Daltroban
Descripción general
Descripción
Fue desarrollado originalmente por Boehringer Mannheim a mediados de la década de 1980 y luego licenciado a Smith Kline Beecham para su posterior desarrollo como agente antitrombótico . Daltroban se ha estudiado por sus posibles efectos protectores en la lesión por reperfusión y su capacidad para aumentar el calcio intracelular en las células del músculo liso vascular .
Métodos De Preparación
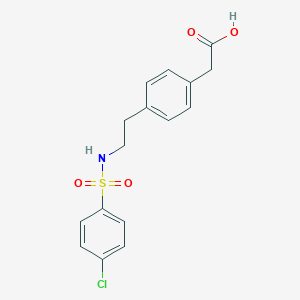
Daltroban se sintetiza en tres pasos a partir de P-feniletilamina. La ruta sintética implica la formación de una sulfonamida sustituida, específicamente ácido 4-[2-(4-clorobenzenosulfonamido)etil]bencenacético . El compuesto tiene un peso molecular de 353.82 y es aquiral, lo que significa que no tiene átomos de carbono asimétricos . Los métodos de producción industrial para this compound suelen implicar el uso de técnicas y reactivos de síntesis orgánica estándar.
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Daltroban se somete a diversas reacciones químicas, incluida la oxidación, la reducción y la sustitución. Los reactivos comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen agentes oxidantes, agentes reductores y nucleófilos. Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones dependen de las condiciones y los reactivos específicos utilizados. Por ejemplo, la oxidación de this compound puede conducir a la formación de sulfóxidos o sulfonas, mientras que la reducción puede resultar en la formación de aminas o alcoholes .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Pharmacological Profile
Daltroban functions primarily as an antagonist to the TxA2 receptor, which plays a critical role in platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. Its pharmacological properties include:
- Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation : this compound effectively inhibits platelet aggregation induced by various agonists, including U-46619, collagen, and adrenaline. In vitro studies have demonstrated that it can suppress collagen-induced platelet aggregation at concentrations as low as 0.4 µg/ml (1 µM) in healthy individuals .
- Cardioprotective Effects : Research indicates that this compound provides significant protection against myocardial reperfusion injury. In a study involving anesthetized cats, this compound reduced the necrotic area following ischemia-reperfusion injury without affecting neutrophil accumulation or coronary endothelial function .
Cardiovascular Diseases
This compound has been investigated for its role in treating ischemic heart disorders. Its ability to inhibit thromboxane A2-mediated platelet aggregation positions it as a potential therapeutic agent in managing conditions such as myocardial infarction and unstable angina.
Case Study : In a study involving patients with ischemic heart disease, this compound was administered prior to reperfusion therapy, resulting in a statistically significant reduction in myocardial necrosis compared to control groups .
Renal Applications
The compound has also been evaluated for its effects on renal function, particularly in patients undergoing hemodialysis. This compound's mechanism of action suggests it may enhance renal perfusion by modulating platelet activity and vascular tone.
Data Table: Effects of this compound on Hemodialysis Patients
| Parameter | Pre-Treatment (Mean ± SD) | Post-Treatment (Mean ± SD) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urea Reduction Ratio (URR) | 65% ± 5 | 75% ± 4 | <0.01 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.5 ± 1.2 | 11.2 ± 1.0 | <0.05 |
This table summarizes the improvements observed in hemodialysis patients treated with this compound, highlighting its potential benefits in enhancing dialysis efficacy .
Thrombosis Management
This compound's application extends to the management of thrombosis due to its antiplatelet effects. It has been suggested that this compound could be utilized to prolong the activity and storage stability of platelets in transfusion medicine.
Use Case : In vitro experiments demonstrated that this compound significantly inhibited platelet aggregation in platelet-rich plasma from various species, indicating its potential utility in clinical settings where platelet function needs to be controlled .
Mecanismo De Acción
Daltroban ejerce sus efectos actuando como antagonista del receptor de tromboxano A2. Se une al receptor de tromboxano A2 e inhibe la unión del tromboxano A2, evitando así la activación de las vías de señalización descendentes . Esto da como resultado la inhibición de la agregación plaquetaria y la contracción del músculo liso vascular, que son procesos clave en el desarrollo de eventos trombóticos . Los objetivos moleculares de this compound incluyen el receptor de tromboxano A2 y las proteínas de señalización asociadas .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Daltroban es único entre los antagonistas del receptor de tromboxano A2 debido a su afinidad de unión específica y propiedades agonistas parciales . Compuestos similares incluyen Seratrodast y Terutroban, que también actúan como antagonistas del receptor de tromboxano A2, pero tienen diferentes estructuras químicas y perfiles farmacológicos . Por ejemplo, Seratrodast es un antagonista selectivo del receptor de tromboxano A2 utilizado en el tratamiento del asma, mientras que Terutroban se utiliza por sus efectos antiplaquetarios y vasodilatadores .
Actividad Biológica
Daltroban is a potent thromboxane A2 (TXA2) receptor antagonist that has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in cardiovascular diseases. By inhibiting the action of TXA2, a molecule involved in vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation, this compound may mitigate various pathological processes associated with ischemia and reperfusion injury.
This compound selectively blocks the TXA2 receptor, which is implicated in promoting platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. This blockade can lead to several beneficial effects, particularly in myocardial ischemia, where TXA2 plays a significant role in exacerbating tissue damage during reperfusion.
Key Mechanisms:
- Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation : this compound reduces platelet activation, which is crucial during thrombus formation.
- Vasodilation : By blocking TXA2-mediated vasoconstriction, this compound can promote vasodilation and improve blood flow to ischemic tissues.
Cardiovascular Protection
This compound has been extensively studied for its cardioprotective effects. In a study involving anesthetized cats subjected to myocardial ischemia followed by reperfusion, this compound significantly reduced the necrotic area of the myocardium compared to control groups. The results indicated that while this compound effectively protected the myocardium from ischemic injury, it did not prevent neutrophil accumulation or protect the coronary endothelium from dysfunction post-ischemia .
Comparative Efficacy
This compound's efficacy as a TXA2 receptor antagonist has been compared with other compounds. For instance, in studies evaluating its effects on pulmonary hypertension models, this compound demonstrated significant reductions in mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), showcasing its potential in treating conditions like pulmonary arterial hypertension .
Table of Biological Activity Findings
Myocardial Ischemia Studies
In a controlled experiment involving feline models, this compound was administered prior to reperfusion. The study found that this compound-treated subjects exhibited a significantly lower percentage of necrotic myocardium compared to those receiving a vehicle treatment. However, it was noted that this compound did not mitigate the increase in myeloperoxidase activity, indicating unchanged neutrophil infiltration levels .
Alzheimer’s Disease Research
Recent studies have explored the role of TXA2 receptor antagonists in neurodegenerative diseases. In models of Alzheimer's disease, this compound was shown to inhibit the secretion of amyloid-beta (Aβ), which is associated with plaque formation in the brain. This suggests that this compound may have neuroprotective properties beyond its cardiovascular benefits .
In Vitro Studies on Platelet Function
In vitro studies have demonstrated that this compound effectively inhibits thromboxane-induced platelet aggregation. This property is crucial for developing therapies aimed at preventing thrombotic events without compromising hemostatic functions essential for wound healing .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonylamino]ethyl]phenyl]acetic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H16ClNO4S/c17-14-5-7-15(8-6-14)23(21,22)18-10-9-12-1-3-13(4-2-12)11-16(19)20/h1-8,18H,9-11H2,(H,19,20) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
IULOBWFWYDMECP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1CCNS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)CC(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H16ClNO4S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6046501 | |
| Record name | Daltroban | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6046501 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
353.8 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
79094-20-5 | |
| Record name | Daltroban [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0079094205 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Daltroban | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6046501 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Daltroban | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DALTROBAN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/S25VDY08ZC | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.
















