Piracetam
Vue d'ensemble
Description
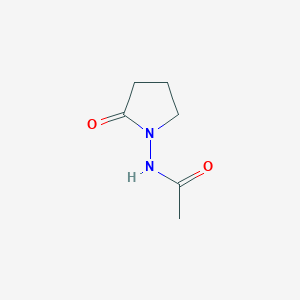
Le Piracétam est un médicament nootropique appartenant au groupe des racétames, dont le nom chimique est 2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acétamide. Il s'agit d'un dérivé cyclique du neurotransmetteur acide gamma-aminobutyrique (GABA). Le Piracétam a été commercialisé pour la première fois par UCB Pharma en 1971 et est connu pour ses propriétés cognitives. Il est utilisé dans divers troubles cognitifs, vertiges, myoclonies corticales, dyslexie et drépanocytose .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions réactionnelles
Le Piracétam peut être synthétisé par plusieurs méthodes. Une méthode courante implique la réaction de la 2-pyrrolidone avec le chloroacétate d'éthyle en présence d'une base, suivie d'une hydrolyse pour produire le Piracétam. Une autre méthode implique la cyclisation de l'acide gamma-aminobutyrique (GABA) avec l'anhydride acétique .
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle du Piracétam implique généralement une synthèse à grande échelle utilisant les méthodes mentionnées ci-dessus. Le processus est optimisé pour un rendement et une pureté élevés, garantissant que le produit final répond aux normes pharmaceutiques. Le processus de production comprend des étapes telles que la cristallisation, la filtration et le séchage pour obtenir le composé pur .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
Le Piracétam subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Le Piracétam peut être oxydé pour former de l'acide 2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylique.
Réduction : La réduction du Piracétam peut produire de la 2-pyrrolidone.
Substitution : Des réactions de substitution peuvent se produire au niveau du groupe acétamide, conduisant à la formation de divers dérivés
Réactifs et conditions courantes
Oxydation : Les agents oxydants courants comprennent le permanganate de potassium et le peroxyde d'hydrogène.
Réduction : Des agents réducteurs tels que l'hydrure de lithium et d'aluminium peuvent être utilisés.
Substitution : Des réactifs comme les halogénoalcanes et les chlorures d'acyle sont couramment utilisés pour les réactions de substitution
Principaux produits formés
Oxydation : Acide 2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylique
Réduction : 2-pyrrolidone
Substitution : Divers dérivés d'acétamide
Applications de recherche scientifique
Le Piracétam a une large gamme d'applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisé comme composé modèle pour étudier les propriétés des amides cycliques et de leurs dérivés.
Biologie : Étudié pour ses effets sur la fluidité des membranes cellulaires et la neuroprotection.
Médecine : Utilisé dans le traitement des troubles cognitifs, de la myoclonie et de la drépanocytose. Il a également été étudié pour ses avantages potentiels dans des conditions comme la démence, les vertiges et la dyslexie.
Industrie : Utilisé dans le développement de compléments nootropiques et de stimulants cognitifs .
Mécanisme d'action
Le mécanisme d'action du Piracétam n'est pas entièrement compris, mais on pense qu'il implique plusieurs voies :
Modulation des neurotransmetteurs : Le Piracétam module la neurotransmission dans les systèmes cholinergique et glutamatergique.
Neuroprotection : Il possède des propriétés neuroprotectrices, améliorant la plasticité neuronale et protégeant contre l'hypoxie.
Effets vasculaires : Le Piracétam réduit l'adhésion des érythrocytes à l'endothélium vasculaire, empêchant les vasospasmes et facilitant la microcirculation .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Piracetam has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound for studying the properties of cyclic amides and their derivatives.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on cell membrane fluidity and neuroprotection.
Medicine: Used in the treatment of cognitive disorders, myoclonus, and sickle cell anemia. It has also been studied for its potential benefits in conditions like dementia, vertigo, and dyslexia.
Industry: Utilized in the development of nootropic supplements and cognitive enhancers .
Mécanisme D'action
Piracetam’s mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve several pathways:
Neurotransmitter Modulation: this compound modulates neurotransmission in cholinergic and glutamatergic systems.
Neuroprotection: It has neuroprotective properties, enhancing neural plasticity and protecting against hypoxia.
Vascular Effects: This compound reduces erythrocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium, hindering vasospasms and facilitating microcirculation .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Le Piracétam est souvent comparé à d'autres racétames, notamment :
Oxiracétam : Connu pour ses effets stimulants et utilisé pour l'amélioration cognitive.
Aniracétam : Possède des propriétés anxiolytiques et est utilisé pour l'anxiété et les troubles cognitifs.
Pramiracetam : Plus puissant que le Piracétam, utilisé pour les déficits cognitifs associés aux lésions cérébrales traumatiques.
Phénylpiracetam : Plus puissant et utilisé pour un éventail plus large d'indications, notamment l'amélioration cognitive et la performance physique .
Le Piracétam est unique par son profil de sécurité bien documenté et sa large gamme d'applications, ce qui en fait un composé polyvalent tant en recherche qu'en clinique.
Activité Biologique
Piracetam, a nootropic compound first synthesized in the 1960s, is widely recognized for its cognitive-enhancing properties. It belongs to the racetam family of drugs and has been extensively studied for its effects on brain function, neuroprotection, and various neurological disorders. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its mechanisms of action, therapeutic applications, and relevant research findings.
This compound exhibits several mechanisms that contribute to its biological activity:
- Neurotransmitter Modulation : this compound modulates neurotransmission by enhancing cholinergic, serotonergic, noradrenergic, and glutamatergic pathways. It increases the density of postsynaptic receptors without binding strongly to them (Ki > 10μM) . This modulation facilitates improved cognitive processes such as learning and memory.
- Membrane Fluidity : The compound interacts with phospholipid membranes, promoting membrane fluidity and stability. This action is crucial for maintaining the structure and function of transmembrane proteins involved in neurotransmission .
- Neuroprotection : this compound has demonstrated neuroprotective effects against various forms of neuronal injury, including oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS). It reduces intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO), which are implicated in neuroinflammation and cell death .
Therapeutic Applications
This compound has been investigated for a range of clinical applications:
- Cognitive Enhancement : Numerous studies have reported improvements in cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and consciousness in both healthy individuals and those with cognitive impairments .
- Neurodegenerative Disorders : Research suggests that this compound may have potential benefits in conditions like Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia by enhancing synaptic plasticity and protecting neurons from damage .
- Anticonvulsant Properties : this compound has been shown to possess anticonvulsant properties, making it a candidate for treating epilepsy .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
A summary of key studies investigating the biological activity of this compound is presented in Table 1:
| Study | Findings | Dosage | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed & Oswal (2010) | Continuous positive allosteric modulation on AMPA receptors; enhances neuronal excitation | 200 mg/kg | Rats |
| Colucci et al. (2012) | Improves acetylcholine functions via muscarinic receptors | 400 mg/kg | Rats |
| Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. (2022) | Reduces LPS-induced oxidative stress; improves SOD levels | 200-400 mg/kg | Mice |
Neuroprotective Effects
A notable study highlighted this compound's capacity to protect against LPS-induced neuronal toxicity. The treatment significantly reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and amyloid-beta, indicating its potential role in mitigating neuroinflammation . Additionally, this compound was found to enhance antioxidant enzyme activities such as catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD), further supporting its neuroprotective profile.
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What are the primary neuropharmacological mechanisms of action for Piracetam, and how are they experimentally validated?
this compound enhances cell membrane fluidity, modulates neurotransmission (particularly cholinergic and glutamatergic systems), and increases oxygen consumption via adenylate kinase activity in the brain . These mechanisms are validated through in vivo models assessing acetylcholine release, membrane permeability assays, and behavioral tests in rodents. For example, studies measuring synaptic plasticity changes or oxygen utilization in ischemic brains provide direct evidence .
Q. What experimental evidence supports this compound’s neuroprotective efficacy in preclinical stroke models?
Meta-analyses of animal stroke models show this compound and derivatives improve outcomes by 30.2% (95% CI: 16.1–44.4), primarily via infarct size reduction and neurological score improvements. However, only two studies directly tested this compound in stroke models, with median quality scores of 4/10, highlighting methodological limitations . Key assays include histopathological analysis of infarct regions and Morris water maze tests for functional recovery .
Q. How is this compound’s dosage optimized in experimental settings, and what factors influence dose-response relationships?
Preclinical studies use dose-ranging protocols (e.g., 80–100 mg/kg/day in rodents) to establish efficacy and safety thresholds. For instance, LD50 values in mice (455.5 mg/kg) inform toxicity limits . Dose-response linearity is observed in epilepsy trials, where 24 g/day in humans showed superior efficacy compared to lower doses . Optimization requires pharmacokinetic profiling (e.g., half-life, blood-brain barrier penetration) and endpoint-specific titration .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How do contradictory findings in this compound’s clinical efficacy for cognitive impairment arise, and what methodological strategies resolve them?
Meta-analyses report odds ratios of 3.43–3.55 for global improvement in dementia but note heterogeneity (I² > 50%) and publication bias . Contradictions stem from:
- Study design : Crossover trials with unanalyzed first-period data inflate effect sizes .
- Population diversity : Mixed cohorts (Alzheimer’s, vascular dementia) obscure subtype-specific responses . Solutions include stratified randomization, intention-to-treat analysis, and adherence to PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews .
Q. What critiques apply to the translational gap between this compound’s preclinical promise and clinical trial outcomes?
Preclinical data for stroke were published 10 years after clinical trials began, suggesting animal models were not foundational to trial design . Discrepancies arise from:
- Timing : Animal studies administer this compound ≤6 hours post-stroke, whereas trials allowed 12-hour delays .
- Outcome measures : Rodent infarct size vs. human functional independence scales (e.g., modified Rankin) lack alignment. Bridging this gap requires co-development of preclinical-clinical protocols and biomarker validation (e.g., neuroimaging correlates) .
Q. Why does this compound fail to enhance cognition in Down syndrome despite efficacy in other neurodevelopmental models?
A randomized crossover trial (N=25) found no cognitive improvement in Down syndrome, with adverse effects (e.g., agitation) . Potential explanations:
- Pathophysiological divergence : Down syndrome’s trisomy 21 may alter drug targets (e.g., GABAergic pathways).
- Dosing mismatch : 80–100 mg/kg/day may inadequately penetrate the blood-brain barrier in this population. Mechanistic studies comparing this compound’s effects on Shank3 vs. DYRK1A pathways could clarify etiology-specific responses .
Q. Methodological Recommendations
- For preclinical studies : Use the STAIR criteria for stroke models, including blinded outcome assessment and sample size calculations .
- For clinical trials : Prioritize adaptive designs to refine dosing (e.g., Bayesian response-adaptive randomization) .
- For meta-analyses : Apply GRADE criteria to evaluate evidence certainty and adjust for unpublished data via trim-and-fill analyses .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)acetamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H10N2O2/c7-5(9)4-8-3-1-2-6(8)10/h1-4H2,(H2,7,9) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
GMZVRMREEHBGGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC(=O)N(C1)CC(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C6H10N2O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID5044491 | |
| Record name | 2-Oxo-1-Pyrrolidineacetamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID5044491 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
142.16 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Boiling Point |
Decomposes | |
| Record name | Piracetam | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09210 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
Piracetam interacts with the polar heads in the phospholipids membrane and the resulting mobile drug-lipid complexes are thought to reorganize the lipids and influence membrane function and fluidity. Such interaction has been reported in a study that investigated the effects of neuronal outgrowth induced by beta amyloid peptides; while amyloid peptides cause lipid disorganization within the cell membranes leading to neuronal death, piracetam demonstrated to decrease the destabilizing effects of amyloid peptide. The authors suggest that piracetam induces a positive curvature of the membrane by occupying the polar groups in the phospholipids to counteract the negative curvature induced by amyloid peptides , which in turn would decrease the likelihood of membrane fusion. This mechanism of action is thought to improve membrane stability, allowing the membrane and transmembrane proteins to maintain and recover the three-dimensional structure or folding for normal function such as membrane transport, chemical secretion, and receptor binding and stimulation. Through restored membrane fluidity, piracetam promotes restored neurotransmission such as glutamatergic and cholinergic systems, enhances neuroplasticity and mediates neuroprotective and anticonvulsant effects at the neuronal level. It is also demonstrated that piracetam also improves the fluidity of platelet membranes. At the vascular level, piracetam decreases adhesion of erythrocytes to cell wall and reduces vasospasm which in turn improves microcirculation including cerebral and renal blood flow., It was found that a drug of the nootropic nature piracetam possessing pronounced antihypoxic properties eliminates calcium chloride-induced disturbances of the cardiac rhythm and significantly raises the threshold of atrial fibrillation during electrical stimulation. The drug's antiarrhythmic effect is followed by a decrease of the rhythm rate and an increase of the contraction amplitude. The animals treated with piracetam in a dose when its antiarrhythmic effects (300 mg/kg) exhibited a decrease of the membrane potential of erythrocytes as compared with control. Similar effects occurred in the animals treated with lidocaine. It can be concluded that in certain types of arrhythmias the use of piracetam restores the normal rhythm of contractions that is perhaps connected with its positive influence on metabolic processes in the myocardium. | |
| Record name | Piracetam | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09210 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | PIRACETAM | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7529 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from isopropanol | |
CAS No. |
7491-74-9 | |
| Record name | Piracetam | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=7491-74-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Piracetam [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0007491749 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Piracetam | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09210 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | piracetam | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=758191 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 2-Oxo-1-Pyrrolidineacetamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID5044491 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Piracetam | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.028.466 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | PIRACETAM | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/ZH516LNZ10 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | PIRACETAM | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7529 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Melting Point |
151.5 - 152.5 °C | |
| Record name | Piracetam | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09210 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | PIRACETAM | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7529 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.















