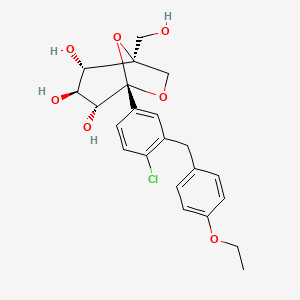
Ertugliflozin
Descripción general
Descripción
La ertugliflozina es un inhibidor selectivo del cotransportador 2 de sodio-glucosa (SGLT2), utilizado principalmente para el tratamiento de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Funciona bloqueando la reabsorción de glucosa en los riñones, lo que lleva a una mayor excreción de glucosa a través de la orina. Esto ayuda a reducir los niveles de glucosa en sangre en pacientes con diabetes tipo 2 .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción: La síntesis de ertugliflozina implica varios pasos, comenzando con la protección del grupo alcohol primario de un compuesto intermedio con un grupo tritilo en presencia de piridina. Esto va seguido de una posterior desprotección con ácido p-toluensulfónico . El proceso también implica el uso de compuestos de Fórmula III, Fórmula IV y Fórmula VII, que están protegidos con grupos protectores adecuados para garantizar una alta pureza y rendimiento .
Métodos de producción industrial: La producción industrial de ertugliflozina sigue rutas sintéticas similares pero a mayor escala. El proceso implica el uso de técnicas y equipos avanzados para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza. El uso de productos químicos peligrosos como la piridina se minimiza para garantizar la seguridad y el cumplimiento de las normas industriales .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Degradation Reactions Under Stress Conditions
Ertugliflozin exhibits stability under thermal, photolytic, neutral, and alkaline hydrolysis conditions but degrades in acidic and oxidative environments. These reactions were studied as per ICH guidelines (Q1A–Q1E) to identify degradation products (DPs) and their mechanisms .
Key Degradation Pathways:
-
Acid Hydrolysis (1N HCl at 60°C for 48 h) :
- Forms four degradation products (DP-1 to DP-4) via:
- Ritter reaction (DP-1: acetonitrile reacts with protonated formaldehyde).
- Benzyl ether cleavage (DP-2: acid-mediated elimination of the ethoxybenzyl group).
- Esterification (DP-3: reaction with acetic acid from sugar decomposition).
- Chlorination (DP-4: SN2 displacement of hydroxymethyl group by chloride) .
- Forms four degradation products (DP-1 to DP-4) via:
- Oxidative Hydrolysis (30% H₂O₂ at RT for 48 h) :
Structural Characterization of Degradation Products
All five degradation products were characterized using UHPLC-MS , HRMS , NMR (1D/2D) , and IR spectroscopy . Key data include:
| Product | Molecular Formula | m/z (Observed) | Key Structural Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP-1 | C₂₅H₃₀ClNO₈ | 508.1724 | Benzylacetamide derivative |
| DP-2 | C₂₁H₁₉ClO₄ | 371.1037 | De-ethoxybenzyl analog |
| DP-5 | C₂₀H₁₇ClO₆ | 413.1139 | Phenolic oxidative product |
Metabolic Reactions
This compound is primarily metabolized via glucuronidation (86%) and minor oxidative pathways (12%) :
- UGT1A9/UGT2B7-mediated glucuronidation : Forms inactive metabolites M5a (2-O-β-glucuronide) and M5c (3-O-β-glucuronide).
- CYP3A4-mediated oxidation : Produces hydroxy (M1/M3) and desethyl (M2) metabolites .
Synthetic Reactions
The commercial synthesis of this compound involves:
- Cocrystallization : this compound is stabilized as a 1:1 cocrystal with L-pyroglutamic acid to enhance solubility and stability .
- Key intermediates : Protection/deprotection steps using formaldehyde and acetonitrile under acidic conditions .
Stability in Formulations
- pH-dependent solubility : Sparingly soluble in water (0.64–0.74 mg/mL at physiological pH) .
- Humidity-induced dissociation : The cocrystal partially converts to amorphous this compound under high humidity but remains bioequivalent .
Interaction with Analytical Reagents
This compound reacts with formaldehyde and dichloromethane during stress testing, leading to DP-1 and DP-4 formation .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Clinical Efficacy in Type 2 Diabetes Management
Ertugliflozin has demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c levels across various studies. In a pivotal phase 3 trial, participants showed a mean reduction in HbA1c of 0.6% to 0.9% compared to placebo after 52 weeks of treatment .
Key Clinical Trials
- VERTIS Trials : These trials evaluated the efficacy and safety of this compound in patients with T2DM and established cardiovascular disease. The results indicated that this compound was noninferior to placebo concerning major adverse cardiovascular events, but it did show trends toward reduced hospitalization for heart failure .
- Long-term Efficacy : A study assessing long-term outcomes reported sustained reductions in HbA1c over two years, with patients on higher doses (15 mg) showing more significant improvements compared to lower doses (5 mg) .
Cardiovascular Benefits
This compound has been associated with cardiovascular benefits beyond glycemic control. The VERTIS CV trial highlighted that this compound reduced the risk of hospitalization for heart failure by approximately 30% compared to placebo .
Cardiovascular Outcomes Summary
| Outcome Measure | This compound (5 mg) | This compound (15 mg) | Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events | Noninferior | Noninferior | Reference |
| Hospitalization for Heart Failure | 2.5% | 2.8% | 3.6% |
| CV Death | 1.8% | 1.9% | 1.9% |
Renal Outcomes
Recent studies have also explored the renal protective effects of this compound. It has shown promise in improving renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and T2DM, demonstrating a reduction in the progression of kidney disease markers .
Renal Outcomes Summary
| Renal Outcome Measure | This compound | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Doubling of Serum Creatinine | Reduced incidence | Higher incidence |
| Need for Dialysis/Transplantation | Lower rates | Higher rates |
Safety Profile
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, some adverse effects have been noted, including an increased risk of genital mycotic infections and urinary tract infections . However, these side effects are manageable and do not outweigh the benefits seen in glycemic control and cardiovascular health.
Combination Therapy
This compound can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents such as metformin or sitagliptin. Clinical trials have shown that such combinations can lead to enhanced glycemic control while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia associated with insulin or sulfonylureas .
Mecanismo De Acción
La ertugliflozina ejerce sus efectos inhibiendo el cotransportador 2 de sodio-glucosa (SGLT2) en los riñones. Esta inhibición previene la reabsorción de glucosa del filtrado glomerular, lo que lleva a una mayor excreción de glucosa urinaria y una reducción de los niveles de glucosa en sangre . Los objetivos moleculares implicados en este proceso incluyen las proteínas SGLT2 ubicadas en los túbulos proximales de los riñones .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
La ertugliflozina forma parte de la clase de medicamentos inhibidores de SGLT2, que también incluye canagliflozina, dapagliflozina y empagliflozina. En comparación con estos compuestos, la ertugliflozina ha mostrado una eficacia similar en la reducción de los niveles de glucosa en sangre, pero puede tener un perfil de seguridad y efectos secundarios diferente . Por ejemplo, se ha encontrado que la ertugliflozina tiene un menor riesgo de causar infecciones del tracto urinario en comparación con algunos otros inhibidores de SGLT2 .
Lista de compuestos similares:- Canagliflozina
- Dapagliflozina
- Empagliflozina
- Bexagliflozina
Actividad Biológica
Ertugliflozin is a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor that plays a significant role in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This compound enhances glycemic control by promoting urinary glucose excretion, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. This article delves into the biological activity of this compound, highlighting its pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and safety profile based on diverse research findings.
This compound selectively inhibits SGLT2, a protein responsible for the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys. By blocking this transporter, this compound increases urinary glucose excretion and decreases blood glucose levels. The selectivity of this compound for SGLT2 over SGLT1 is significant, with an IC50 value of 0.877 nM for SGLT2 compared to 1960 nM for SGLT1, indicating a greater than 2000-fold selectivity .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic properties:
- Bioavailability : Approximately 100% when administered orally.
- Peak Concentration : Achieved within 1-2 hours post-dose.
- Half-life : Approximately 16.6 hours in T2DM patients, supporting once-daily dosing.
- Metabolism : Primarily metabolized by UGT1A9 and UGT2B7 through O-glucuronidation into inactive metabolites .
Clinical Efficacy
This compound has been evaluated in multiple clinical trials assessing its efficacy as monotherapy and in combination with other antidiabetic agents. Key findings include:
- VERTIS-CV Trial : Demonstrated a reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure among patients treated with this compound compared to placebo .
- Long-term Studies : A 104-week study showed significant reductions in HbA1c levels (up to -0.84% at week 104) and improvements in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and body weight .
Table 1: Summary of Key Clinical Trials Involving this compound
| Trial Name | Population | Duration | Outcome Measures | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VERTIS-CV | Patients with T2DM & CVD | 3.5 years | Hospitalizations for heart failure | Reduced hospitalizations vs placebo |
| Phase III Study | T2DM patients inadequately controlled on metformin | 104 weeks | HbA1c, FPG, body weight | HbA1c reduction up to -0.84% |
| Efficacy Study | Various T2DM populations | Varies | HbA1c, FPG | Significant reductions compared to placebo |
Safety Profile
While this compound is generally well-tolerated, it is associated with some adverse effects:
- Genital Mycotic Infections : Higher incidence reported among patients treated with this compound compared to placebo.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Rare cases have been documented, particularly in patients with underlying conditions such as Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adulthood (LADA) .
- Bone Mineral Density : Minimal changes observed; however, some reductions were noted at the hip region after long-term use .
Case Studies
Several case studies have highlighted the real-world efficacy and safety of this compound:
- Case Study on Cardiovascular Outcomes : A patient with established cardiovascular disease showed improved cardiovascular outcomes after initiating treatment with this compound alongside standard diabetes management.
- Long-term Management Case : A patient inadequately controlled on metformin alone achieved target HbA1c levels after adding this compound to their regimen over a period of six months.
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
(1S,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-1-(hydroxymethyl)-6,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H25ClO7/c1-2-28-16-6-3-13(4-7-16)9-14-10-15(5-8-17(14)23)22-20(27)18(25)19(26)21(11-24,30-22)12-29-22/h3-8,10,18-20,24-27H,2,9,11-12H2,1H3/t18-,19-,20+,21-,22-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MCIACXAZCBVDEE-CUUWFGFTSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)C34C(C(C(C(O3)(CO4)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)[C@@]34[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@](O3)(CO4)CO)O)O)O)Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H25ClO7 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID40153120 | |
| Record name | PF-04971729 | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40153120 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
436.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Very slightly soluble | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11827 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
As part of a normal process, the glucose from the blood is filtered for excretion and reabsorbed in the glomerulus so less than one percent of this glucose is excreted in the urine. The reabsorption is mediated by the sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter (SGLT), mainly the type 2 which is responsible for 90% of the reabsorbed glucose. Ertugliflozin is a small inhibitor of the SGLT2 and its activity increases glucose excretion, reducing hyperglycemia without the requirement of excessive insulin secretion. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11827 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1210344-57-2, 1431329-06-4, 1210344-83-4 | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1210344-57-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1210344572 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11827 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | PF-04971729 | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID40153120 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 1,6-Anhydro-1-C-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-5-C-(hydroxymethyl)-beta-L-idopyranose | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Ertugliflozin | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6C282481IP | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.















