Floxacrine
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Floxacrin ist eine antimalarielle Verbindung, die zur Klasse der Phenylchinoline gehört. Es wurde auf sein Potenzial zur Behandlung von Malaria, insbesondere von Stämmen, die gegen andere antimalarielle Medikamente resistent sind, untersucht. Floxacrin und seine Derivate haben eine vielversprechende Aktivität gegen verschiedene Stämme von Plasmodium gezeigt, dem Parasiten, der für Malaria verantwortlich ist .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: Floxacrin kann durch eine Reihe von chemischen Reaktionen unter Beteiligung des Chinolinkern synthetisiert werden. Ein übliches Verfahren beinhaltet die Reaktion von (N,N)-Dimethylaminoethylacrylat mit Aminopropanolen in Methylbenzol, gefolgt von der Zugabe von Lewis-Base und Trimethylchlorsilan, um Hydroxyl- und Amidogruppen zu schützen . Die Reaktion wird durch Zugabe von Tetrafluorbenzoylchlorid abgeschlossen, gefolgt von saurer Wäsche und Entfernung der Schutzgruppen .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: Die industrielle Produktion von Floxacrin beinhaltet die Optimierung des Synthesewegs, um die Ausbeute zu erhöhen und Verunreinigungen zu reduzieren. Dazu gehört der Schutz von Hydroxyl- und Amidogruppen mit Trimethylchlorsilan, was die Verwendung von Tetrafluorbenzoylchlorid verbessert und die Reaktionsausbeute der Zwischenstufe Difluorcarbonsäure um 10 Prozent erhöht .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Floxacrin unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution. Diese Reaktionen sind unerlässlich, um die Verbindung zu modifizieren, um ihre antimalariellen Eigenschaften zu verbessern.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen: Häufige Reagenzien, die bei den Reaktionen mit Floxacrin verwendet werden, sind Lewis-Basen, Trimethylchlorsilan und Tetrafluorbenzoylchlorid . Die Reaktionen werden typischerweise unter kontrollierten Bedingungen durchgeführt, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden: Die Hauptprodukte, die aus den Reaktionen mit Floxacrin gebildet werden, umfassen verschiedene Derivate mit verbesserter antimalarieller Aktivität. Diese Derivate werden auf ihre Wirksamkeit gegen arzneimittelresistente Stämme von Plasmodium untersucht .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Chemical Profile
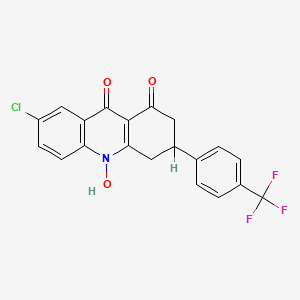
- Chemical Name : 7-chloro-10-hydroxy-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroacridine-1,9(2H, 10H)-dione
- Molecular Formula : C17H15ClF3N
- Molecular Weight : 343.76 g/mol
Antimalarial Activity
Floxacrine has been extensively studied for its efficacy against malaria, particularly in the following areas:
Efficacy Against Plasmodium Species
- Plasmodium berghei :
- Plasmodium cynomolgi :
- Resistance Development :
Comparative Efficacy
This compound's prophylactic effects were found to be superior to primaquine but inferior to pyrimethamine in certain studies . Additionally, it has shown effectiveness against other parasites:
- Eimeria species : Effective at 100 ppm in chickens.
- Fasciola hepatica : Effective at 1000 mg/kg orally in rats.
- Heterakis spumosa : Effective at doses between 300-800 mg/kg orally in rats .
Clinical Trials and Studies
- Study on Blood Schizontocide Activity :
- Prophylactic Studies :
- Comparative Studies with Other Antimalarials :
Summary Table of Efficacy Against Various Parasites
| Parasite | Effective Dose (mg/kg) | Route | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmodium berghei | 0.7 | Oral | Blood schizontocide activity |
| Plasmodium cynomolgi | 0.625 | Oral | Complete prophylaxis |
| Eimeria species | 100 ppm | Oral | Effective in chickens |
| Fasciola hepatica | 1000 | Oral | Effective in rats |
| Heterakis spumosa | 300-800 | Oral | Effective in rats |
Wirkmechanismus
Floxacrine exerts its effects by targeting the blood schizontocidal stages of Plasmodium. It interferes with the parasite’s ability to replicate and survive within the host’s red blood cells . The exact molecular targets and pathways involved in its mechanism of action are still under investigation, but it is believed to disrupt the parasite’s metabolic processes .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Floxacrin wird mit anderen antimalariellen Verbindungen wie Chloroquin, Amodiaquin, Isoquin und Tebuquin verglichen . Während diese Verbindungen bei der Behandlung von Malaria wirksam waren, hat Floxacrin eine überlegene Aktivität gegen arzneimittelresistente Stämme gezeigt . Andere ähnliche Verbindungen sind Endochin, ICI-56780 und verschiedene endochinähnliche Chinolone . Die einzigartige Struktur und der Wirkmechanismus von Floxacrin machen es zu einer wertvollen Ergänzung des Arsenals von antimalariellen Medikamenten.
Biologische Aktivität
Floxacrine, chemically known as 7-chloro-10-hydroxy-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroacridine-1,9(2H, 10H)-dione, is a compound primarily investigated for its antimalarial properties. It has shown significant efficacy against various strains of malaria parasites, particularly Plasmodium berghei, P. vinckei, and P. cynomolgi. This article synthesizes research findings on the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its mechanisms of action, efficacy in different models, and potential therapeutic applications.
Efficacy Against Malaria Parasites
This compound has demonstrated potent antimalarial activity in both in vitro and in vivo studies:
- Blood Schizontocidal Action : this compound exhibits a high level of activity against both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of Plasmodium berghei. In mouse models, the effective dose (ED50) against sensitive strains was found to be approximately 0.7 mg/kg when administered subcutaneously .
- Resistance Profiles : The compound maintains effectiveness against strains resistant to chloroquine and other common antimalarials. However, resistance can develop with repeated subcurative doses .
Dosage and Administration
This compound's dosage requirements vary significantly based on the infection stage and parasite strain:
| Parasite Strain | Effective Dose (mg/kg) | Administration Route | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. berghei | 0.7 | Subcutaneous | Effective against sensitive strains |
| P. cynomolgi | 0.625 | Daily during incubation | Complete protection against infection |
| Chloroquine-resistant strains | 1.25 - 2.5 | Daily | Temporary clearance of parasitemia |
The precise mechanism by which this compound exerts its antimalarial effects differs from those of traditional antimalarials like chloroquine. Research indicates that it affects the pigment cytoplasm and nucleus of erythrocytic stages in malaria parasites, leading to structural changes that inhibit their growth .
Study on Owl Monkeys
In a study involving owl monkeys infected with chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum, this compound was administered at daily doses ranging from 1.25 to 2.5 mg/kg:
- Results : The compound achieved temporary clearance of parasitemia but required significantly higher doses for curing established infections—up to 64 times more than those needed for initial clearance.
- Resistance Development : Rapid development of resistance was noted, indicating the need for careful management in therapeutic settings .
Efficacy in Rodent Models
In rodent studies, this compound was also tested for its prophylactic potential:
- Prophylactic Dosing : A subcutaneous dose showed moderate prophylactic effects due to a "depot effect," where the drug remains active for extended periods .
- Tolerance Levels : The compound demonstrated good tolerance in both rodents and rhesus monkeys, with a wide margin between effective and maximum tolerated doses .
Eigenschaften
CAS-Nummer |
53966-34-0 |
|---|---|
Molekularformel |
C20H13ClF3NO3 |
Molekulargewicht |
407.8 g/mol |
IUPAC-Name |
7-chloro-10-hydroxy-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-acridine-1,9-dione |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H13ClF3NO3/c21-13-5-6-15-14(9-13)19(27)18-16(25(15)28)7-11(8-17(18)26)10-1-3-12(4-2-10)20(22,23)24/h1-6,9,11,28H,7-8H2 |
InChI-Schlüssel |
AWHZKKVSUJJVNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES |
C1C(CC(=O)C2=C1N(C3=C(C2=O)C=C(C=C3)Cl)O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(F)(F)F |
Kanonische SMILES |
C1C(CC(=O)C2=C1N(C3=C(C2=O)C=C(C=C3)Cl)O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(F)(F)F |
Aussehen |
Solid powder |
Reinheit |
>98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis) |
Haltbarkeit |
>2 years if stored properly |
Löslichkeit |
Soluble in DMSO |
Lagerung |
Dry, dark and at 0 - 4 C for short term (days to weeks) or -20 C for long term (months to years). |
Synonyme |
7-chloro-10-hydroxy-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroacridine-1,9(2H,10H)-dione floxacrine HOE 991 |
Herkunft des Produkts |
United States |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
















