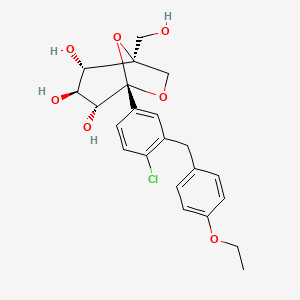
Ertugliflozin
Overview
Description
Ertugliflozin is a selective inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), primarily used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It works by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion through urine. This helps in lowering blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of ertugliflozin involves multiple steps, starting with the protection of the primary alcohol moiety of an intermediate compound with a trityl group in the presence of pyridine. This is followed by subsequent deprotection with p-toluenesulfonic acid . The process also involves the use of compounds of Formula III, Formula IV, and Formula VII, which are protected with suitable protecting groups to ensure high purity and yield .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process involves the use of advanced techniques and equipment to ensure high yield and purity. The use of hazardous chemicals like pyridine is minimized to ensure safety and compliance with industrial standards .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Degradation Reactions Under Stress Conditions
Ertugliflozin exhibits stability under thermal, photolytic, neutral, and alkaline hydrolysis conditions but degrades in acidic and oxidative environments. These reactions were studied as per ICH guidelines (Q1A–Q1E) to identify degradation products (DPs) and their mechanisms .
Key Degradation Pathways:
-
Acid Hydrolysis (1N HCl at 60°C for 48 h) :
- Forms four degradation products (DP-1 to DP-4) via:
- Ritter reaction (DP-1: acetonitrile reacts with protonated formaldehyde).
- Benzyl ether cleavage (DP-2: acid-mediated elimination of the ethoxybenzyl group).
- Esterification (DP-3: reaction with acetic acid from sugar decomposition).
- Chlorination (DP-4: SN2 displacement of hydroxymethyl group by chloride) .
- Forms four degradation products (DP-1 to DP-4) via:
- Oxidative Hydrolysis (30% H₂O₂ at RT for 48 h) :
Structural Characterization of Degradation Products
All five degradation products were characterized using UHPLC-MS , HRMS , NMR (1D/2D) , and IR spectroscopy . Key data include:
| Product | Molecular Formula | m/z (Observed) | Key Structural Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP-1 | C₂₅H₃₀ClNO₈ | 508.1724 | Benzylacetamide derivative |
| DP-2 | C₂₁H₁₉ClO₄ | 371.1037 | De-ethoxybenzyl analog |
| DP-5 | C₂₀H₁₇ClO₆ | 413.1139 | Phenolic oxidative product |
Metabolic Reactions
This compound is primarily metabolized via glucuronidation (86%) and minor oxidative pathways (12%) :
- UGT1A9/UGT2B7-mediated glucuronidation : Forms inactive metabolites M5a (2-O-β-glucuronide) and M5c (3-O-β-glucuronide).
- CYP3A4-mediated oxidation : Produces hydroxy (M1/M3) and desethyl (M2) metabolites .
Synthetic Reactions
The commercial synthesis of this compound involves:
- Cocrystallization : this compound is stabilized as a 1:1 cocrystal with L-pyroglutamic acid to enhance solubility and stability .
- Key intermediates : Protection/deprotection steps using formaldehyde and acetonitrile under acidic conditions .
Stability in Formulations
- pH-dependent solubility : Sparingly soluble in water (0.64–0.74 mg/mL at physiological pH) .
- Humidity-induced dissociation : The cocrystal partially converts to amorphous this compound under high humidity but remains bioequivalent .
Interaction with Analytical Reagents
This compound reacts with formaldehyde and dichloromethane during stress testing, leading to DP-1 and DP-4 formation .
Scientific Research Applications
Clinical Efficacy in Type 2 Diabetes Management
Ertugliflozin has demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c levels across various studies. In a pivotal phase 3 trial, participants showed a mean reduction in HbA1c of 0.6% to 0.9% compared to placebo after 52 weeks of treatment .
Key Clinical Trials
- VERTIS Trials : These trials evaluated the efficacy and safety of this compound in patients with T2DM and established cardiovascular disease. The results indicated that this compound was noninferior to placebo concerning major adverse cardiovascular events, but it did show trends toward reduced hospitalization for heart failure .
- Long-term Efficacy : A study assessing long-term outcomes reported sustained reductions in HbA1c over two years, with patients on higher doses (15 mg) showing more significant improvements compared to lower doses (5 mg) .
Cardiovascular Benefits
This compound has been associated with cardiovascular benefits beyond glycemic control. The VERTIS CV trial highlighted that this compound reduced the risk of hospitalization for heart failure by approximately 30% compared to placebo .
Cardiovascular Outcomes Summary
| Outcome Measure | This compound (5 mg) | This compound (15 mg) | Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events | Noninferior | Noninferior | Reference |
| Hospitalization for Heart Failure | 2.5% | 2.8% | 3.6% |
| CV Death | 1.8% | 1.9% | 1.9% |
Renal Outcomes
Recent studies have also explored the renal protective effects of this compound. It has shown promise in improving renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and T2DM, demonstrating a reduction in the progression of kidney disease markers .
Renal Outcomes Summary
| Renal Outcome Measure | This compound | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Doubling of Serum Creatinine | Reduced incidence | Higher incidence |
| Need for Dialysis/Transplantation | Lower rates | Higher rates |
Safety Profile
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, some adverse effects have been noted, including an increased risk of genital mycotic infections and urinary tract infections . However, these side effects are manageable and do not outweigh the benefits seen in glycemic control and cardiovascular health.
Combination Therapy
This compound can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents such as metformin or sitagliptin. Clinical trials have shown that such combinations can lead to enhanced glycemic control while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia associated with insulin or sulfonylureas .
Mechanism of Action
Ertugliflozin exerts its effects by inhibiting the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in the kidneys. This inhibition prevents the reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate, leading to increased urinary glucose excretion and reduced blood glucose levels . The molecular targets involved in this process include the SGLT2 proteins located in the proximal tubules of the kidneys .
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Ertugliflozin is part of the SGLT2 inhibitor class of medications, which also includes canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin. Compared to these compounds, this compound has shown similar efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels but may have a different safety and side effect profile . For instance, this compound has been found to have a lower risk of causing urinary tract infections compared to some other SGLT2 inhibitors .
List of Similar Compounds:- Canagliflozin
- Dapagliflozin
- Empagliflozin
- Bexagliflozin
Biological Activity
Ertugliflozin is a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor that plays a significant role in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This compound enhances glycemic control by promoting urinary glucose excretion, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and safety profile based on diverse research findings.
This compound selectively inhibits SGLT2, a protein responsible for the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys. By blocking this transporter, this compound increases urinary glucose excretion and decreases blood glucose levels. The selectivity of this compound for SGLT2 over SGLT1 is significant, with an IC50 value of 0.877 nM for SGLT2 compared to 1960 nM for SGLT1, indicating a greater than 2000-fold selectivity .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic properties:
- Bioavailability : Approximately 100% when administered orally.
- Peak Concentration : Achieved within 1-2 hours post-dose.
- Half-life : Approximately 16.6 hours in T2DM patients, supporting once-daily dosing.
- Metabolism : Primarily metabolized by UGT1A9 and UGT2B7 through O-glucuronidation into inactive metabolites .
Clinical Efficacy
This compound has been evaluated in multiple clinical trials assessing its efficacy as monotherapy and in combination with other antidiabetic agents. Key findings include:
- VERTIS-CV Trial : Demonstrated a reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure among patients treated with this compound compared to placebo .
- Long-term Studies : A 104-week study showed significant reductions in HbA1c levels (up to -0.84% at week 104) and improvements in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and body weight .
Table 1: Summary of Key Clinical Trials Involving this compound
| Trial Name | Population | Duration | Outcome Measures | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VERTIS-CV | Patients with T2DM & CVD | 3.5 years | Hospitalizations for heart failure | Reduced hospitalizations vs placebo |
| Phase III Study | T2DM patients inadequately controlled on metformin | 104 weeks | HbA1c, FPG, body weight | HbA1c reduction up to -0.84% |
| Efficacy Study | Various T2DM populations | Varies | HbA1c, FPG | Significant reductions compared to placebo |
Safety Profile
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with some adverse effects:
- Genital Mycotic Infections : Higher incidence reported among patients treated with this compound compared to placebo.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Rare cases have been documented, particularly in patients with underlying conditions such as Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adulthood (LADA) .
- Bone Mineral Density : Minimal changes observed; however, some reductions were noted at the hip region after long-term use .
Case Studies
Several case studies have highlighted the real-world efficacy and safety of this compound:
- Case Study on Cardiovascular Outcomes : A patient with established cardiovascular disease showed improved cardiovascular outcomes after initiating treatment with this compound alongside standard diabetes management.
- Long-term Management Case : A patient inadequately controlled on metformin alone achieved target HbA1c levels after adding this compound to their regimen over a period of six months.
Q & A
Basic Research Questions
Q. What are the primary efficacy endpoints of ertugliflozin in phase III clinical trials, and how were they statistically validated?
this compound demonstrated clinically meaningful reductions in HbA1c, body weight, and systolic blood pressure across the VERTIS phase III trials (e.g., VERTIS CV, VERTIS SU, VERTIS MET). These outcomes were assessed using mixed-model repeated measures (MMRM) and last observation carried forward (LOCF) imputation for missing data. For example, in VERTIS SU, placebo-adjusted HbA1c reductions were −0.69% (5 mg) and −0.76% (15 mg) at 18 weeks, with p < 0.001 . Secondary endpoints like fasting plasma glucose and blood pressure changes were analyzed using logistic regression and log-rank tests for time-to-event outcomes .
Q. How was cardiovascular safety established for this compound in high-risk type 2 diabetes (T2DM) populations?
The VERTIS CV trial (N=8,246) demonstrated non-inferiority of this compound versus placebo for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE; HR 0.97, 95.6% CI 0.85–1.11). The trial design included a double-blind, placebo-controlled protocol with pooled 5 mg/15 mg dosing and a pre-specified non-inferiority margin of 1.3. Secondary outcomes, such as cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization, showed a non-significant trend toward benefit (HR 0.88, 95.8% CI 0.75–1.03) .
Q. What methodologies are used to evaluate this compound’s renal effects in long-term studies?
Post hoc analyses of pooled data from VERTIS MET and VERTIS SU trials (N=1,237) assessed renal outcomes over 104 weeks. Changes in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models. This compound showed a 19% relative risk reduction in composite renal endpoints (e.g., eGFR decline, ESKD) compared to non-ertugliflozin treatments, with adjustments for baseline covariates like UACR category .
Advanced Research Questions
Q. How do contradictory findings between cardiovascular and renal outcomes inform mechanistic hypotheses for this compound?
While this compound did not show superiority in MACE reduction, its renal benefits (e.g., 19% risk reduction in composite renal endpoints) suggest distinct pathways. Mediation analyses from empagliflozin trials propose mechanisms such as hematocrit elevation (indicating plasma volume reduction) and metabolic effects (e.g., uric acid reduction). These findings highlight the need for targeted studies on hemodynamic versus metabolic mediators in this compound’s organ protection .
Q. What statistical approaches address missing data in this compound trials, and how do they impact validity?
Trials like VERTIS SU used multiple imputation based on a constrained longitudinal data analysis (cLDA) model for missing HbA1c data at week 18. Sensitivity analyses comparing LOCF and MMRM methods confirmed robustness, with consistent HbA1c reductions (placebo-adjusted LS mean: −0.6% to −0.7%) across methodologies . However, residual bias from unmeasured confounders in imputation models remains a limitation .
Q. How do subgroup analyses by baseline HbA1c, age, or eGFR influence the interpretation of this compound’s efficacy?
In VERTIS CV sub-studies, this compound’s HbA1c reductions were consistent across subgroups (e.g., baseline HbA1c ≥8.5%: −0.8% vs. placebo). However, in patients with eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m², the glycemic effect attenuated, necessitating stratified dosing recommendations. These analyses used interaction tests with Bonferroni correction to control for Type I error .
Q. What evidence supports or refutes the association between this compound and amputations?
Pooled phase III data reported amputation rates of 2.0% (5 mg) and 2.1% (15 mg) versus 1.6% for placebo, with exposure-adjusted incidence rates of 5.0–6.8 vs. 4.3 per 1,000 patient-years. However, the VERTIS CV trial found no statistically significant increase (HR 1.14, 95% CI 0.75–1.74), suggesting confounding by baseline risk factors (e.g., peripheral artery disease) .
Q. Methodological Considerations
Q. How are composite renal endpoints defined and validated in this compound trials?
Renal endpoints in VERTIS trials included a clinically relevant hierarchy: ≥40% eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), or renal death. These were adjudicated by blinded endpoint committees using standardized criteria. Sensitivity analyses excluding non-adjudicated events confirmed consistency in effect sizes .
Q. What are the limitations of indirect treatment comparisons (ITCs) for this compound versus other SGLT2 inhibitors?
ITCs in the 2018 PBAC report highlighted heterogeneity in trial designs (e.g., background therapies, follow-up duration) and inappropriate handling of multi-arm trials. For example, this compound showed non-inferiority to dapagliflozin in HbA1c reduction but had wider CIs due to fewer trials, limiting reliability .
Q. How do post hoc and prespecified analyses differ in interpreting this compound’s heart failure outcomes?
Prespecified analyses in VERTIS CV showed no significant reduction in heart failure hospitalization (HR 0.88, p=0.11), but sensitivity analyses using fixed-effect models suggested clinically meaningful benefits. This discrepancy underscores the importance of pre-registered statistical plans to avoid Type I error inflation .
Properties
IUPAC Name |
(1S,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-1-(hydroxymethyl)-6,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H25ClO7/c1-2-28-16-6-3-13(4-7-16)9-14-10-15(5-8-17(14)23)22-20(27)18(25)19(26)21(11-24,30-22)12-29-22/h3-8,10,18-20,24-27H,2,9,11-12H2,1H3/t18-,19-,20+,21-,22-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MCIACXAZCBVDEE-CUUWFGFTSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)C34C(C(C(C(O3)(CO4)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)[C@@]34[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@](O3)(CO4)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H25ClO7 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID40153120 | |
| Record name | PF-04971729 | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40153120 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
436.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Very slightly soluble | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11827 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
As part of a normal process, the glucose from the blood is filtered for excretion and reabsorbed in the glomerulus so less than one percent of this glucose is excreted in the urine. The reabsorption is mediated by the sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter (SGLT), mainly the type 2 which is responsible for 90% of the reabsorbed glucose. Ertugliflozin is a small inhibitor of the SGLT2 and its activity increases glucose excretion, reducing hyperglycemia without the requirement of excessive insulin secretion. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11827 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1210344-57-2, 1431329-06-4, 1210344-83-4 | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1210344-57-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1210344572 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11827 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | PF-04971729 | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40153120 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 1,6-Anhydro-1-C-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-5-C-(hydroxymethyl)-beta-L-idopyranose | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6C282481IP | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.















