Zanubrutinib
Overview
Description
Zanubrutinib, marketed under the brand name Brukinsa, is a second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. It is primarily used for the treatment of various B-cell malignancies, including mantle cell lymphoma, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, marginal zone lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia . This compound has shown significant efficacy and safety improvements over first-generation BTK inhibitors, making it a promising option for patients with these conditions .
Preparation Methods
The synthesis of zanubrutinib involves several key steps. One of the primary synthetic routes includes the coupling of a phenoxyphenyl derivative with a piperidinyl-pyrazolopyrimidine intermediate. The final product is obtained through chiral high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separation . Industrial production methods focus on optimizing yield, chemical purity, and optical purity, ensuring the compound is suitable for large-scale manufacturing .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Zanubrutinib undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized under specific conditions, leading to the formation of degradation products.
Reduction: The compound can also undergo reductive stress, resulting in different degradation products.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can occur, particularly involving the phenoxyphenyl moiety.
Common reagents used in these reactions include acids, bases, and oxidizing agents. The major products formed from these reactions are typically degradation products that are analyzed to ensure the stability and efficacy of the compound .
Scientific Research Applications
Clinical Applications
Zanubrutinib is primarily approved for the treatment of several hematological malignancies:
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
- Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM)
- Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL)
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
In head-to-head trials against ibrutinib, this compound demonstrated superior efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory CLL. The ALPINE trial showed that this compound achieved an overall response rate of 78.3% compared to 62.5% for ibrutinib. Additionally, progression-free survival was significantly higher at 94.9% for this compound versus 84.0% for ibrutinib at the 12-month mark .
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
This compound has shown promising results in MCL, with a reported overall response rate of 83.7% in clinical trials. The long-term follow-up indicated a high rate of complete responses and durable remissions among patients treated with this compound .
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia
In WM, this compound has been evaluated in large-scale studies, demonstrating favorable safety and efficacy profiles similar to those observed in CLL and MCL .
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Recently, this compound received accelerated approval for use in relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma in combination with obinutuzumab. In clinical trials, this combination yielded an overall response rate of 69%, significantly higher than obinutuzumab monotherapy .
Safety Profile
This compound's safety profile is notably improved compared to earlier BTK inhibitors:
- Reduced rates of atrial fibrillation (2.5% vs. 10.1% with ibrutinib).
- Lower incidence of major hemorrhages and treatment discontinuation due to adverse events .
Comparative Efficacy
The following table summarizes the comparative efficacy of this compound against other treatments:
| Condition | This compound Efficacy | Comparison Treatment | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Higher overall response | Ibrutinib | 78.3% vs 62.5% |
| Mantle Cell Lymphoma | High overall response | N/A | 83.7% |
| Waldenström Macroglobulinemia | Favorable | N/A | N/A |
| Marginal Zone Lymphoma | Combined therapy | Obinutuzumab | 69% |
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Ongoing clinical trials are assessing the potential of this compound in various combinations with other therapies and exploring its efficacy in additional hematological malignancies and autoimmune diseases. The focus on enhancing patient outcomes while minimizing side effects continues to drive research initiatives.
Mechanism of Action
Zanubrutinib exerts its effects by selectively inhibiting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, a crucial enzyme in the B-cell receptor signaling pathway. By binding to the active site of BTK, this compound prevents the phosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling molecules, ultimately leading to the inhibition of B-cell proliferation and survival . This targeted action reduces tumor growth and improves patient outcomes in B-cell malignancies .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Zanubrutinib is often compared with other BTK inhibitors, such as ibrutinib and acalabrutinib. While all three compounds target BTK, this compound has shown higher selectivity and potency, resulting in fewer off-target effects and improved safety profiles . Additionally, this compound provides continuous exposure above its inhibitory concentration, enhancing its efficacy .
Similar Compounds
Ibrutinib: The first-generation BTK inhibitor with broader off-target effects.
Acalabrutinib: Another second-generation BTK inhibitor with a different safety and efficacy profile compared to this compound.
Biological Activity
Zanubrutinib, a selective Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, has emerged as a significant therapeutic agent for various B-cell malignancies. This article delves into its biological activity, highlighting its pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, safety profile, and comparative studies with other BTK inhibitors, particularly ibrutinib.
This compound is designed to irreversibly bind to BTK, inhibiting its activity and thereby blocking B-cell receptor signaling pathways essential for the survival and proliferation of malignant B-cells. The compound was developed to enhance specificity and reduce off-target effects compared to earlier BTK inhibitors like ibrutinib. Preclinical studies indicated that this compound exhibits greater selectivity for BTK, with over 50% inhibition in only seven kinases compared to 17 kinases for ibrutinib .
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetic Profile:
- This compound demonstrates a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with a higher area-under-the-curve (AUC) compared to ibrutinib. It achieves 100% peripheral blood BTK blockade at a dose of 40 mg daily and maintains significant BTK occupancy in lymph nodes at approved doses .
- The steady-state exposures of this compound ensure sustained BTK inhibition, which is crucial for therapeutic efficacy .
Pharmacodynamic Effects:
- Clinical trials have shown that this compound maintains over 95% BTK occupancy in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and lymph nodes, which correlates with its clinical efficacy .
- In a Phase 1 study involving patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), this compound achieved an overall response rate (ORR) of 96.2%, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 100% at 12 months .
Clinical Efficacy
This compound has been evaluated in multiple clinical trials across various B-cell malignancies:
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL):
- Waldenström Macroglobulinemia:
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma:
Safety Profile
This compound's safety profile is characterized by a lower incidence of major toxicities compared to traditional therapies:
- The most common adverse events are grade 1/2 toxicities, with neutropenia being the only grade 3/4 toxicity observed in more than two patients during clinical trials .
- The reduced off-target effects contribute to its improved tolerability and patient adherence compared to other BTK inhibitors like ibrutinib .
Comparative Studies
The following table summarizes key findings from comparative studies between this compound and ibrutinib:
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. How can researchers assess BTK inhibition by zanubrutinib in preclinical models?
Methodological Answer:
- Use kinase activity assays (e.g., ADP-Glo™ Kinase Assay) to measure BTK enzymatic inhibition.
- Validate target engagement via Western blotting for phosphorylated BTK (p-BTK) in B-cell lines (e.g., MCL cell lines).
- Employ xenograft models to evaluate tumor growth suppression, correlating plasma drug levels with p-BTK reduction. Ensure reproducibility by detailing protocols for dosing, sampling intervals, and control groups .
Q. What are key considerations for dose optimization in early-phase this compound trials?
Methodological Answer:
- Conduct phase I dose-escalation studies using a 3+3 design to identify the maximum tolerated dose (MTD).
- Monitor pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters (e.g., Cmax, AUC) and pharmacodynamic (PD) markers (e.g., BTK occupancy in peripheral blood).
- Reference long-term safety data (e.g., 35.2-month follow-up) to predefine adverse event thresholds, such as neutropenia or atrial fibrillation rates .
Q. How should researchers validate biomarkers predictive of this compound response?
Methodological Answer:
- Perform genomic profiling (e.g., whole-exome sequencing) on tumor samples to identify mutations (e.g., TP53) associated with resistance.
- Use multivariate Cox regression to correlate baseline biomarker levels (e.g., serum CXCL13) with progression-free survival (PFS).
- Standardize assays across labs using guidelines from Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) to ensure reproducibility .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How can conflicting efficacy data between this compound and other BTK inhibitors be reconciled in cross-trial comparisons?
Methodological Answer:
- Apply matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) to adjust for differences in patient demographics (e.g., prior therapy lines, ECOG scores).
- Stratify analyses by risk factors (e.g., high-risk MCL subtypes) and trial design variables (e.g., follow-up duration).
- Critically evaluate endpoints (e.g., ORR vs. PFS) and censoring rules, as variations may bias outcomes .
Q. What statistical methods address censored data in this compound survival analyses?
Methodological Answer:
- Use Kaplan-Meier estimators with log-rank tests for unadjusted survival comparisons.
- For multivariate analysis, apply Cox proportional hazards models with time-dependent covariates (e.g., treatment discontinuation).
- Address non-proportional hazards using restricted mean survival time (RMST) or parametric survival models (e.g., Weibull) .
Q. How can real-world evidence (RWE) be integrated with clinical trial data for this compound?
Methodological Answer:
- Link electronic health records (EHRs) with trial databases using unique patient identifiers, ensuring compliance with GDPR/HIPAA.
- Apply propensity score matching to balance confounding variables (e.g., comorbidities) between RWE and trial cohorts.
- Validate findings through sensitivity analyses (e.g., varying inclusion criteria) .
Q. What strategies mitigate heterogeneity in patient responses during this compound trials?
Methodological Answer:
- Pre-stratify randomization by molecular subtypes (e.g., SOX11+ vs. SOX11– MCL).
- Use adaptive trial designs to enrich subgroups showing early response signals.
- Report subgroup analyses with Bonferroni correction to control for type I error .
Q. How should meta-analyses reconcile differing endpoints across this compound trials?
Methodological Answer:
- Harmonize endpoints using standardized criteria (e.g., Lugano 2014 for lymphoma).
- Perform individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis to pool raw datasets, enabling uniform endpoint definitions.
- Quantify heterogeneity via I² statistics and explore sources using meta-regression .
Q. What ethical considerations are critical when recruiting R/R MCL patients for this compound trials?
Methodological Answer:
- Obtain informed consent detailing risks (e.g., bleeding, infections) and alternatives (e.g., CAR-T therapy).
- Establish Data Safety Monitoring Boards (DSMBs) to review interim safety data.
- Follow ICH-GCP guidelines for vulnerable populations (e.g., elderly patients with comorbidities) .
Q. How can reproducibility be ensured in this compound preclinical studies?
Methodological Answer:
- Publish detailed protocols for animal models (e.g., NOD-SCID mice), including dosing schedules and endpoint criteria.
- Share raw data and code in public repositories (e.g., GitHub) for independent validation.
- Adopt BLISS (Biological Loopholes for Experimental Standardization) guidelines to minimize batch effects .
Properties
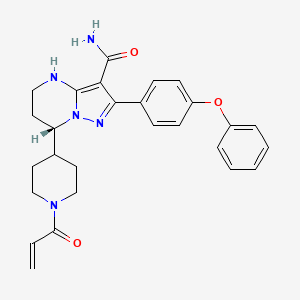
IUPAC Name |
(7S)-2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-7-(1-prop-2-enoylpiperidin-4-yl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H29N5O3/c1-2-23(33)31-16-13-18(14-17-31)22-12-15-29-27-24(26(28)34)25(30-32(22)27)19-8-10-21(11-9-19)35-20-6-4-3-5-7-20/h2-11,18,22,29H,1,12-17H2,(H2,28,34)/t22-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
RNOAOAWBMHREKO-QFIPXVFZSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)C2CCNC3=C(C(=NN23)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C=CC(=O)N1CCC(CC1)[C@@H]2CCNC3=C(C(=NN23)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC5=CC=CC=C5)C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C27H29N5O3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID701026208 | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701026208 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
471.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor kinase and a signalling molecule for the B cell receptors expressed on the peripheral B cell surface. The BCR signalling pathway plays a crucial role in normal B-cell development but also the proliferation and survival of malignant B cells in many B cell malignancies, including mantle-cell lymphoma (MCL). Once activated by upstream Src-family kinases, BTK phosphorylates phospholipase-Cγ (PLCγ), leading to Ca2+ mobilization and activation of NF-κB and MAP kinase pathways. These downstream cascades promote the expression of genes involved in B cell proliferation and survival. The BCR signalling pathway also induces the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL and regulates the integrin α4β1 (VLA-4)-mediated adhesion of B cells to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and fibronectin via BTK. Apart from the direct downstream signal transduction pathway of B cells, BTK is also involved in chemokine receptor, Toll-like receptor (TLR) and Fc receptor signalling pathways. Zanubrutinib inhibits BTK by forming a covalent bond with cysteine 481 residue in the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–binding pocket of BTK, which is the enzyme's active site. This binding specificity is commonly seen with other BTK inhibitors. Due to this binding profile, zanubrutinib may also bind with varying affinities to related and unrelated ATP-binding kinases that possess a cysteine residue at this position. By blocking the BCR signalling pathway, zanubrutinib inhibits the proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion of malignant B cells, ultimately leading to reduced tumour size. Zanubrutinib was also shown to downregulate programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-1) expression and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) on CD4+ T cells. | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB15035 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1691249-45-2 | |
| Record name | (7S)-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-7-[1-(1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl)-4-piperidinyl]-2-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1691249-45-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1691249452 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB15035 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Zanubrutinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701026208 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | ZANUBRUTINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/AG9MHG098Z | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.
















