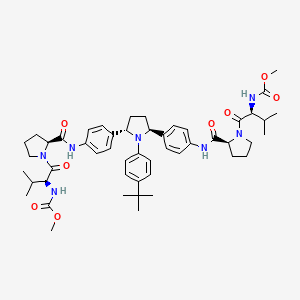
Ombitasvir
Overview
Description
Ombitasvir is an antiviral drug used for the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. It is a direct-acting antiviral agent that inhibits the nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A), which is essential for viral replication and virion assembly . This compound is commonly used in combination with other antiviral agents such as paritaprevir, ritonavir, and dasabuvir to achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR) in patients with chronic hepatitis C .
Mechanism of Action
Target of Action
Ombitasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent that primarily targets the nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . NS5A is a multifunctional protein that plays crucial roles in viral replication and assembly .
Mode of Action
This compound acts by inhibiting NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly . By binding to NS5A, this compound disrupts the formation of the replication complex, thereby preventing the replication of the HCV RNA genome .
Biochemical Pathways
The inhibition of NS5A by this compound disrupts the HCV replication cycle. This disruption prevents the production of new viral particles, thereby reducing the viral load in patients with HCV infection . The exact biochemical pathways affected by this compound are still under investigation.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound displays linear pharmacokinetics with minimal accumulation . It is predominantly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by oxidative metabolism . This compound is a substrate of P-glycoprotein, a protein that pumps foreign substances out of cells . It is eliminated via metabolism and biliary excretion, with a negligible amount of unchanged drug excreted in urine . The elimination half-life of this compound is approximately 21 to 25 hours .
Result of Action
The result of this compound’s action is a significant reduction in HCV viral load, leading to a sustained virologic response (SVR) after 12 weeks of daily therapy . SVR and eradication of HCV infection are associated with significant long-term health benefits, including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality .
Biochemical Analysis
Biochemical Properties
Ombitasvir is a potent inhibitor of NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly . It displays linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range evaluated . This compound is predominantly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by oxidative metabolism, and has low potential for drug interactions .
Cellular Effects
This compound, as part of combination therapy, is used to treat chronic Hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . It acts by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A, which is essential for viral replication and virion assembly .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves the inhibition of the HCV protein NS5A . NS5A is a protein that is essential for viral replication and virion assembly. By inhibiting this protein, this compound prevents the virus from replicating and assembling new virions .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, this compound has shown to be effective in achieving a sustained virologic response (SVR) after 12 weeks of daily therapy . The treatment with this compound is associated with very minimal side effects, with the most common being headache and fatigue .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is mainly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by CYP2C8-mediated oxidative metabolism . The drug is mainly excreted in the feces (90.2%) with very little excreted in the urine (1.91%) .
Transport and Distribution
This compound displays high plasma protein binding (~99.9%) and has an apparent volume of distribution of 173 liters . The drug is mainly excreted in the feces (90.2%) with very little excreted in the urine (1.91%) .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it can be inferred that this compound likely interacts with the HCV NS5A protein within the host cell where the viral replication and assembly occur .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of ombitasvir involves multiple steps, including the formation of key intermediates and their subsequent couplingThe reaction conditions often involve the use of organic solvents, catalysts, and reagents such as acetonitrile, phosphate buffer, and ammonium acetate .
Industrial Production Methods
In industrial production, this compound is synthesized using large-scale chemical processes that ensure high yield and purity. The process involves the optimization of reaction conditions, purification steps, and quality control measures to meet regulatory standards. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) are commonly used analytical techniques to monitor the synthesis and ensure the quality of the final product .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions
Ombitasvir undergoes several types of chemical reactions, including:
Substitution: The synthesis of this compound involves substitution reactions to introduce various functional groups onto the pyrrolidine ring.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in the synthesis and reactions of this compound include acetonitrile, phosphate buffer, ammonium acetate, and various organic solvents. The reaction conditions are carefully controlled to achieve the desired chemical transformations and ensure the stability of the compound .
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from the reactions involving this compound include its active metabolites, which retain the antiviral activity and contribute to the overall therapeutic effect .
Scientific Research Applications
Treatment of Hepatitis C
Ombitasvir is primarily indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, especially in genotypes 1 and 4. It is used in combination regimens that may include:
- Paritaprevir : A protease inhibitor.
- Ritonavir : A booster that enhances the effectiveness of paritaprevir.
- Dasabuvir : An additional polymerase inhibitor.
- Ribavirin : An older antiviral that can be added to enhance response rates.
Efficacy Data
Clinical trials have demonstrated high sustained virologic response rates (SVR12) in patients treated with this compound-based regimens. Table 1 summarizes some key efficacy findings from various studies:
Safety Profile
The safety profile of this compound has been generally favorable. Most adverse events reported are mild to moderate, with serious adverse events being rare. Common side effects include fatigue, headache, and nausea. The overall safety outcomes are consistent with those observed in clinical trials.
Adverse Events Summary
| Adverse Event | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | 10 - 15 |
| Headache | 5 - 10 |
| Nausea | 5 - 10 |
| Serious AEs | <1 |
Real-World Evidence
Real-world studies have confirmed the efficacy of this compound-based treatments outside controlled clinical trial settings. For instance, a study involving over 800 patients showed an SVR12 rate of approximately 98%, indicating that outcomes in routine practice are comparable to those seen in clinical trials .
Case Studies
- Case Study: Treatment-Naïve Patients
- Case Study: Patients with Cirrhosis
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Ombitasvir is part of a class of direct-acting antivirals known as NS5A inhibitors. Similar compounds in this class include:
Ledipasvir: Another NS5A inhibitor used in combination with sofosbuvir for the treatment of hepatitis C.
Daclatasvir: An NS5A inhibitor used in combination with other antiviral agents for the treatment of hepatitis C.
Elbasvir: An NS5A inhibitor used in combination with grazoprevir for the treatment of hepatitis C.
Compared to these similar compounds, this compound is unique in its combination with paritaprevir, ritonavir, and dasabuvir, which provides a comprehensive antiviral regimen with high efficacy and minimal side effects .
Biological Activity
Ombitasvir is a direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent primarily used in the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It functions by inhibiting the HCV non-structural protein 5A (NS5A), which plays a crucial role in viral replication and assembly. This article explores the biological activity of this compound, including its pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, safety profiles, and real-world applications.
This compound specifically targets the NS5A protein of HCV, which is essential for the virus's lifecycle. The inhibition of NS5A disrupts several processes:
- Viral Replication : this compound impedes the replication complex formation necessary for viral RNA synthesis.
- Virion Assembly : By affecting the assembly of new virions, it reduces the overall viral load in infected individuals.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of this compound is characterized by:
- Absorption : Peak plasma concentrations are reached approximately 5 hours post-administration, with an absolute bioavailability of 48%. Fatty meals can significantly increase its exposure.
- Distribution : this compound has a large volume of distribution (173 liters) and is highly protein-bound (99.9%).
- Metabolism and Elimination : It undergoes amide hydrolysis followed by CYP2C8-mediated metabolism, with approximately 90% excreted via feces and a half-life ranging from 21 to 25 hours .
Efficacy in Clinical Trials
This compound is often used in combination with other DAAs such as paritaprevir and ritonavir. The effectiveness of these combinations has been demonstrated in multiple clinical trials:
In a notable study involving 209 patients, a sustained virologic response (SVR) was achieved in 99% of participants at 12 weeks post-treatment, indicating high efficacy even in previously treated patients .
Safety Profile
The safety profile of this compound is generally favorable. Commonly reported adverse effects include:
- Mild Symptoms : Headaches and fatigue are the most frequently observed side effects.
- Serious Adverse Events : Occurred in about 3.8% of patients, including hepatic decompensation and renal insufficiency .
In a comprehensive analysis involving over 3,800 patients, adverse events were predominantly mild and manageable, confirming its tolerability across diverse patient populations .
Case Studies
Several case studies reinforce the efficacy and safety of this compound in real-world settings:
- AMBER Study : This study evaluated the effectiveness of OBV/PTV/r ± DSV ± RBV in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Results showed that all Child–Pugh B patients achieved SVR, highlighting its utility even in those with moderate liver disease .
- Spanish Cohort Study : A representative sample of patients demonstrated that this compound-based regimens were effective and well-tolerated among both monoinfected and HIV-coinfected individuals, with SVR rates consistent with clinical trial data .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[4-[(2S,5S)-1-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-5-[4-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]phenyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]phenyl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C50H67N7O8/c1-30(2)42(53-48(62)64-8)46(60)55-28-10-12-40(55)44(58)51-35-20-14-32(15-21-35)38-26-27-39(57(38)37-24-18-34(19-25-37)50(5,6)7)33-16-22-36(23-17-33)52-45(59)41-13-11-29-56(41)47(61)43(31(3)4)54-49(63)65-9/h14-25,30-31,38-43H,10-13,26-29H2,1-9H3,(H,51,58)(H,52,59)(H,53,62)(H,54,63)/t38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PIDFDZJZLOTZTM-KHVQSSSXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3CCC(N3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(C)(C)C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)C6CCCN6C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)[C@@H]3CC[C@H](N3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(C)(C)C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)[C@@H]6CCCN6C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C50H67N7O8 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID201027920 | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201027920 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
894.1 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ombitasvir is an inhibitor of the HCV non-structural protein 5A. While the precise role of this protein is unknown, it is essential to viral replication and virion assembly. Potential modes of action of NS5A inhibitors like Elbasvir include blocking signaling interactions, redistribution of NS5A from the endoplasmic reticulum to the surface of lipid droplets, and modification of the HCV replication complex. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09296 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1258226-87-7 | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1258226-87-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1258226877 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09296 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201027920 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | OMBITASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/2302768XJ8 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.
















