オムビタスビル
説明
オムビタスビルは、C型肝炎ウイルス(HCV)感染症の治療に使用される抗ウイルス薬です。 これは、ウイルス複製およびビリオン集合に不可欠な非構造タンパク質5A(NS5A)を阻害する直接作用型抗ウイルス薬です . オムビタスビルは、慢性C型肝炎患者において持続的なウイルス学的反応(SVR)を達成するために、パリタプレビル、リトナビル、ダサブビルなどの他の抗ウイルス薬と組み合わせて使用されることがよくあります .
科学的研究の応用
Treatment of Hepatitis C
Ombitasvir is primarily indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, especially in genotypes 1 and 4. It is used in combination regimens that may include:
- Paritaprevir : A protease inhibitor.
- Ritonavir : A booster that enhances the effectiveness of paritaprevir.
- Dasabuvir : An additional polymerase inhibitor.
- Ribavirin : An older antiviral that can be added to enhance response rates.
Efficacy Data
Clinical trials have demonstrated high sustained virologic response rates (SVR12) in patients treated with ombitasvir-based regimens. Table 1 summarizes some key efficacy findings from various studies:
Safety Profile
The safety profile of ombitasvir has been generally favorable. Most adverse events reported are mild to moderate, with serious adverse events being rare. Common side effects include fatigue, headache, and nausea. The overall safety outcomes are consistent with those observed in clinical trials.
Adverse Events Summary
| Adverse Event | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | 10 - 15 |
| Headache | 5 - 10 |
| Nausea | 5 - 10 |
| Serious AEs | <1 |
Real-World Evidence
Real-world studies have confirmed the efficacy of ombitasvir-based treatments outside controlled clinical trial settings. For instance, a study involving over 800 patients showed an SVR12 rate of approximately 98%, indicating that outcomes in routine practice are comparable to those seen in clinical trials .
Case Studies
- Case Study: Treatment-Naïve Patients
- Case Study: Patients with Cirrhosis
作用機序
オムビタスビルは、C型肝炎ウイルスの非構造タンパク質5A(NS5A)を阻害することで抗ウイルス効果を発揮します。 NS5Aはウイルス複製と集合に不可欠であり、その阻害はウイルスライフサイクルを破壊し、ウイルス量の減少につながります . オムビタスビルはNS5Aに結合し、他のウイルスおよび宿主細胞成分との相互作用を阻止し、それによってウイルスの複製を阻害します .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Ombitasvir is a potent inhibitor of NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly . It displays linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range evaluated . Ombitasvir is predominantly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by oxidative metabolism, and has low potential for drug interactions .
Cellular Effects
Ombitasvir, as part of combination therapy, is used to treat chronic Hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . It acts by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A, which is essential for viral replication and virion assembly .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Ombitasvir involves the inhibition of the HCV protein NS5A . NS5A is a protein that is essential for viral replication and virion assembly. By inhibiting this protein, Ombitasvir prevents the virus from replicating and assembling new virions .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, Ombitasvir has shown to be effective in achieving a sustained virologic response (SVR) after 12 weeks of daily therapy . The treatment with Ombitasvir is associated with very minimal side effects, with the most common being headache and fatigue .
Metabolic Pathways
Ombitasvir is mainly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by CYP2C8-mediated oxidative metabolism . The drug is mainly excreted in the feces (90.2%) with very little excreted in the urine (1.91%) .
Transport and Distribution
Ombitasvir displays high plasma protein binding (~99.9%) and has an apparent volume of distribution of 173 liters . The drug is mainly excreted in the feces (90.2%) with very little excreted in the urine (1.91%) .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it can be inferred that Ombitasvir likely interacts with the HCV NS5A protein within the host cell where the viral replication and assembly occur .
準備方法
合成経路および反応条件
オムビタスビルの合成には、重要な中間体の形成とその後のカップリングを含む複数のステップが含まれます反応条件は、アセトニトリル、リン酸緩衝液、酢酸アンモニウムなどの有機溶媒、触媒、試薬の使用を伴うことがよくあります .
工業生産方法
工業生産では、オムビタスビルは、高い収率と純度を保証する大規模化学プロセスを使用して合成されます。このプロセスには、反応条件の最適化、精製手順、および規制基準を満たすための品質管理対策が含まれます。 高速液体クロマトグラフィー(HPLC)および液体クロマトグラフィータンデム質量分析(LC-MS / MS)は、合成を監視し、最終製品の品質を保証するために一般的に使用される分析技術です .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類
オムビタスビルは、以下を含むいくつかの種類の化学反応を起こします。
一般的な試薬および条件
オムビタスビルの合成および反応で使用される一般的な試薬には、アセトニトリル、リン酸緩衝液、酢酸アンモニウム、およびさまざまな有機溶媒が含まれます。 反応条件は、目的の化学的変換を達成し、化合物の安定性を確保するために慎重に制御されます .
生成される主な生成物
オムビタスビルを含む反応から生成される主な生成物には、その活性代謝物が含まれ、これらは抗ウイルス活性を保持し、全体的な治療効果に貢献します .
科学研究への応用
オムビタスビルには、以下を含むいくつかの科学研究への応用があります。
医学: オムビタスビルは、主に慢性C型肝炎感染症の治療に使用されます。 .
生物学: オムビタスビルに関する研究は、ウイルス複製メカニズムとC型肝炎ウイルスライフサイクルにおけるNS5Aの役割に関する洞察を提供してきました.
類似化合物との比較
オムビタスビルは、NS5A阻害剤として知られる直接作用型抗ウイルスのクラスに属しています。このクラスの類似化合物には以下が含まれます。
レディパスビル: C型肝炎の治療にソフォスブビルと組み合わせて使用される別のNS5A阻害剤。
ダクラタスビル: C型肝炎の治療に他の抗ウイルス薬と組み合わせて使用されるNS5A阻害剤。
エルバスビル: C型肝炎の治療にグラゾプレビルと組み合わせて使用されるNS5A阻害剤。
これらの類似化合物と比較して、オムビタスビルはパリタプレビル、リトナビル、ダサブビルとの組み合わせがユニークであり、高い有効性と最小限の副作用を持つ包括的な抗ウイルス療法を提供します .
生物活性
Ombitasvir is a direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent primarily used in the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It functions by inhibiting the HCV non-structural protein 5A (NS5A), which plays a crucial role in viral replication and assembly. This article explores the biological activity of Ombitasvir, including its pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, safety profiles, and real-world applications.
Ombitasvir specifically targets the NS5A protein of HCV, which is essential for the virus's lifecycle. The inhibition of NS5A disrupts several processes:
- Viral Replication : Ombitasvir impedes the replication complex formation necessary for viral RNA synthesis.
- Virion Assembly : By affecting the assembly of new virions, it reduces the overall viral load in infected individuals.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of Ombitasvir is characterized by:
- Absorption : Peak plasma concentrations are reached approximately 5 hours post-administration, with an absolute bioavailability of 48%. Fatty meals can significantly increase its exposure.
- Distribution : Ombitasvir has a large volume of distribution (173 liters) and is highly protein-bound (99.9%).
- Metabolism and Elimination : It undergoes amide hydrolysis followed by CYP2C8-mediated metabolism, with approximately 90% excreted via feces and a half-life ranging from 21 to 25 hours .
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
Ombitasvir is often used in combination with other DAAs such as paritaprevir and ritonavir. The effectiveness of these combinations has been demonstrated in multiple clinical trials:
In a notable study involving 209 patients, a sustained virologic response (SVR) was achieved in 99% of participants at 12 weeks post-treatment, indicating high efficacy even in previously treated patients .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of Ombitasvir is generally favorable. Commonly reported adverse effects include:
- Mild Symptoms : Headaches and fatigue are the most frequently observed side effects.
- Serious Adverse Events : Occurred in about 3.8% of patients, including hepatic decompensation and renal insufficiency .
In a comprehensive analysis involving over 3,800 patients, adverse events were predominantly mild and manageable, confirming its tolerability across diverse patient populations .
Case Studies
Several case studies reinforce the efficacy and safety of Ombitasvir in real-world settings:
- AMBER Study : This study evaluated the effectiveness of OBV/PTV/r ± DSV ± RBV in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Results showed that all Child–Pugh B patients achieved SVR, highlighting its utility even in those with moderate liver disease .
- Spanish Cohort Study : A representative sample of patients demonstrated that Ombitasvir-based regimens were effective and well-tolerated among both monoinfected and HIV-coinfected individuals, with SVR rates consistent with clinical trial data .
特性
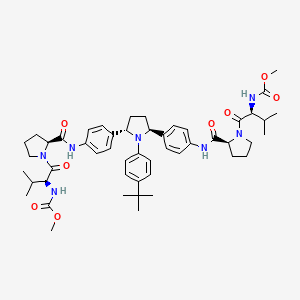
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[4-[(2S,5S)-1-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-5-[4-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]phenyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]phenyl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C50H67N7O8/c1-30(2)42(53-48(62)64-8)46(60)55-28-10-12-40(55)44(58)51-35-20-14-32(15-21-35)38-26-27-39(57(38)37-24-18-34(19-25-37)50(5,6)7)33-16-22-36(23-17-33)52-45(59)41-13-11-29-56(41)47(61)43(31(3)4)54-49(63)65-9/h14-25,30-31,38-43H,10-13,26-29H2,1-9H3,(H,51,58)(H,52,59)(H,53,62)(H,54,63)/t38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PIDFDZJZLOTZTM-KHVQSSSXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3CCC(N3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(C)(C)C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)C6CCCN6C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)[C@@H]3CC[C@H](N3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(C)(C)C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)[C@@H]6CCCN6C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C50H67N7O8 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID201027920 | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201027920 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
894.1 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ombitasvir is an inhibitor of the HCV non-structural protein 5A. While the precise role of this protein is unknown, it is essential to viral replication and virion assembly. Potential modes of action of NS5A inhibitors like Elbasvir include blocking signaling interactions, redistribution of NS5A from the endoplasmic reticulum to the surface of lipid droplets, and modification of the HCV replication complex. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09296 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1258226-87-7 | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1258226-87-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1258226877 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09296 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201027920 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | OMBITASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/2302768XJ8 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。















