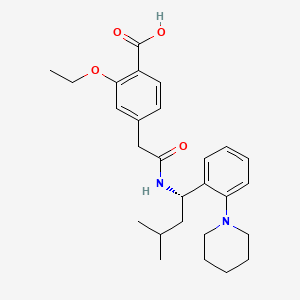
Repaglinide
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Il appartient à la classe des méglitinides, des sécrétagogues d'insuline à action courte, qui agissent en se liant aux cellules β du pancréas pour stimuler la libération d'insuline . La répaglinide est connue pour son début d'action rapide et sa courte durée d'action, ce qui la rend efficace pour contrôler la glycémie postprandiale .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions de réaction
La répaglinide peut être synthétisée par un processus en plusieurs étapes impliquant plusieurs intermédiaires clés. Une méthode courante implique les étapes suivantes :
Estérification : L'acide 3-hydroxyphénylacétique est estérifié pour former l'éthyl 3-hydroxyphénylacetate.
Formylation : L'ester est ensuite formylé pour produire l'éthyl 3-formyl-4-hydroxyphénylacetate.
Oxydation : Le groupe formyle est oxydé en acide carboxylique, ce qui donne l'éthyl 3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphénylacetate.
Éthérification : Le groupe hydroxyle est éthérifié pour former l'éthyl 3-carboxy-4-éthoxyphénylacetate.
Hydrolyse sélective : L'ester est hydrolysé sélectivement pour produire l'acide 3-carboxy-4-éthoxyphénylacétique, un intermédiaire clé dans la synthèse de la répaglinide.
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle de répaglinide implique l'optimisation des conditions de réaction pour maximiser le rendement et la pureté. Cela comprend le contrôle de la température de réaction, du temps, du solvant et des rapports de substrats . Le processus est conçu pour être évolutif et respectueux de l'environnement, avec un minimum d'impuretés.
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
La répaglinide subit plusieurs types de réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : La répaglinide peut être oxydée pour former divers métabolites.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction peuvent modifier les groupes fonctionnels de la molécule de répaglinide.
Substitution : Des réactions de substitution peuvent se produire à différentes positions sur le cycle aromatique et les chaînes latérales.
Réactifs et conditions courants
Les réactifs courants utilisés dans la synthèse et la modification de la répaglinide comprennent :
Agents oxydants : tels que le permanganate de potassium et le peroxyde d'hydrogène.
Agents réducteurs : tels que le borohydrure de sodium et l'hydrure de lithium et d'aluminium.
Réactifs de substitution : tels que les halogènes et les agents alkylants.
Principaux produits
Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent divers métabolites et dérivés de la répaglinide, qui peuvent être caractérisés à l'aide de techniques telles que la spectroscopie FT-IR, RMN et UV-Vis .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
La répaglinide a plusieurs applications de recherche scientifique, notamment :
Chimie : Utilisé comme composé modèle pour étudier la synthèse et la modification des médicaments antidiabétiques.
Biologie : Étudié pour ses effets sur les cellules β pancréatiques et la sécrétion d'insuline.
Médecine : Utilisé dans les essais cliniques pour évaluer son efficacité et sa sécurité dans le traitement du diabète de type 2.
Industrie : Employé dans le développement de nouvelles formulations de médicaments et systèmes d'administration pour améliorer la biodisponibilité et les résultats thérapeutiques
Mécanisme d'action
La répaglinide exerce ses effets en se liant aux canaux potassiques sensibles à l'ATP sur les cellules β du pancréas. Cette liaison inhibe l'efflux d'ions potassium, ce qui entraîne la dépolarisation de la membrane cellulaire. La dépolarisation ouvre les canaux calciques dépendants du voltage, permettant aux ions calcium d'entrer dans la cellule. L'afflux d'ions calcium déclenche l'exocytose des granules d'insuline, ce qui entraîne une augmentation de la libération d'insuline . Ce mécanisme est dépendant du glucose, ce qui signifie que la libération d'insuline n'est stimulée qu'en présence de glucose, réduisant le risque d'hypoglycémie .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Repaglinide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus . It helps regulate blood glucose levels by stimulating the pancreas to release insulin . It is particularly effective in controlling postprandial glucose levels .
Monotherapy
This compound can be used as a monotherapy to manage blood sugar levels. A study comparing this compound monotherapy to nateglinide monotherapy showed that this compound was more effective in reducing HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) values after 16 weeks of treatment . After 16 weeks, the mean reduction in HbA1c was significantly greater with this compound than with nateglinide (-1.57% vs -1.04%; P=0.002). Additionally, the mean changes in FPG demonstrated greater efficacy for this compound than nateglinide (-57 vs -18 mg/dl; P<0.001) .
Combination Therapy
This compound can be used in combination with other oral anti-diabetic drugs . this compound is also effective in lowering blood glucose concentrations in both sulfonylurea-treated patients and those who are new to oral hypoglycemic agents .
Glycemic Efficacy
Studies have demonstrated that reductions in A1c levels achieved with meglitinides like this compound are similar to, or slightly less than, those observed with sulfonylurea or metformin treatment when used as monotherapy . In a study comparing this compound to nateglinide in patients with type 2 diabetes, this compound was more effective in reducing A1c levels (1.57% vs. 1.04%) .
Safety and Tolerability
This compound is generally well-tolerated . However, like sulfonylureas, meglitinides can cause hypoglycemia, although the risk of severe hypoglycemia is less . Weight gain is another potential side effect .
Dosage and Administration
The recommended starting dose of this compound for patients with an A1c less than 8% is 0.5 mg before each meal (1-30 minutes prior). For those with an A1c of 8% or greater, the starting dose is 1 or 2 mg orally before each meal. The dose can be doubled up to 4mg with each meal until satisfactory glycemic control is achieved, with a one-week interval between dose increases. The maximum daily dose is 16 mg per day . this compound should be taken with meals, and doses should be skipped if a meal is skipped .
This compound vs. Nateglinide
Mécanisme D'action
Repaglinide exerts its effects by binding to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the β cells of the pancreas. This binding inhibits the efflux of potassium ions, leading to depolarization of the cell membrane. The depolarization opens voltage-dependent calcium channels, allowing calcium ions to enter the cell. The influx of calcium ions triggers the exocytosis of insulin granules, resulting in increased insulin release . This mechanism is glucose-dependent, meaning that insulin release is stimulated only in the presence of glucose, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
La répaglinide est souvent comparée à d'autres médicaments antidiabétiques, tels que :
Nateglinide : Un autre méglitinide ayant un mécanisme d'action similaire mais une durée d'effet plus courte.
Sulfonylurées : telles que la glibenclamide et la glimépiride, qui stimulent également la libération d'insuline mais ont une durée d'action plus longue et un risque plus élevé d'hypoglycémie.
Métformine : Une biguanide qui réduit la production hépatique de glucose et améliore la sensibilité à l'insuline, mais ne stimule pas la libération d'insuline
La répaglinide est unique en son genre par son début d'action rapide et sa courte durée d'action, ce qui la rend particulièrement efficace pour contrôler la glycémie postprandiale sans provoquer d'hypoglycémie prolongée .
Activité Biologique
Repaglinide is an oral antidiabetic medication belonging to the class of meglitinides, primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Its mechanism of action involves stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells in response to elevated blood glucose levels. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, supported by data tables, case studies, and detailed research findings.
This compound functions by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K-ATP channels) in pancreatic β-cells. This inhibition leads to membrane depolarization, opening L-type calcium channels, and subsequently increasing intracellular calcium concentrations. The rise in calcium levels triggers the exocytosis of insulin granules, enhancing insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. Unlike sulfonylureas, this compound's effect is minimal in the absence of glucose, making it particularly effective for postprandial blood glucose control .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of this compound is characterized by rapid absorption and a short duration of action:
- Absorption : Rapidly absorbed with peak plasma concentrations reached within 0.5 to 1.4 hours after oral administration.
- Bioavailability : Approximately 56%, indicating that a significant portion of the drug reaches systemic circulation.
- Volume of Distribution : About 31 L following intravenous administration.
- Protein Binding : Over 98%, primarily to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein .
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
-
Efficacy in Type 2 Diabetes Management :
A phase II multicenter trial involving 99 patients demonstrated that this compound significantly reduced glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels from 8.5% to 7.8% compared to an increase from 8.1% to 9.3% in the placebo group (P < 0.0001). Additionally, fasting plasma glucose levels decreased significantly in the this compound group . -
Comparison with Other Antidiabetics :
In a study comparing this compound with nateglinide over 16 weeks, this compound resulted in a greater reduction in HbA1c (1.57% vs. 1.04%, P = 0.002) and was more effective at controlling postprandial glucose levels . -
Pharmacogenomic Studies :
Research involving newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients indicated that genetic factors could influence the efficacy of this compound, with significant associations found between genetic scores and reductions in fasting glucose and HbA1c levels .
Safety Profile
This compound is generally well tolerated, with common adverse effects including:
- Hypoglycemia : Occurred in approximately 16% of patients, similar to other sulfonylureas but without increased risk when meals were missed.
- Other Adverse Events : Upper respiratory infections (10%), rhinitis (7%), bronchitis (6%), and headache (9%) were also reported .
Summary Table of Key Findings
| Parameter | Value/Outcome |
|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibition of K-ATP channels leading to insulin secretion |
| Peak Plasma Concentration | 0.5 - 1.4 hours after administration |
| Bioavailability | ~56% |
| Reduction in HbA1c | From 8.5% to 7.8% (P < 0.0001) |
| Common Adverse Effects | Hypoglycemia (16%), upper respiratory infection (10%) |
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What are the key methodological considerations when designing preclinical studies to evaluate repaglinide’s pharmacokinetics and safety?
- Methodological Answer : Preclinical studies must adhere to NIH guidelines for experimental rigor and reproducibility. Key factors include:
- Sample Size and Power Analysis : Use statistical tools (e.g., G*Power) to determine adequate sample sizes, minimizing Type I/II errors .
- In Vivo Model Selection : Rodent models should be justified based on metabolic similarities to humans, with documentation of strain, age, and housing conditions .
- Dosage Rationale : Align with human-equivalent doses (HED) derived from body surface area scaling, as per FDA guidance.
- Ethical Compliance : Include Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) approval details .
Q. How can researchers formulate focused research questions for optimizing this compound formulations using frameworks like PICO or FINER?
- Methodological Answer :
- PICO Framework : Define Population (e.g., diabetic rat models), Intervention (e.g., floating tablets with HPMC K-100M), Comparison (e.g., immediate-release formulations), and Outcome (e.g., gastric retention time) .
- FINER Criteria : Ensure questions are Feasible (e.g., lab resources for sustained-release testing), Interesting (e.g., novel polymer combinations), Novel (e.g., addressing gaps in floating mechanisms), Ethical, and Relevant (e.g., clinical translation potential) .
Q. What strategies ensure rigorous literature reviews for identifying gaps in this compound delivery systems?
- Methodological Answer :
- Systematic Search : Use databases (PubMed, Scopus) with Boolean operators (e.g., "this compound AND floating tablets NOT metformin").
- Quality Assessment : Apply PRISMA guidelines to filter studies by robustness (e.g., peer-reviewed journals, sample size >30) .
- Gap Analysis : Map existing studies using tools like VOSviewer to visualize under-researched areas (e.g., long-term stability of gastroretentive formulations) .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How do response surface methodologies (RSM) such as Central Composite Design (CCD) and D-Optimal Design compare in optimizing this compound formulations?
- Methodological Answer :
- Model Accuracy : CCD typically achieves R² > 0.85 but requires more runs (e.g., 20 runs for 3 factors), whereas D-Optimal reduces runs (e.g., 15) with comparable predictive power (relative error < 4%) .
- Diagnostic Tools : Use ANOVA for model significance (p < 0.05), residual plots for variance homogeneity, and leverage 3D contour plots to visualize interactions (e.g., HPMC K-100M concentration vs. floating lag time) .
- Software : Implement Design-Expert® or JMP® for automated optimization, prioritizing "desirability functions" to balance conflicting responses (e.g., drug release vs. buoyancy) .
Q. What statistical approaches resolve contradictions in this compound’s pharmacokinetic data across heterogeneous patient cohorts?
- Methodological Answer :
- Mixed-Effects Modeling : Account for inter-individual variability (e.g., CYP2C8 polymorphism) using NONMEM® or Monolix® .
- Sensitivity Analysis : Identify covariates (e.g., BMI, renal function) via stepwise covariate modeling (SCM) .
- Meta-Regression : Pool data from multiple studies (e.g., Cochrane Library) to adjust for confounders like dosing regimens .
Q. How should researchers structure the Methods section to meet reproducibility standards for complex this compound formulations?
- Methodological Answer :
- Granularity : Specify excipient sources (e.g., Eudragit RSPO from Evonik Industries), tablet hardness (e.g., 8–10 kp), and dissolution conditions (e.g., USP Apparatus II, 50 rpm, 37°C) .
- Validation : Include HPLC parameters (column: C18, 5 µm; mobile phase: acetonitrile-phosphate buffer) and validation metrics (e.g., LOD/LOQ, recovery rate 98–102%) .
- Ethnography for Adherence Studies : For patient-centric research, detail interview protocols (e.g., semi-structured questionnaires) and coding frameworks (e.g., NVivo® for thematic analysis) .
Q. Data Analysis & Interpretation
Q. What advanced techniques validate the robustness of this compound’s in vitro-in vivo correlation (IVIVC)?
- Methodological Answer :
- Level A IVIVC : Use deconvolution methods (e.g., Wagner-Nelson) to correlate dissolution profiles (e.g., f2 similarity factor >50) with plasma concentration-time curves .
- Bootstrap Validation : Resample data 1000x to compute 95% confidence intervals for predicted AUC and Cmax .
Q. How can machine learning improve this compound formulation development?
- Methodological Answer :
- Feature Engineering : Input variables include polymer viscosity, drug-polymer ratio, and compression force.
- Algorithm Selection : Compare Random Forest (interpretability) vs. Neural Networks (nonlinearity handling) using metrics like RMSE .
- Validation : Apply k-fold cross-validation (k=10) to prevent overfitting .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
2-ethoxy-4-[2-[[(1S)-3-methyl-1-(2-piperidin-1-ylphenyl)butyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H36N2O4/c1-4-33-25-17-20(12-13-22(25)27(31)32)18-26(30)28-23(16-19(2)3)21-10-6-7-11-24(21)29-14-8-5-9-15-29/h6-7,10-13,17,19,23H,4-5,8-9,14-16,18H2,1-3H3,(H,28,30)(H,31,32)/t23-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FAEKWTJYAYMJKF-QHCPKHFHSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCOC1=C(C=CC(=C1)CC(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C2=CC=CC=C2N3CCCCC3)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCOC1=C(C=CC(=C1)CC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C2=CC=CC=C2N3CCCCC3)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C27H36N2O4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID3023552 | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3023552 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
452.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015048 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>67.9 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), 2.94e-03 g/L | |
| Record name | SID49648522 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015048 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Repaglinide activity is dependent on the presence functioning β cells and glucose. In contrast to sulfonylurea insulin secretatogogues, repaglinide has no effect on insulin release in the absence of glucose. Rather, it potentiates the effect of extracellular glucose on ATP-sensitive potassium channel and has little effect on insulin levels between meals and overnight. As such, repaglinide is more effective at reducing postprandial blood glucose levels than fasting blood glucose levels and requires a longer duration of therapy (approximately one month) before decreases in fasting blood glucose are observed. The insulinotropic effects of repaglinide are highest at intermediate glucose levels (3 to 10 mmol/L) and it does not increase insulin release already stimulated by high glucose concentrations (greater than 15 mmol/L). Repaglinide appears to be selective for pancreatic β cells and does not appear to affect skeletal or cardiac muscle or thyroid tissue. | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00912 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
135062-02-1 | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=135062-02-1 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Repaglinide [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0135062021 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00912 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759893 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3023552 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | (+)-2-Ethoxy-alpha-(((S)-alpha-isobutyl-o-piperidinobenzyl)carbamoyl)-p-toluic acid | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | REPAGLINIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/668Z8C33LU | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015048 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
130-131 °C, 130 - 131 °C | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00912 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Repaglinide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015048 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details






Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.













