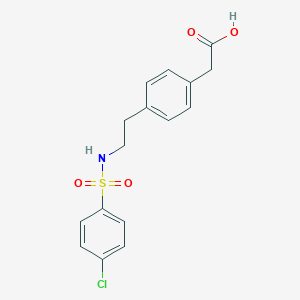
Daltroban
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Es wurde ursprünglich Mitte der 1980er Jahre von Boehringer Mannheim entwickelt und später an Smith Kline Beecham zur Weiterentwicklung als Antithrombotikum lizenziert . Daltroban wurde auf seine potenziellen schützenden Wirkungen bei Reperfusionsverletzungen und seine Fähigkeit untersucht, den intrazellulären Kalziumgehalt in glatten Gefäßmuskelzellen zu erhöhen .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Daltroban wird in drei Schritten aus P-Phenylethylamin synthetisiert. Der Syntheseweg beinhaltet die Bildung eines substituierten Sulfonamids, insbesondere 4-[2-(4-Chlorbenzolsulfonamido)ethyl]benzolessigsäure . Die Verbindung hat ein Molekulargewicht von 353,82 und ist achiral, d. h. sie besitzt keine asymmetrischen Kohlenstoffatome . Industrielle Produktionsverfahren für this compound umfassen typischerweise die Verwendung standardmäßiger organischer Synthesetechniken und Reagenzien.
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
This compound unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution. Häufige Reagenzien, die in diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, sind Oxidationsmittel, Reduktionsmittel und Nukleophile. Die wichtigsten Produkte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, hängen von den spezifischen Bedingungen und Reagenzien ab, die verwendet werden. Beispielsweise kann die Oxidation von this compound zur Bildung von Sulfoxiden oder Sulfonen führen, während die Reduktion zur Bildung von Aminen oder Alkoholen führen kann .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
This compound wurde in verschiedenen Bereichen, einschließlich Chemie, Biologie, Medizin und Industrie, ausgiebig auf seine wissenschaftlichen Forschungsanwendungen untersucht. In der Chemie wird this compound als Modellverbindung verwendet, um die Mechanismen von Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor-Antagonisten zu untersuchen . In der Biologie wurde es verwendet, um die Rolle von Thromboxan A2 in verschiedenen physiologischen Prozessen wie der Thrombozytenaggregation und der Kontraktion der glatten Gefäßmuskulatur zu untersuchen . In der Medizin wurde this compound auf seine potenziellen therapeutischen Anwendungen bei Erkrankungen wie Myokardischämie, Thrombose und pulmonaler arterieller Hypertonie untersucht . In der Industrie wird this compound als Referenzverbindung für die Entwicklung neuer Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor-Antagonisten verwendet .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Daltroban undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution. Common reagents used in these reactions include oxidizing agents, reducing agents, and nucleophiles. The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific conditions and reagents used. For example, oxidation of this compound can lead to the formation of sulfoxides or sulfones, while reduction can result in the formation of amines or alcohols .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Pharmacological Profile
Daltroban functions primarily as an antagonist to the TxA2 receptor, which plays a critical role in platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. Its pharmacological properties include:
- Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation : this compound effectively inhibits platelet aggregation induced by various agonists, including U-46619, collagen, and adrenaline. In vitro studies have demonstrated that it can suppress collagen-induced platelet aggregation at concentrations as low as 0.4 µg/ml (1 µM) in healthy individuals .
- Cardioprotective Effects : Research indicates that this compound provides significant protection against myocardial reperfusion injury. In a study involving anesthetized cats, this compound reduced the necrotic area following ischemia-reperfusion injury without affecting neutrophil accumulation or coronary endothelial function .
Cardiovascular Diseases
This compound has been investigated for its role in treating ischemic heart disorders. Its ability to inhibit thromboxane A2-mediated platelet aggregation positions it as a potential therapeutic agent in managing conditions such as myocardial infarction and unstable angina.
Case Study : In a study involving patients with ischemic heart disease, this compound was administered prior to reperfusion therapy, resulting in a statistically significant reduction in myocardial necrosis compared to control groups .
Renal Applications
The compound has also been evaluated for its effects on renal function, particularly in patients undergoing hemodialysis. This compound's mechanism of action suggests it may enhance renal perfusion by modulating platelet activity and vascular tone.
Data Table: Effects of this compound on Hemodialysis Patients
| Parameter | Pre-Treatment (Mean ± SD) | Post-Treatment (Mean ± SD) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urea Reduction Ratio (URR) | 65% ± 5 | 75% ± 4 | <0.01 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.5 ± 1.2 | 11.2 ± 1.0 | <0.05 |
This table summarizes the improvements observed in hemodialysis patients treated with this compound, highlighting its potential benefits in enhancing dialysis efficacy .
Thrombosis Management
This compound's application extends to the management of thrombosis due to its antiplatelet effects. It has been suggested that this compound could be utilized to prolong the activity and storage stability of platelets in transfusion medicine.
Use Case : In vitro experiments demonstrated that this compound significantly inhibited platelet aggregation in platelet-rich plasma from various species, indicating its potential utility in clinical settings where platelet function needs to be controlled .
Wirkmechanismus
Daltroban entfaltet seine Wirkung, indem es als Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor-Antagonist wirkt. Es bindet an den Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor und hemmt die Bindung von Thromboxan A2, wodurch die Aktivierung von nachgeschalteten Signalwegen verhindert wird . Dies führt zur Hemmung der Thrombozytenaggregation und der Kontraktion der glatten Gefäßmuskulatur, die Schlüsselprozesse bei der Entwicklung thrombotischer Ereignisse sind . Die molekularen Ziele von this compound umfassen den Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor und assoziierte Signalproteine .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Daltroban ist einzigartig unter den Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor-Antagonisten aufgrund seiner spezifischen Bindungsaffinität und seiner partiellen Agonisten-Eigenschaften . Ähnliche Verbindungen umfassen Seratrodast und Terutroban, die ebenfalls als Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor-Antagonisten wirken, jedoch unterschiedliche chemische Strukturen und pharmakologische Profile aufweisen . Beispielsweise ist Seratrodast ein selektiver Thromboxan-A2-Rezeptor-Antagonist, der zur Behandlung von Asthma verwendet wird, während Terutroban aufgrund seiner antithrombotischen und vasodilatierenden Wirkung eingesetzt wird .
Biologische Aktivität
Daltroban is a potent thromboxane A2 (TXA2) receptor antagonist that has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in cardiovascular diseases. By inhibiting the action of TXA2, a molecule involved in vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation, this compound may mitigate various pathological processes associated with ischemia and reperfusion injury.
This compound selectively blocks the TXA2 receptor, which is implicated in promoting platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. This blockade can lead to several beneficial effects, particularly in myocardial ischemia, where TXA2 plays a significant role in exacerbating tissue damage during reperfusion.
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation : this compound reduces platelet activation, which is crucial during thrombus formation.
- Vasodilation : By blocking TXA2-mediated vasoconstriction, this compound can promote vasodilation and improve blood flow to ischemic tissues.
Cardiovascular Protection
This compound has been extensively studied for its cardioprotective effects. In a study involving anesthetized cats subjected to myocardial ischemia followed by reperfusion, this compound significantly reduced the necrotic area of the myocardium compared to control groups. The results indicated that while this compound effectively protected the myocardium from ischemic injury, it did not prevent neutrophil accumulation or protect the coronary endothelium from dysfunction post-ischemia .
Comparative Efficacy
This compound's efficacy as a TXA2 receptor antagonist has been compared with other compounds. For instance, in studies evaluating its effects on pulmonary hypertension models, this compound demonstrated significant reductions in mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), showcasing its potential in treating conditions like pulmonary arterial hypertension .
Table of Biological Activity Findings
Myocardial Ischemia Studies
In a controlled experiment involving feline models, this compound was administered prior to reperfusion. The study found that this compound-treated subjects exhibited a significantly lower percentage of necrotic myocardium compared to those receiving a vehicle treatment. However, it was noted that this compound did not mitigate the increase in myeloperoxidase activity, indicating unchanged neutrophil infiltration levels .
Alzheimer’s Disease Research
Recent studies have explored the role of TXA2 receptor antagonists in neurodegenerative diseases. In models of Alzheimer's disease, this compound was shown to inhibit the secretion of amyloid-beta (Aβ), which is associated with plaque formation in the brain. This suggests that this compound may have neuroprotective properties beyond its cardiovascular benefits .
In Vitro Studies on Platelet Function
In vitro studies have demonstrated that this compound effectively inhibits thromboxane-induced platelet aggregation. This property is crucial for developing therapies aimed at preventing thrombotic events without compromising hemostatic functions essential for wound healing .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonylamino]ethyl]phenyl]acetic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H16ClNO4S/c17-14-5-7-15(8-6-14)23(21,22)18-10-9-12-1-3-13(4-2-12)11-16(19)20/h1-8,18H,9-11H2,(H,19,20) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
IULOBWFWYDMECP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1CCNS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)CC(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H16ClNO4S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6046501 | |
| Record name | Daltroban | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6046501 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
353.8 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
79094-20-5 | |
| Record name | Daltroban [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0079094205 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Daltroban | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6046501 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Daltroban | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DALTROBAN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/S25VDY08ZC | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.















