weight is 504.5 g/mol.
Q5: How stable is Valganciclovir in solution?
A: While Valganciclovir has good oral bioavailability, it can undergo degradation in aqueous solutions. []
Q6: How is Valganciclovir absorbed and metabolized in the body?
A: Valganciclovir exhibits excellent oral bioavailability (around 60%) due to its rapid hydrolysis to Ganciclovir. [, ] This is significantly higher than the bioavailability of oral Ganciclovir. [, , ]
Q7: Does renal function affect Valganciclovir dosing?
A: Yes, Valganciclovir dosage adjustments are crucial for patients with renal impairment, as its clearance is primarily renal. [, , , ] Dosage adjustments based on estimated creatinine clearance are frequently necessary, especially in the context of solid organ transplantation. [, ]
Q8: Has the pharmacokinetic profile of Valganciclovir been studied in specific populations, like children?
A: Yes, research indicates the need for careful dose individualization in children, as younger patients and those with lower body surface area may exhibit significantly lower Ganciclovir exposure. [, ]
Q9: Is Valganciclovir effective for both prophylaxis and treatment of CMV infection?
A: Research supports the use of Valganciclovir for both the prevention and treatment of CMV infection in various clinical settings, including solid organ transplant recipients and individuals with AIDS. [, , , , , , ]
Q10: What is the evidence supporting Valganciclovir's efficacy in preventing CMV retinitis?
A: Clinical trials have demonstrated that oral Valganciclovir is as effective as intravenous Ganciclovir for both induction and maintenance treatment of CMV retinitis in patients with AIDS. [, ]
Q11: How does the efficacy of Valganciclovir prophylaxis compare to preemptive therapy in kidney transplant recipients?
A: While both strategies can effectively prevent CMV disease, studies suggest that Valganciclovir prophylaxis may be associated with a lower incidence of CMV infection and disease, particularly in donor-positive/recipient-positive patients. [, , ]
Q12: Does resistance to Valganciclovir develop?
A: Resistance to Ganciclovir, and therefore Valganciclovir, can emerge, primarily through mutations in the UL97 gene encoding the viral kinase that phosphorylates Ganciclovir. [, , ]
Q13: Are there specific drug delivery strategies being explored for Valganciclovir?
A: While the provided research primarily focuses on oral administration, the development of targeted drug delivery systems could potentially enhance its efficacy and minimize off-target effects. []
Q14: What are some important research tools and resources for studying Valganciclovir?
A14: Key resources include:
- In vitro cell culture models: These allow for investigating the antiviral activity of Valganciclovir and studying resistance mechanisms. []
- Animal models: These are crucial for preclinical evaluation of efficacy and safety. [, ]
- Clinical trial databases: These provide valuable data on the efficacy and safety of Valganciclovir in various patient populations. [, , , , , , , ]
- Pharmacokinetic modeling software: This aids in understanding the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of Valganciclovir, especially in specific populations. []
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。















